
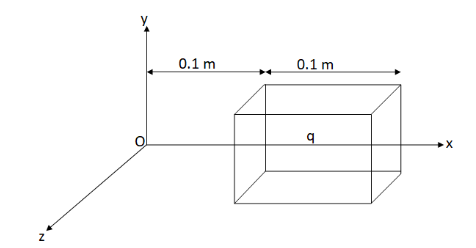
If the electric field components due to electric charge in cube shown in figure are \[{E_x} = 600{x^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\] and \[{E_y} = 0\] and \[{E_z} = 0\], then charge within the cube ______

Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint:We are asked to find the total charge within the cube. To find the total charge, first we need to find the net flux through the cube. To find out the net flux, you will need to use Gauss law to find the flux through the faces of the cube and then use these values to find the charge within the cube.
Complete step by step answer:
Given the electric field components due to the electric charge in cube,
\[{E_x} = 600{x^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\] and \[{E_y} = 0\] and \[{E_z} = 0\]
The side of the cube is \[d = 0.1\,{\text{m}}\]
To find the charge within the cube, we will first find the electric flux through the cube.
From Gauss law, we have the formula for electric flux through a surface as,
\[\phi = \overrightarrow E .\overrightarrow A = EA\cos \theta = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _o}}}\] …………(i)
where \[E\] is the electric field, \[A\] is the area, \[\theta \] is the angle between area vector \[\overrightarrow A \] and electric field vector \[\overrightarrow E \], \[q\] is the total charge within the closed surface and \[{\varepsilon _o} = 8.854 \times {10^{ - 12}}\,{{\text{C}}^{\text{2}}}{{\text{m}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}{{\text{N}}^{{\text{ - 1}}}}\] is permittivity of free space.
The formula for area of each face of the cube is
\[A = {a^2}\] …………...(ii)
where \[a\] is the side of the cube
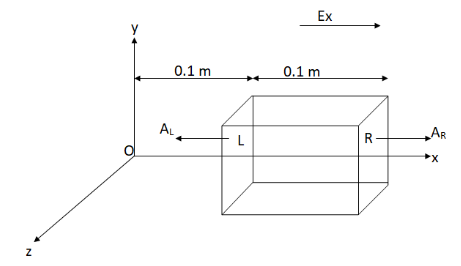
We find the electric flux through the left face (L) of the cube.
The angle between electric field \[\overrightarrow {{E_x}} \] and area vector of left side of cube \[\overrightarrow {{A_L}} \] is \[{180^ \circ }\].
Electric flux through left face (L) of the cube will be (using equation (i)),
\[{\phi _L} = {E_x}{A_L}\cos \left( {{{180}^ \circ }} \right)\] (iii)
The area \[{A_L}\] using equation (ii), is
\[{A_L} = {d^2}\]
Putting the values of \[{A_L}\] and \[{E_x}\] in equation (iii), we get
\[{\phi _L} = 600{x^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}{d^2}\cos \left( {{{180}^ \circ }} \right)\]
For face L, the value of \[x\] is \[0.1\,{\text{m}}\], putting this value and the value of \[d\] in above equation we get
\[{\phi _L} = 600{\left( {0.1} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}{\left( {0.1} \right)^2}\cos \left( {{{180}^ \circ }} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\phi _L} = 600\left( {0.316} \right)\left( {0.01} \right)\left( { - 1} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\phi _L} = - 1.896\,{\text{N}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}{{\text{C}}^{{\text{ - 1}}}}\]
Now, we find the electric flux through the right face (R) of the cube.The angle between electric field \[\overrightarrow {{E_x}} \] and area vector of left side of cube \[\overrightarrow {{A_L}} \] is \[{0^ \circ }\].
Electric flux through right face (R) of the cube will be (using equation (i)),
\[{\phi _R} = {E_x}{A_R}\cos \left( {{0^ \circ }} \right)\] …………....(iii)
The area \[{A_R}\] using equation (ii), is
\[{A_R} = {d^2}\]
Putting the values of \[{A_R}\] and \[{E_x}\] in equation (iii), we get
\[{\phi _R} = 600{x^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}{d^2}\cos \left( {{0^ \circ }} \right)\]
For face R, the value of \[x\] is \[\left( {0.1\,{\text{m}} + 0.1\,{\text{m}}} \right) = 0.2{\text{m}}\], putting this value and the value of \[d\] in above equation we get
\[{\phi _R} = 600{\left( {0.2} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}{\left( {0.1} \right)^2}\cos \left( {{0^ \circ }} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\phi _R} = 600\left( {0.447} \right)\left( {0.01} \right)\left( 1 \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\phi _R} = 2.683\,{\text{N}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}{{\text{C}}^{{\text{ - 1}}}}\]
The electric flux through other faces will be zero as the electric field along the y-axis and z-axis is zero.So, the net electric flux through the cube will be just addition of flux through L and R face.
\[\therefore \phi = {\phi _L} + {\phi _R}\]
Putting the values of \[{\phi _L}\] and \[{\phi _R}\] we get,
\[\phi = - 1.896 + 2.683\]
\[ \Rightarrow \phi = 0.787{\text{N}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}{{\text{C}}^{{\text{ - 1}}}}\] ……....(iii)
From equation (i), we have,
\[\phi = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _o}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow q = \phi {\varepsilon _o}\]
Putting the values of \[\phi \] and \[{\varepsilon _o}\] we get,
\[q = \left( {0.787} \right)\left( {8.854 \times {{10}^{ - 12}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow q = 6.96 \times {10^{ - 12}}{\text{C}}\]
\[ \therefore q \approx 7 \times {10^{ - 12}}\,{\text{C}}\]
Therefore, the charge within the cube is \[7 \times {10^{ - 12}}\,{\text{C}}\].
