
If the value of \[sin\text{ }\theta =\dfrac{11}{15}\] , find the value of other trigonometric ratios.
Answer
609k+ views
Hint: In this question, we are given the value of \[\sin \theta \] and we are asked to find all other trigonometric ratios. We have to find all the trigonometric ratios, step by step. We know the identity, \[{{\sin }^{2}}\theta +\text{ co}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\theta =1\] . Using this relation, \[\cos \theta \] can be obtained. Now, we have the value of \[\sin \theta \] and \[\cos \theta \] . Using the value of \[\sin \theta \] and \[\cos \theta \], \[\tan \theta \] can be calculated. Now, other remaining trigonometric ratios can be calculated by finding the reciprocal of these trigonometric ratios.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, according to question, it is given that \[sin\text{ }\theta =\dfrac{11}{15}\]………………….(1)
We know the identity, \[{{\sin }^{2}}\theta +\text{ co}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\theta =1\]……………………(2)
Taking \[{{\sin }^{2}}\theta \] to the RHS in the equation (2), we get
\[{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta \] …………….(3)
Now, \[\cos \theta \] can be easily expressed in terms of \[\sin \theta \] .
Taking square root in both LHS and RHS in equation (3), we get
\[\cos \theta =\sqrt{1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta }\]……………(4)
In question, we are given the value of \[\sin \theta \]. Putting the value of \[\sin \theta \]
from equation (1) in equation (4), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \cos \theta =\sqrt{1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta } \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \theta =\sqrt{1-{{\left( \dfrac{11}{15} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \theta =\sqrt{1-\dfrac{121}{225}} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \theta =\sqrt{\dfrac{225-121}{225}} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \theta =\sqrt{\dfrac{104}{225}} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \theta =\dfrac{\sqrt{104}}{15} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we have, \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{\sqrt{104}}{15}\]……………….(5)
From equation (1) and equation (5), we have got the values of \[\cos \theta \] and \[\sin
\theta \] .
Using equation (1) and equation (5), we can find the value of \[\tan \theta \] .
We know that, \[\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }=\tan \theta\]…………………….(6)
Putting the values of cos θ and sin θ in equation (6), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta } \\
& \Rightarrow \tan \theta =\dfrac{\dfrac{11}{15}}{\dfrac{\sqrt{104}}{15}} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan \theta =\dfrac{11}{\sqrt{104}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we also have \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{11}{\sqrt{104}}\]………………..(7)
We have to find other remaining trigonometric ratios that are \[\sec \theta \] ,
\[\operatorname{cosec}\theta \] ,
and \[\cot \theta \] . We know that \[\sec \theta \] , \[\operatorname{cosec}\theta \], and
\[\cot \theta \] is reciprocal of \[\cos \theta \], \[\sin \theta \] and \[\tan \theta
\]respectively.
\[\begin{align}
& \sin \theta =\dfrac{11}{15}, \\
& \operatorname{cosec}\theta =\dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }=\dfrac{15}{11}. \\
\end{align}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \cos \theta =\dfrac{\sqrt{104}}{15}, \\
& sec\theta =\dfrac{1}{cos\theta }=\dfrac{15}{\sqrt{104}}. \\
\end{align}\]
\[\begin{align}
& tan\theta =\dfrac{11}{\sqrt{104}}, \\
& \cot \theta =\dfrac{1}{tan\theta }=\dfrac{\sqrt{104}}{11}. \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we have got all the trigonometric ratios.
Note: This question can also be solved by using the Pythagoras theorem.
We have, \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{11}{15}\] .
Now, using a right-angled triangle, we can get the value of \[\cos \theta \] .
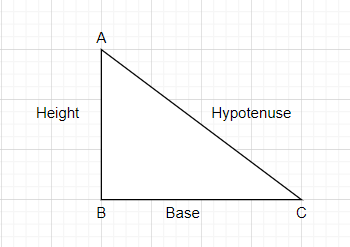
Using Pythagoras theorem, we can find the base.
Base = \[\sqrt{{{\left( hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( height \right)}^{2}}}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \sqrt{{{\left( 15 \right)}^{2}}-{{11}^{2}}} \\
& =\sqrt{225-121} \\
& =\sqrt{104} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \cos \theta =\dfrac{base}{hypotenuse} \\
& \cos \theta =\dfrac{\sqrt{104}}{15} \\
\end{align}\]
We know that,
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{height}{base}\]
