
In a cell, electrons move from
a)Positive electrode to negative electrode
b)Negative electrode to positive electrode
c)Both A and B
d)Electrons do not move and only negative charge moves from one place to another place.
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint:Remember that an atom is made up of three particles of different charges. Positive, negative, and neutral. Negatively charged particles are called electrons, positively charged particles are called protons, and neutral particles are called neutrons. Particles of similar charges attract each other whereas particles of opposite charge repel each other.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that a cell has a positive electrode and a negative electrode as shown in the figure below:-
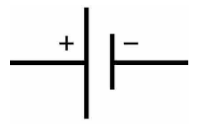
a) We know that electrons are negatively charged particles and protons are positively charged particles. We can assume that the negative electrode of the cell has a concentration of negatively charged electrons on it.
b) And since opposite charges attract each other the negatively charged electrons move toward the positively charged electrode.
c)In an electrode only the electrons move not the protons this is because protons are present in the nucleus of an atom and therefore they cannot move freely outside the atom as electrons do.
d)Therefore, it gets attracted to the positive electrode of the cell. So, in a cell, the electrons move from negative electrodes to positive electrodes.
Therefore, the answer is option B.
Additional information: The charged particles carrying positive charge are called holes just like electrons that carry a negative charge. These holes may be caused by an ion leaving its respect space in the lattice. The movement of these positively charged holes in the lattice may also give rise to current.
Note: In a cell, the electrodes play an important role in the movement of electrons from one electrode to the other electrode. Particles of similar charges attract each other whereas particles of opposite charge repel each other. This gives rise to an electric current for which the cell is used.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that a cell has a positive electrode and a negative electrode as shown in the figure below:-
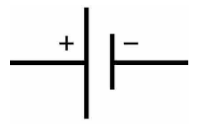
a) We know that electrons are negatively charged particles and protons are positively charged particles. We can assume that the negative electrode of the cell has a concentration of negatively charged electrons on it.
b) And since opposite charges attract each other the negatively charged electrons move toward the positively charged electrode.
c)In an electrode only the electrons move not the protons this is because protons are present in the nucleus of an atom and therefore they cannot move freely outside the atom as electrons do.
d)Therefore, it gets attracted to the positive electrode of the cell. So, in a cell, the electrons move from negative electrodes to positive electrodes.
Therefore, the answer is option B.
Additional information: The charged particles carrying positive charge are called holes just like electrons that carry a negative charge. These holes may be caused by an ion leaving its respect space in the lattice. The movement of these positively charged holes in the lattice may also give rise to current.
Note: In a cell, the electrodes play an important role in the movement of electrons from one electrode to the other electrode. Particles of similar charges attract each other whereas particles of opposite charge repel each other. This gives rise to an electric current for which the cell is used.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




