
If the sides be 18, 24, 30cms, then radius of in-circle is
A. 2
B. 4
C. 6
D. 9
Answer
624k+ views
Hint: Find the area of triangle to find the radius of incircle using the formula,
Area= $\dfrac{1}{2}\times \text{base}\times \text{height}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
The sides of the triangle given in the question are 18cm, 24cm, 30cm.
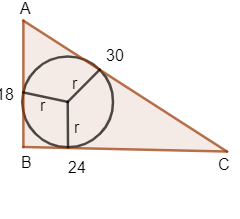
Let AB be 18cm, BC be 24cm and AC be 30cm.
$A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{18}^{2}}+{{24}^{2}}={{30}^{2}}$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 324+579={{30}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 900=900 \\
\end{align}$
Thus the sides of $\Delta $ ABC satisfy Pythagora's theorem.
Hence ABC is a right angled triangle.
Let ABC be a triangle with AB=18cm, BC=24cm and AC=30cm and a circle is inserted in triangle with radius ‘r’.
Let O be the centre of the circle.
Area of $\Delta $ ABC = Area of AOB + Area of BOC + Area of COA…….. (1)
Area of right angled triangle = $\dfrac{1}{2}\times \text{base}\times \text{height}$
Substituting the corresponding values, we get
Area of $\Delta $ ABC $=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 18\times 24=216$
Area of $\Delta $ AOB =$\dfrac{1}{2}\times r\times 18=9r$
Area of $\Delta $ BOC =$\dfrac{1}{2}\times r\times 24=12r$
Area of $\Delta $ COA =$\dfrac{1}{2}\times r\times 30=15r$
So, putting back the values in the equation (1) we get,
$\begin{align}
& 216=9r+12r+15r \\
& \Rightarrow 36r=216 \\
& \Rightarrow r=6 \\
\end{align}$
So, the answer is C.
Note: There is a shortcut to solve this problem using the formula, radius = $\left( \dfrac{a+b-c}{2} \right)$ if a, b are the sides and c is the hypotenuse of the triangle. This shortcut can be used only when the triangle is a right angled triangle.
Area= $\dfrac{1}{2}\times \text{base}\times \text{height}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
The sides of the triangle given in the question are 18cm, 24cm, 30cm.

Let AB be 18cm, BC be 24cm and AC be 30cm.
$A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{18}^{2}}+{{24}^{2}}={{30}^{2}}$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 324+579={{30}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 900=900 \\
\end{align}$
Thus the sides of $\Delta $ ABC satisfy Pythagora's theorem.
Hence ABC is a right angled triangle.
Let ABC be a triangle with AB=18cm, BC=24cm and AC=30cm and a circle is inserted in triangle with radius ‘r’.
Let O be the centre of the circle.
Area of $\Delta $ ABC = Area of AOB + Area of BOC + Area of COA…….. (1)
Area of right angled triangle = $\dfrac{1}{2}\times \text{base}\times \text{height}$
Substituting the corresponding values, we get
Area of $\Delta $ ABC $=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 18\times 24=216$
Area of $\Delta $ AOB =$\dfrac{1}{2}\times r\times 18=9r$
Area of $\Delta $ BOC =$\dfrac{1}{2}\times r\times 24=12r$
Area of $\Delta $ COA =$\dfrac{1}{2}\times r\times 30=15r$
So, putting back the values in the equation (1) we get,
$\begin{align}
& 216=9r+12r+15r \\
& \Rightarrow 36r=216 \\
& \Rightarrow r=6 \\
\end{align}$
So, the answer is C.
Note: There is a shortcut to solve this problem using the formula, radius = $\left( \dfrac{a+b-c}{2} \right)$ if a, b are the sides and c is the hypotenuse of the triangle. This shortcut can be used only when the triangle is a right angled triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

Which are the three major ports of Tamil Nadu A Chennai class 10 social science CBSE

The highest dam in India is A Bhakra dam B Tehri dam class 10 social science CBSE

Describe the process of Unification of Italy class 10 social science CBSE