Note: Before applying Gauss law always check whether the surface is a closed surface or not as, Gauss law is applicable only for closed surfaces and applying Gauss law we can find the total charge within a closed surface. The closed surface through which the flux is obtained is called Gaussian surface.
Complete step by step answer:
Given the electric field components due to the electric charge in cube,
\[{E_x} = 600{x^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\] and \[{E_y} = 0\] and \[{E_z} = 0\]
The side of the cube is \[d = 0.1\,{\text{m}}\]
To find the charge within the cube, we will first find the electric flux through the cube.
From Gauss law, we have the formula for electric flux through a surface as,
\[\phi = \overrightarrow E .\overrightarrow A = EA\cos \theta = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _o}}}\] …………(i)
where \[E\] is the electric field, \[A\] is the area, \[\theta \] is the angle between area vector \[\overrightarrow A \] and electric field vector \[\overrightarrow E \], \[q\] is the total charge within the closed surface and \[{\varepsilon _o} = 8.854 \times {10^{ - 12}}\,{{\text{C}}^{\text{2}}}{{\text{m}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}{{\text{N}}^{{\text{ - 1}}}}\] is permittivity of free space.
The formula for area of each face of the cube is
\[A = {a^2}\] …………...(ii)
where \[a\] is the side of the cube

We find the electric flux through the left face (L) of the cube.
The angle between electric field \[\overrightarrow {{E_x}} \] and area vector of left side of cube \[\overrightarrow {{A_L}} \] is \[{180^ \circ }\].
Electric flux through left face (L) of the cube will be (using equation (i)),
\[{\phi _L} = {E_x}{A_L}\cos \left( {{{180}^ \circ }} \right)\] (iii)
The area \[{A_L}\] using equation (ii), is
\[{A_L} = {d^2}\]
Putting the values of \[{A_L}\] and \[{E_x}\] in equation (iii), we get
\[{\phi _L} = 600{x^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}{d^2}\cos \left( {{{180}^ \circ }} \right)\]
For face L, the value of \[x\] is \[0.1\,{\text{m}}\], putting this value and the value of \[d\] in above equation we get
\[{\phi _L} = 600{\left( {0.1} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}{\left( {0.1} \right)^2}\cos \left( {{{180}^ \circ }} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\phi _L} = 600\left( {0.316} \right)\left( {0.01} \right)\left( { - 1} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\phi _L} = - 1.896\,{\text{N}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}{{\text{C}}^{{\text{ - 1}}}}\]
Now, we find the electric flux through the right face (R) of the cube.The angle between electric field \[\overrightarrow {{E_x}} \] and area vector of left side of cube \[\overrightarrow {{A_L}} \] is \[{0^ \circ }\].
Electric flux through right face (R) of the cube will be (using equation (i)),
\[{\phi _R} = {E_x}{A_R}\cos \left( {{0^ \circ }} \right)\] …………....(iii)
The area \[{A_R}\] using equation (ii), is
\[{A_R} = {d^2}\]
Putting the values of \[{A_R}\] and \[{E_x}\] in equation (iii), we get
\[{\phi _R} = 600{x^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}{d^2}\cos \left( {{0^ \circ }} \right)\]
For face R, the value of \[x\] is \[\left( {0.1\,{\text{m}} + 0.1\,{\text{m}}} \right) = 0.2{\text{m}}\], putting this value and the value of \[d\] in above equation we get
\[{\phi _R} = 600{\left( {0.2} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}{\left( {0.1} \right)^2}\cos \left( {{0^ \circ }} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\phi _R} = 600\left( {0.447} \right)\left( {0.01} \right)\left( 1 \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\phi _R} = 2.683\,{\text{N}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}{{\text{C}}^{{\text{ - 1}}}}\]
The electric flux through other faces will be zero as the electric field along the y-axis and z-axis is zero.So, the net electric flux through the cube will be just addition of flux through L and R face.
\[\therefore \phi = {\phi _L} + {\phi _R}\]
Putting the values of \[{\phi _L}\] and \[{\phi _R}\] we get,
\[\phi = - 1.896 + 2.683\]
\[ \Rightarrow \phi = 0.787{\text{N}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}{{\text{C}}^{{\text{ - 1}}}}\] ……....(iii)
From equation (i), we have,
\[\phi = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _o}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow q = \phi {\varepsilon _o}\]
Putting the values of \[\phi \] and \[{\varepsilon _o}\] we get,
\[q = \left( {0.787} \right)\left( {8.854 \times {{10}^{ - 12}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow q = 6.96 \times {10^{ - 12}}{\text{C}}\]
\[ \therefore q \approx 7 \times {10^{ - 12}}\,{\text{C}}\]
Therefore, the charge within the cube is \[7 \times {10^{ - 12}}\,{\text{C}}\].
Note: Before applying Gauss law always check whether the surface is a closed surface or not as, Gauss law is applicable only for closed surfaces and applying Gauss law we can find the total charge within a closed surface. The closed surface through which the flux is obtained is called Gaussian surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




