
If z is a complex number satisfying the equation\[\left| {z + i} \right| + \left| {z - i} \right| = 8\], on the complex plane then maximum value of \[\left| z \right|\] is
A.2
B.4
C.6
D.8
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: Complex number is a number generally represented as \[z = a + ib\], where \[a\] and \[b\] is real number represented on real axis whereas \[i\] is an imaginary unit represented on imaginary axis whose value is \[i = \sqrt { - 1} \]. Modulus of a complex number is length of line segment on real and imaginary axis generally denoted by \[\left| z \right|\] whereas angle subtended by line segment on real axis is argument of matrix denoted by argument (z) calculated by trigonometric value. Argument of complex numbers is denoted by \[\arg (z) = \theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{b}{a}\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we need to determine the maximum value of \[\left| z \right|\] such that \[\left| {z + i} \right| + \left| {z - i} \right| = 8\] have to be satisfied. For this we will use the properties of the complex numbers as discussed above.
\[\left| {z + i} \right| + \left| {z - i} \right| = 8 - - (i)\]
This equation can be written as
\[\left| {z - \left( { - i} \right)} \right| + \left| {z - i} \right| = 8 - - (ii)\]
We know imaginary unit \[i\]is represented on a plane as
Now it is given that a point z is on the plane whose sum of distance from points \[i\] and \[ - i\] is given as 8 as shown in the diagram below
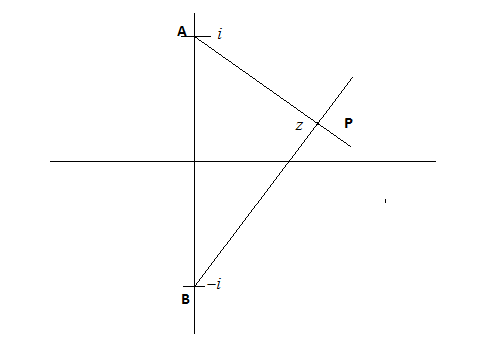
We know the equation of the locus from point P for the sum of distance between two fixed points is constant \[PA + PB = 2a - - (iii)\]and this constant form an ellipse
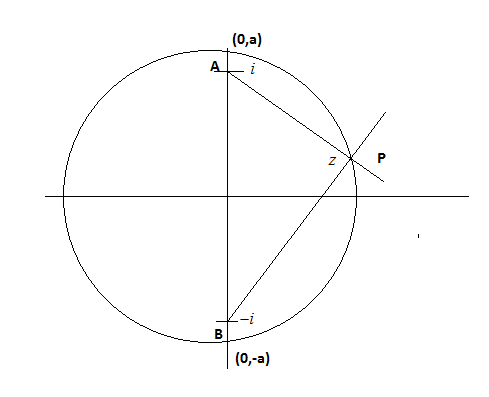
Now if we compare equation (iii) with the equation (i), we can say
\[
2a = 8 \\
a = 4 \\
\]
Where \[a = 4\] is the maximum value from which the ellipse pass, hence we can say the maximum value of \[\left| z \right|\] is \[ = 4\]
Note: Complex numbers are always written in the form of \[z = a + ib\] where $a$ and $b$ are real numbers whereas \[i\]being imaginary part. We can convert a degree into radian by multiplying it by \[\dfrac{\pi }{{180}}\]. Argument of complex numbers is denoted by \[\arg (z) = \theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{b}{a}\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we need to determine the maximum value of \[\left| z \right|\] such that \[\left| {z + i} \right| + \left| {z - i} \right| = 8\] have to be satisfied. For this we will use the properties of the complex numbers as discussed above.
\[\left| {z + i} \right| + \left| {z - i} \right| = 8 - - (i)\]
This equation can be written as
\[\left| {z - \left( { - i} \right)} \right| + \left| {z - i} \right| = 8 - - (ii)\]
We know imaginary unit \[i\]is represented on a plane as

Now it is given that a point z is on the plane whose sum of distance from points \[i\] and \[ - i\] is given as 8 as shown in the diagram below

We know the equation of the locus from point P for the sum of distance between two fixed points is constant \[PA + PB = 2a - - (iii)\]and this constant form an ellipse

Now if we compare equation (iii) with the equation (i), we can say
\[
2a = 8 \\
a = 4 \\
\]
Where \[a = 4\] is the maximum value from which the ellipse pass, hence we can say the maximum value of \[\left| z \right|\] is \[ = 4\]
Note: Complex numbers are always written in the form of \[z = a + ib\] where $a$ and $b$ are real numbers whereas \[i\]being imaginary part. We can convert a degree into radian by multiplying it by \[\dfrac{\pi }{{180}}\]. Argument of complex numbers is denoted by \[\arg (z) = \theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{b}{a}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




