
If the points $A(a, 0)$, $B(0, b)$ and $C(1, 1)$ are collinear then-
$\begin{align}
&{\text{A}}.\;\dfrac{1}{{\text{a}}} + \dfrac{1}{{\text{b}}} = 1 \\
&{\text{B}}.\;{\text{a}} + {\text{b}} = 1 \\
&{\text{C}}.\;{\text{a}} + {\text{b}} = 2 \\
&{\text{D}}.\;\dfrac{1}{{\text{a}}} - \dfrac{1}{{\text{b}}} = 1 \\
\end{align} $
Answer
616.5k+ views
Hint: For the points to be collinear, the area of the triangle formed by these three points as vertices should be equal to zero. We will use this formula to find the relation between a and b. Mathematically it is given as-
$\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{{\text{x}}_1}\left( {{{\text{y}}_2} - {{\text{y}}_3}} \right) + {{\text{x}}_2}\left( {{{\text{y}}_3} - {{\text{y}}_1}} \right) + {{\text{x}}_3}\left( {{{\text{y}}_1} - {{\text{y}}_2}} \right)} \right] = 0$
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given that the points $A(a, 0)$, $B(0, b)$ and $C(1, 1)$ are collinear. This means that the area of the triangle formed by these three points is zero.
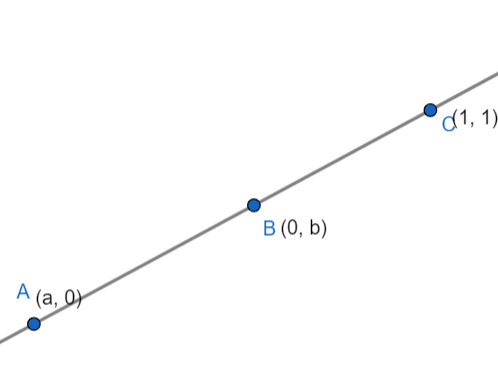
Let $A(a, 0)$, $B(0, b)$ and $C(1, 1)$. We will apply the triangle formula to these three points as-
$\begin{align}
&\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{\text{a}}\left( {{\text{b}} - 1} \right) + 0\left( {1 - 0} \right) + 1\left( {0 - {\text{b}}} \right)} \right] = 0 \\
&ab - {\text{a}} - {\text{b}} = 0 \\
&{\text{a}} + {\text{b}} = ab \\
\end{align} $
Dividing this by ab,
$\dfrac{1}{{\text{b}}} + \dfrac{1}{{\text{a}}} = 1 \\ $
By this equation we can see that the correct option is A.
Note: In such types of questions, we need to use a particular property of collinear points to form the equation. Another condition for the points to be collinear is that the slope of any two pairs are equal. That is-
$\begin{align}
&Slop{e_{AB}} = Slop{e_{BC}} \\
&\dfrac{{{\text{b}} - 0}}{{0 - {\text{a}}}} = \dfrac{{{\text{b}} - 1}}{{0 - 1}} \\
&\dfrac{{\text{b}}}{{\text{a}}} = - \left( {{\text{b}} - 1} \right) \\
&{\text{b}} = ab - {\text{a}} \\
&{\text{a}} + {\text{b}} = ab \\
&\dfrac{1}{{\text{a}}} + \dfrac{1}{{\text{b}}} = 1 \\
\end{align} $
$\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{{\text{x}}_1}\left( {{{\text{y}}_2} - {{\text{y}}_3}} \right) + {{\text{x}}_2}\left( {{{\text{y}}_3} - {{\text{y}}_1}} \right) + {{\text{x}}_3}\left( {{{\text{y}}_1} - {{\text{y}}_2}} \right)} \right] = 0$
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given that the points $A(a, 0)$, $B(0, b)$ and $C(1, 1)$ are collinear. This means that the area of the triangle formed by these three points is zero.

Let $A(a, 0)$, $B(0, b)$ and $C(1, 1)$. We will apply the triangle formula to these three points as-
$\begin{align}
&\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{\text{a}}\left( {{\text{b}} - 1} \right) + 0\left( {1 - 0} \right) + 1\left( {0 - {\text{b}}} \right)} \right] = 0 \\
&ab - {\text{a}} - {\text{b}} = 0 \\
&{\text{a}} + {\text{b}} = ab \\
\end{align} $
Dividing this by ab,
$\dfrac{1}{{\text{b}}} + \dfrac{1}{{\text{a}}} = 1 \\ $
By this equation we can see that the correct option is A.
Note: In such types of questions, we need to use a particular property of collinear points to form the equation. Another condition for the points to be collinear is that the slope of any two pairs are equal. That is-
$\begin{align}
&Slop{e_{AB}} = Slop{e_{BC}} \\
&\dfrac{{{\text{b}} - 0}}{{0 - {\text{a}}}} = \dfrac{{{\text{b}} - 1}}{{0 - 1}} \\
&\dfrac{{\text{b}}}{{\text{a}}} = - \left( {{\text{b}} - 1} \right) \\
&{\text{b}} = ab - {\text{a}} \\
&{\text{a}} + {\text{b}} = ab \\
&\dfrac{1}{{\text{a}}} + \dfrac{1}{{\text{b}}} = 1 \\
\end{align} $
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




