
If the ratio of maximum and minimum intensities in an interference pattern is $36:1$ then What will be the ratio of amplitudes of two interfering waves?
A. $5:7$
B. $7:4$
C. $4:7$
D. $7:5$
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: The wave interference pattern is formed when two waves intersect each other. While intersecting, the intensity will change according to the intensity of the two waves. Similarly, the amplitude also gets changed based on the amplitude of the two waves. Using the given ratio of intensity, the ratio of amplitude can be calculated.
Formula used:
In wave interference, the maximum intensity, ${I_{\max }} = {\left( {\sqrt {\dfrac{{{I_1}}}{{{I_2}}}} + 1} \right)^2}$
And the minimum intensity, ${I_{\min }} = {\left( {\sqrt {\dfrac{{{I_1}}}{{{I_2}}}} - 1} \right)^2}$
Also, the relation between intensity and amplitude,
$I \propto {A^2}$
Complete step by step answer:
Given, the ratio of maximum and minimum intensities in an interference pattern,
${I_{\max }}:{I_{\min }} = 36:1$
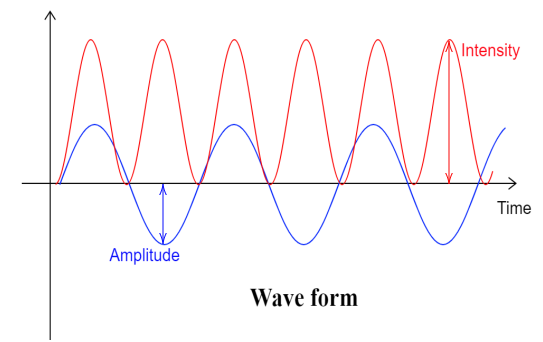
Thus, $\dfrac{{{I_{\max }}}}{{{I_{\min }}}} = \dfrac{{36}}{1}$
By substituting the values of ${I_{\max }}$ and ${I_{\min }}$ in above equation, we get
$\dfrac{{{{\left( {\sqrt {\dfrac{{{I_1}}}{{{I_2}}}} + 1} \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( {\sqrt {\dfrac{{{I_1}}}{{{I_2}}}} - 1} \right)}^2}}} = \dfrac{{36}}{1}\;.....................................\left( 1 \right)$
Since, the relation between intensity and amplitude,
$I \propto {A^2}$
So, $A \propto \sqrt I $, used in equation (1).
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\left( {\dfrac{{{A_1}}}{{{A_2}}} + 1} \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( {\dfrac{{{A_1}}}{{{A_2}}} - 1} \right)}^2}}} = \dfrac{{36}}{1}\;$
Taking square root on both sides,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{{{A_1}}}{{{A_2}}} + 1} \right)}}{{\left( {\dfrac{{{A_1}}}{{{A_2}}} - 1} \right)}} = \sqrt {36} \;$
By rearranging the terms, we get
$
\Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{{A_1}}}{{{A_2}}} + 1} \right) = 6 \times \left( {\dfrac{{{A_1}}}{{{A_2}}} - 1} \right)\; \\
\Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{{A_1} + {A_2}}}{{{A_2}}}} \right) = 6 \times \left( {\dfrac{{{A_1} - {A_2}}}{{{A_2}}}} \right)\; \\
$
Canceling common tern in both sides,
$
\Rightarrow \left( {{A_1} + {A_2}} \right) = 6\left( {{A_1} - {A_2}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow {A_1} + {A_2} = 6{A_1} - 6{A_2} \\
$
By performing arithmetic operations,
$
\Rightarrow {A_2} + 6{A_2} = 6{A_1} - {A_1} \\
\Rightarrow 7{A_2} = 5{A_1} \\
$
Hence, the final ratio $\dfrac{{{A_1}}}{{{A_2}}} = \dfrac{7}{5}$
$\therefore {A_1}:{A_2} = 7:5$
$\therefore $ The ratio of amplitudes of two interfering waves is$7:5$. Hence, the option (D) is correct.
Note:
The intensity of the wave is directly proportional to the amplitude of the wave. When the amplitude gets increased, then the intensity gets increased. Intensity is proportional to the square of the amplitude. It means the negative side of the wave gets multiplied to the positive side to get intensity. Thus, the sign doesn’t matter in intensity.
Formula used:
In wave interference, the maximum intensity, ${I_{\max }} = {\left( {\sqrt {\dfrac{{{I_1}}}{{{I_2}}}} + 1} \right)^2}$
And the minimum intensity, ${I_{\min }} = {\left( {\sqrt {\dfrac{{{I_1}}}{{{I_2}}}} - 1} \right)^2}$
Also, the relation between intensity and amplitude,
$I \propto {A^2}$
Complete step by step answer:
Given, the ratio of maximum and minimum intensities in an interference pattern,
${I_{\max }}:{I_{\min }} = 36:1$

Thus, $\dfrac{{{I_{\max }}}}{{{I_{\min }}}} = \dfrac{{36}}{1}$
By substituting the values of ${I_{\max }}$ and ${I_{\min }}$ in above equation, we get
$\dfrac{{{{\left( {\sqrt {\dfrac{{{I_1}}}{{{I_2}}}} + 1} \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( {\sqrt {\dfrac{{{I_1}}}{{{I_2}}}} - 1} \right)}^2}}} = \dfrac{{36}}{1}\;.....................................\left( 1 \right)$
Since, the relation between intensity and amplitude,
$I \propto {A^2}$
So, $A \propto \sqrt I $, used in equation (1).
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\left( {\dfrac{{{A_1}}}{{{A_2}}} + 1} \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( {\dfrac{{{A_1}}}{{{A_2}}} - 1} \right)}^2}}} = \dfrac{{36}}{1}\;$
Taking square root on both sides,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{{{A_1}}}{{{A_2}}} + 1} \right)}}{{\left( {\dfrac{{{A_1}}}{{{A_2}}} - 1} \right)}} = \sqrt {36} \;$
By rearranging the terms, we get
$
\Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{{A_1}}}{{{A_2}}} + 1} \right) = 6 \times \left( {\dfrac{{{A_1}}}{{{A_2}}} - 1} \right)\; \\
\Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{{A_1} + {A_2}}}{{{A_2}}}} \right) = 6 \times \left( {\dfrac{{{A_1} - {A_2}}}{{{A_2}}}} \right)\; \\
$
Canceling common tern in both sides,
$
\Rightarrow \left( {{A_1} + {A_2}} \right) = 6\left( {{A_1} - {A_2}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow {A_1} + {A_2} = 6{A_1} - 6{A_2} \\
$
By performing arithmetic operations,
$
\Rightarrow {A_2} + 6{A_2} = 6{A_1} - {A_1} \\
\Rightarrow 7{A_2} = 5{A_1} \\
$
Hence, the final ratio $\dfrac{{{A_1}}}{{{A_2}}} = \dfrac{7}{5}$
$\therefore {A_1}:{A_2} = 7:5$
$\therefore $ The ratio of amplitudes of two interfering waves is$7:5$. Hence, the option (D) is correct.
Note:
The intensity of the wave is directly proportional to the amplitude of the wave. When the amplitude gets increased, then the intensity gets increased. Intensity is proportional to the square of the amplitude. It means the negative side of the wave gets multiplied to the positive side to get intensity. Thus, the sign doesn’t matter in intensity.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