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{11}{\sqrt{104}}\]
Now, other remaining trigonometric ratios can be calculated by finding the reciprocal of these trigonometric ratios.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, according to question, it is given that \[sin\text{ }\theta =\dfrac{11}{15}\]………………….(1)
We know the identity, \[{{\sin }^{2}}\theta +\text{ co}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\theta =1\]……………………(2)
Taking \[{{\sin }^{2}}\theta \] to the RHS in the equation (2), we get
\[{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta \] …………….(3)
Now, \[\cos \theta \] can be easily expressed in terms of \[\sin \theta \] .
Taking square root in both LHS and RHS in equation (3), we get
\[\cos \theta =\sqrt{1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta }\]……………(4)
In question, we are given the value of \[\sin \theta \]. Putting the value of \[\sin \theta \]
from equation (1) in equation (4), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \cos \theta =\sqrt{1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta } \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \theta =\sqrt{1-{{\left( \dfrac{11}{15} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \theta =\sqrt{1-\dfrac{121}{225}} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \theta =\sqrt{\dfrac{225-121}{225}} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \theta =\sqrt{\dfrac{104}{225}} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \theta =\dfrac{\sqrt{104}}{15} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we have, \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{\sqrt{104}}{15}\]……………….(5)
From equation (1) and equation (5), we have got the values of \[\cos \theta \] and \[\sin
\theta \] .
Using equation (1) and equation (5), we can find the value of \[\tan \theta \] .
We know that, \[\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }=\tan \theta\]…………………….(6)
Putting the values of cos θ and sin θ in equation (6), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta } \\
& \Rightarrow \tan \theta =\dfrac{\dfrac{11}{15}}{\dfrac{\sqrt{104}}{15}} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan \theta =\dfrac{11}{\sqrt{104}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we also have \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{11}{\sqrt{104}}\]………………..(7)
We have to find other remaining trigonometric ratios that are \[\sec \theta \] ,
\[\operatorname{cosec}\theta \] ,
and \[\cot \theta \] . We know that \[\sec \theta \] , \[\operatorname{cosec}\theta \], and
\[\cot \theta \] is reciprocal of \[\cos \theta \], \[\sin \theta \] and \[\tan \theta
\]respectively.
\[\begin{align}
& \sin \theta =\dfrac{11}{15}, \\
& \operatorname{cosec}\theta =\dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }=\dfrac{15}{11}. \\
\end{align}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \cos \theta =\dfrac{\sqrt{104}}{15}, \\
& sec\theta =\dfrac{1}{cos\theta }=\dfrac{15}{\sqrt{104}}. \\
\end{align}\]
\[\begin{align}
& tan\theta =\dfrac{11}{\sqrt{104}}, \\
& \cot \theta =\dfrac{1}{tan\theta }=\dfrac{\sqrt{104}}{11}. \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we have got all the trigonometric ratios.
Note: This question can also be solved by using the Pythagoras theorem.
We have, \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{11}{15}\] .
Now, using a right-angled triangle, we can get the value of \[\cos \theta \] .

Using Pythagoras theorem, we can find the base.
Base = \[\sqrt{{{\left( hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( height \right)}^{2}}}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \sqrt{{{\left( 15 \right)}^{2}}-{{11}^{2}}} \\
& =\sqrt{225-121} \\
& =\sqrt{104} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \cos \theta =\dfrac{base}{hypotenuse} \\
& \cos \theta =\dfrac{\sqrt{104}}{15} \\
\end{align}\]
We know that,
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{height}{base}\]
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{11}{\sqrt{104}}\]
Now, other remaining trigonometric ratios can be calculated by finding the reciprocal of these trigonometric ratios.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Who Won 36 Oscar Awards? Record Holder Revealed

What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Who was Subhash Chandra Bose Why was he called Net class 10 english CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

Who is the executive head of the government APresident class 10 social science CBSE




