
If two cubical dice are thrown simultaneously, then find the probability of getting the sum of numbers ‘more than 7’ or ‘less than 7’.
Answer
627.3k+ views
Hint: Find out total number of outcomes when two dice are thrown simultaneously. Then find the total number of events in which the sum of the numbers on two dice is ‘more than 7’ and ‘less than 7’. Divide the number of desirable outcomes with the total number of outcomes to find the probability of both the cases.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Since, a cubical dice has six faces and each face has a number that range from 1 to 6. So, the total number of outcomes when 1 dice is thrown is 6. Therefore, when two dice are thrown, the total number of outcomes will be the total combinations of the 6 numbers of one die with the 6 numbers of the other die.
Now, let us come to the question.
Total number of outcomes or total number of sample space $=n(S)=6\times 6=36$
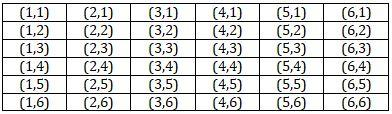
Combinations in which sum is more than 7 are: (2, 6); (3, 5); (3, 6); (4, 4); (4, 5); (4, 6); (5, 3); (5, 4); (5, 5); (5, 6); (6, 2); (6, 3); (6, 4); (6, 5); (6, 6).
Therefore, the total number of outcomes in which sum is more than 7 $=n({{E}_{1}})$$=15$.
Combinations in which sum is less than 7 are: (1, 1); (1, 2); (1, 3); (1, 4); (1, 5); (2, 1); (2, 2);
(2, 3); (2, 4); (3, 1); (3, 2); (3, 3); (4, 1); (4, 2); (4, 3).
Therefore, the total number of outcomes in which sum is less than 7 $=n({{E}_{2}})$$=15$.
We know that, probability of an event $=\dfrac{\text{number of desired
outcome}}{\text{total number of outcome}}=\dfrac{n(E)}{n(S)}$.
Therefore, probability of getting the sum more than 7
$=\dfrac{n({{E}_{1}})}{n(S)}=\dfrac{15}{36}=\dfrac{5}{12}$.
Also, probability of getting the sum less than 7
$=\dfrac{n({{E}_{2}})}{n(S)}=\dfrac{15}{36}=\dfrac{5}{12}$.
Note: It would be favourable for us to note all the outcomes in a table otherwise we may get confused in counting the desirable number of events. It is important to note that if ‘n’ number of dice is rolled simultaneously then the total number of outcomes will be ${{6}^{n}}$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Since, a cubical dice has six faces and each face has a number that range from 1 to 6. So, the total number of outcomes when 1 dice is thrown is 6. Therefore, when two dice are thrown, the total number of outcomes will be the total combinations of the 6 numbers of one die with the 6 numbers of the other die.
Now, let us come to the question.
Total number of outcomes or total number of sample space $=n(S)=6\times 6=36$

Combinations in which sum is more than 7 are: (2, 6); (3, 5); (3, 6); (4, 4); (4, 5); (4, 6); (5, 3); (5, 4); (5, 5); (5, 6); (6, 2); (6, 3); (6, 4); (6, 5); (6, 6).
Therefore, the total number of outcomes in which sum is more than 7 $=n({{E}_{1}})$$=15$.
Combinations in which sum is less than 7 are: (1, 1); (1, 2); (1, 3); (1, 4); (1, 5); (2, 1); (2, 2);
(2, 3); (2, 4); (3, 1); (3, 2); (3, 3); (4, 1); (4, 2); (4, 3).
Therefore, the total number of outcomes in which sum is less than 7 $=n({{E}_{2}})$$=15$.
We know that, probability of an event $=\dfrac{\text{number of desired
outcome}}{\text{total number of outcome}}=\dfrac{n(E)}{n(S)}$.
Therefore, probability of getting the sum more than 7
$=\dfrac{n({{E}_{1}})}{n(S)}=\dfrac{15}{36}=\dfrac{5}{12}$.
Also, probability of getting the sum less than 7
$=\dfrac{n({{E}_{2}})}{n(S)}=\dfrac{15}{36}=\dfrac{5}{12}$.
Note: It would be favourable for us to note all the outcomes in a table otherwise we may get confused in counting the desirable number of events. It is important to note that if ‘n’ number of dice is rolled simultaneously then the total number of outcomes will be ${{6}^{n}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which country won the ICC Men's ODI World Cup in 2023?

In cricket, how many legal balls are there in a standard over?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

What does "powerplay" mean in limited-overs cricket?

What is the "Powerplay" in T20 cricket?




