
If the lengths of the sides of a triangle are in A.P and the greatest angle is double the smallest, then the ratio of the lengths of the sides of this triangle is:
(a) 5:9:13
(b) 5:6:7
(c) 4:5:6
(d) 3:4:5
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, first, we will apply the condition of A.P for three consecutive numbers. After that, we will find the angle B. Then using the sine rule of the triangle we will get a quadratic equation in terms of cosine. Then we will solve the quadratic equation by splitting the middle term and get values of cos. After that, we will write values of sides a, b and c in ratio and by using solved values we will get the ratio in which sides are.
Complete step by step answer:
Let first us draw the figure.
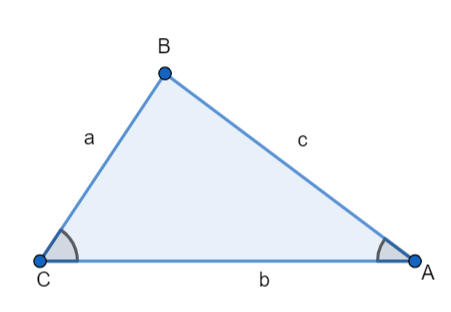
$\Rightarrow$ Let there be a triangle $\vartriangle ABC$ , with sides BC = a, AB = c and CA = b. and let angles be $\angle A,$ $\angle B,$and$\angle C$ and let $\angle C=2\angle A$.
Now, in question, it is given that sides of the triangle are in A.P
We know that if three numbers a, b, c are in A.P, then 2b = a + c
So, we have 2b = a + c
Also, it is given that a larger angle is twice the smaller angle. So let $\angle A$be a larger angle and $\angle C$ be a smaller angle, then $\angle C=2\angle A$.
So, if $\angle A=\theta $, then $\angle C=2\theta $.
We know that sum of the interior angle of the triangle equals to ${{180}^{{}^\circ }}.$
So, in $\vartriangle ABC$
$\Rightarrow$ $\angle A+\angle B+\angle C=180$
$\Rightarrow$ Then, $\theta +\angle B+2\theta =180$
$\Rightarrow$ $\angle B=180-3\theta $
Now for triangle we know that there is sine rule, which states that $\dfrac{a}{\sin A}=\dfrac{b}{\operatorname{sinB}}=\dfrac{c}{\operatorname{sinC}}=k$
$\Rightarrow$ So, for triangle $\vartriangle ABC$,
$\dfrac{a}{\sin \theta }=\dfrac{b}{\sin 3\theta }=\dfrac{c}{\sin 2\theta }=k$
Now, we can say that $\dfrac{b}{\sin 3\theta }=k$
$\Rightarrow$ $b=k\sin 3\theta $
Also, we know that 2b = a + c
$\Rightarrow$ So, $2k\sin 3\theta =a+c$
But from sine rule,
$a=k\sin \theta $ and $c=k\sin 2\theta $
So, we can say that
$2k\sin 3\theta =k\sin \theta +k\sin 2\theta $
$\Rightarrow$ $2sin3\theta =\sin \theta +\sin 2\theta $
$\Rightarrow$ We know that $sin3\theta =3\sin \theta -4{{\sin }^{3}}\theta $
So, we have
$\Rightarrow$ $2\left( 3\sin \theta -4{{\sin }^{3}}\theta \right)=\sin \theta +\sin 2\theta $
$\Rightarrow$ $6\sin \theta -8{{\sin }^{3}}\theta =\sin \theta +\sin 2\theta $
We know that \[\sin 2\theta =2\sin \theta \cos \theta \]
So, $6\sin \theta -8{{\sin }^{3}}\theta =\sin \theta +2\sin \theta \cos \theta $
$\Rightarrow$ $6-8{{\sin }^{2}}\theta =1+2\cos \theta $
We know that ${{\sin }^{2}}\theta =1-{{\cos }^{2}}\theta $
So, $6-8\left( 1-{{\cos }^{2}}\theta \right)=1+2\cos \theta $
On simplifying, we get
$\Rightarrow$ $8{{\cos }^{2}}\theta -2\cos \theta -3=0$
$\Rightarrow$ $8{{\cos }^{2}}\theta -6\cos \theta +4\cos \theta -3=0$
$\Rightarrow$ $2\cos \theta (4\cos \theta -3)+(4\cos \theta -3)=0$
$\Rightarrow$ So, we have $\cos \theta =\dfrac{3}{4}$ or $\cos \theta =-\dfrac{1}{2}$
So, case of $\cos \theta =-\dfrac{1}{2}$will be rejected as all angles lies in first quadrant.
