
If the position vector of a point A is \[\vec a + 2\vec b\] and \[\vec a\] divides \[\overrightarrow {AB} \] in the ratio 2:3, then the position vector of b is?
A.\[2\vec a - \vec b\]
B.\[\vec b - 2\vec a\]
C.\[\vec a - 3\vec b\]
D.\[\vec b\]
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: We are given a vector \[\overrightarrow {AB} \] such a way that the position vector of a point A is \[\vec a + 2\vec b\] and \[\vec a\] divides \[\overrightarrow {AB} \] in the ratio 2:3. We need to find the position vector of b. For that we will consider \[\vec x\] as position vector of b. then we will use the section formula.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let’s get the problem with the help of a diagram.
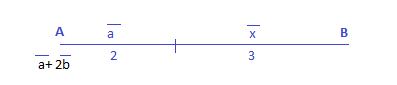
Now in the diagram above we can see that AB is divided in the ratio 2:3.
Let’s use the section formula then.
\[\vec a = \dfrac{{2\vec x + 3\left( {\vec a + 2\vec b} \right)}}{{2 + 3}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \vec a = \dfrac{{2\vec x + 3\left( {\vec a + 2\vec b} \right)}}{5}\]
Cross multiplying with 5,
\[ \Rightarrow 5\vec a = 2\vec x + 3\vec a + 6\vec b\]
Taking position vector of b on one side separately,
\[ \Rightarrow 5\vec a - 3\vec a - 6\vec b = 2\vec x\]
On performing the necessary mathematical operations,
\[ \Rightarrow 2\vec x = 2\vec a - 6\vec b\]
Dividing both sides by 2,
\[ \Rightarrow \vec x = \vec a - 3\vec b\]
And this is our answer for the position vector of b equals \[\vec x = \vec a - 3\vec b\]
So the correct option is C.
Note: Section formula is used when a vector divides a segment either internally or externally. Here we have used internal division as shown in the diagram. If the point is somewhere on the segment then we call it internal division and if it is dividing the segment but not on segment then we call it external division.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let’s get the problem with the help of a diagram.

Now in the diagram above we can see that AB is divided in the ratio 2:3.
Let’s use the section formula then.
\[\vec a = \dfrac{{2\vec x + 3\left( {\vec a + 2\vec b} \right)}}{{2 + 3}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \vec a = \dfrac{{2\vec x + 3\left( {\vec a + 2\vec b} \right)}}{5}\]
Cross multiplying with 5,
\[ \Rightarrow 5\vec a = 2\vec x + 3\vec a + 6\vec b\]
Taking position vector of b on one side separately,
\[ \Rightarrow 5\vec a - 3\vec a - 6\vec b = 2\vec x\]
On performing the necessary mathematical operations,
\[ \Rightarrow 2\vec x = 2\vec a - 6\vec b\]
Dividing both sides by 2,
\[ \Rightarrow \vec x = \vec a - 3\vec b\]
And this is our answer for the position vector of b equals \[\vec x = \vec a - 3\vec b\]
So the correct option is C.
Note: Section formula is used when a vector divides a segment either internally or externally. Here we have used internal division as shown in the diagram. If the point is somewhere on the segment then we call it internal division and if it is dividing the segment but not on segment then we call it external division.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