Now, we have to find ratio of sides of triangle that is a:b:c
$\Rightarrow$ $k\sin \theta $:$k\sin 3\theta $:$k\sin 2\theta $
$\Rightarrow$ $\sin \theta $:$3\sin \theta -4{{\sin }^{3}}\theta $:$2\sin \theta \cos \theta $
$\Rightarrow$ 1:$3-4{{\sin }^{2}}\theta $:$2\cos \theta $
$\Rightarrow$ 1:$3-4(1-{{\cos }^{2}}\theta )$:$2\cos \theta $
$\Rightarrow$ 1:$4{{\cos }^{2}}\theta -1$:$2\cos \theta $
Putting, $\cos \theta =\dfrac{3}{4}$, we get
1:$4{{\left( \dfrac{3}{4} \right)}^{2}}-1$:$2.\dfrac{3}{4}$
$\Rightarrow$ 1:$\left( \dfrac{9}{4} \right)-1$:$\dfrac{3}{2}$
1:$\left( \dfrac{5}{4} \right)$:$\dfrac{3}{2}$
Multiplying by 4, we get
4:5:6
$\Rightarrow$ Hence, option ( c ) is correct.
Note:
To solve such questions one must know if three numbers a, b, c are in A.P, then 2b = a + c and sine rule for triangles which states $\dfrac{a}{\sin \theta }=\dfrac{b}{\sin 3\theta }=\dfrac{c}{\sin 2\theta }=k$. Also, remember some trigonometric formulas such as ${{\sin }^{2}}\theta =1-{{\cos }^{2}}\theta $, ${{\sin }^{2}}\theta =1-{{\cos }^{2}}\theta $, $sin3\theta =3\sin \theta -4{{\sin }^{3}}\theta $ etc. Try not to make any calculation mistake as this will make solution more complex.
Complete step by step answer:
Let first us draw the figure.

$\Rightarrow$ Let there be a triangle $\vartriangle ABC$ , with sides BC = a, AB = c and CA = b. and let angles be $\angle A,$ $\angle B,$and$\angle C$ and let $\angle C=2\angle A$.
Now, in question, it is given that sides of the triangle are in A.P
We know that if three numbers a, b, c are in A.P, then 2b = a + c
So, we have 2b = a + c
Also, it is given that a larger angle is twice the smaller angle. So let $\angle A$be a larger angle and $\angle C$ be a smaller angle, then $\angle C=2\angle A$.
So, if $\angle A=\theta $, then $\angle C=2\theta $.
We know that sum of the interior angle of the triangle equals to ${{180}^{{}^\circ }}.$
So, in $\vartriangle ABC$
$\Rightarrow$ $\angle A+\angle B+\angle C=180$
$\Rightarrow$ Then, $\theta +\angle B+2\theta =180$
$\Rightarrow$ $\angle B=180-3\theta $
Now for triangle we know that there is sine rule, which states that $\dfrac{a}{\sin A}=\dfrac{b}{\operatorname{sinB}}=\dfrac{c}{\operatorname{sinC}}=k$
$\Rightarrow$ So, for triangle $\vartriangle ABC$,
$\dfrac{a}{\sin \theta }=\dfrac{b}{\sin 3\theta }=\dfrac{c}{\sin 2\theta }=k$
Now, we can say that $\dfrac{b}{\sin 3\theta }=k$
$\Rightarrow$ $b=k\sin 3\theta $
Also, we know that 2b = a + c
$\Rightarrow$ So, $2k\sin 3\theta =a+c$
But from sine rule,
$a=k\sin \theta $ and $c=k\sin 2\theta $
So, we can say that
$2k\sin 3\theta =k\sin \theta +k\sin 2\theta $
$\Rightarrow$ $2sin3\theta =\sin \theta +\sin 2\theta $
$\Rightarrow$ We know that $sin3\theta =3\sin \theta -4{{\sin }^{3}}\theta $
So, we have
$\Rightarrow$ $2\left( 3\sin \theta -4{{\sin }^{3}}\theta \right)=\sin \theta +\sin 2\theta $
$\Rightarrow$ $6\sin \theta -8{{\sin }^{3}}\theta =\sin \theta +\sin 2\theta $
We know that \[\sin 2\theta =2\sin \theta \cos \theta \]
So, $6\sin \theta -8{{\sin }^{3}}\theta =\sin \theta +2\sin \theta \cos \theta $
$\Rightarrow$ $6-8{{\sin }^{2}}\theta =1+2\cos \theta $
We know that ${{\sin }^{2}}\theta =1-{{\cos }^{2}}\theta $
So, $6-8\left( 1-{{\cos }^{2}}\theta \right)=1+2\cos \theta $
On simplifying, we get
$\Rightarrow$ $8{{\cos }^{2}}\theta -2\cos \theta -3=0$
$\Rightarrow$ $8{{\cos }^{2}}\theta -6\cos \theta +4\cos \theta -3=0$
$\Rightarrow$ $2\cos \theta (4\cos \theta -3)+(4\cos \theta -3)=0$
$\Rightarrow$ So, we have $\cos \theta =\dfrac{3}{4}$ or $\cos \theta =-\dfrac{1}{2}$
So, case of $\cos \theta =-\dfrac{1}{2}$will be rejected as all angles lies in first quadrant.
Now, we have to find ratio of sides of triangle that is a:b:c
$\Rightarrow$ $k\sin \theta $:$k\sin 3\theta $:$k\sin 2\theta $
$\Rightarrow$ $\sin \theta $:$3\sin \theta -4{{\sin }^{3}}\theta $:$2\sin \theta \cos \theta $
$\Rightarrow$ 1:$3-4{{\sin }^{2}}\theta $:$2\cos \theta $
$\Rightarrow$ 1:$3-4(1-{{\cos }^{2}}\theta )$:$2\cos \theta $
$\Rightarrow$ 1:$4{{\cos }^{2}}\theta -1$:$2\cos \theta $
Putting, $\cos \theta =\dfrac{3}{4}$, we get
1:$4{{\left( \dfrac{3}{4} \right)}^{2}}-1$:$2.\dfrac{3}{4}$
$\Rightarrow$ 1:$\left( \dfrac{9}{4} \right)-1$:$\dfrac{3}{2}$
1:$\left( \dfrac{5}{4} \right)$:$\dfrac{3}{2}$
Multiplying by 4, we get
4:5:6
$\Rightarrow$ Hence, option ( c ) is correct.
Note:
To solve such questions one must know if three numbers a, b, c are in A.P, then 2b = a + c and sine rule for triangles which states $\dfrac{a}{\sin \theta }=\dfrac{b}{\sin 3\theta }=\dfrac{c}{\sin 2\theta }=k$. Also, remember some trigonometric formulas such as ${{\sin }^{2}}\theta =1-{{\cos }^{2}}\theta $, ${{\sin }^{2}}\theta =1-{{\cos }^{2}}\theta $, $sin3\theta =3\sin \theta -4{{\sin }^{3}}\theta $ etc. Try not to make any calculation mistake as this will make solution more complex.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




