
If the coefficient of friction between an insect and the bowl is $\mu $ and the radius of the bowl is $r$ the maximum height to which the insect can crawl in the bowl is:

Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: First we will draw the free body diagram of an insect that is crawling in the bowl after doing that we will find the forces acting on the insect. By doing so we will lead to our solution.
Formula used:
${{F}_{L}}=\mu N$
Complete step by step solution:
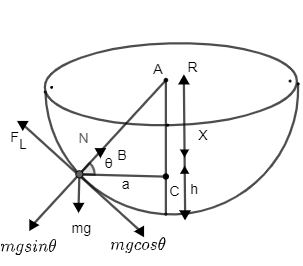
$\to $ From the figure we can give below formula
$N=mg\sin \theta ....\left( 1 \right)$
And frictional force will be equal to
${{F}_{L}}=mg\cos \theta ....\left( 2 \right)$
$\to $Now let’s divide equation (1) by equation (2) we will get
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{N}{{{F}_{L}}}=\dfrac{mg\sin \theta }{mg\cos \theta } \\
& \therefore \tan \theta =\dfrac{N}{{{F}_{L}}}.....\left( 3 \right) \\
\end{align}$
$\to $From figure (1) if we consider
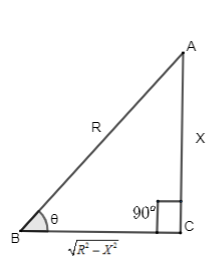
$\to $From the triangle ABC
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \tan \theta =\dfrac{AC}{BC} \\
& \therefore \tan \theta =\dfrac{X}{\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}-{{X}^{2}}}}......(4) \\
\end{align}$
$\to $Now let’s equalize equation (3) and equation (4) we will get
$\dfrac{N}{{{F}_{L}}}=\dfrac{X}{\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}-{{X}^{2}}}}....\left( 5 \right)$
$\to $We know that frictional force
${{F}_{L}}=\mu N$
${{F}_{L}}$ = frictional force
$\mu $ = coefficient of the friction
N = normal force
$\to $Substitute value at ${{F}_{L}}$ in equation (5)
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{N}{\mu N}=\dfrac{X}{\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}-{{X}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\mu }=\dfrac{X}{\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}-{{X}^{2}}}} \\
& \therefore X=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}-{{X}^{2}}}}{\mu } \\
\end{align}$
$\to $Taking square on the both sides
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{X}^{2}}=\dfrac{{{R}^{2}}-{{X}^{2}}}{{{\mu }^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\mu }^{2}}{{X}^{2}}+{{X}^{2}}={{R}^{2}} \\
& \therefore {{X}^{2}}\left( {{\mu }^{2}}+1 \right)={{R}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
$\to $Taking under root on the both sides we get
$X=\dfrac{R}{\sqrt{{{\mu }^{2}}+1}}....\left( 6 \right)$
$\to $Now from the figure (1) height (h) is
$h=R-X....\left( 7 \right)$
$\to $Now substitute value of x in equation (7) we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow h=R-\dfrac{R}{\sqrt{{{\mu }^{2}}+1}} \\
& \therefore h=R\left( 1-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{{{\mu }^{2}}+1}} \right).....\left( 8 \right) \\
\end{align}$
$\to $Hence the height to which the insect can crawl in the bowl is given by the equation (8).
Additional information:
Definition of frictional force:
“Frictional force can be defined as the force generated by two surface that are in contact and slide against each other.”
Definition of Pseudo force:
“It is an apparent force that acts on all masses whose motion is described using a non-inertial frame of reference frame, such as a rotating reference frame.”
Note:
This question is all dependent on the free body diagram of the insect. If we make any mistake in any single force then it will lead us to the incorrect solution. So be careful when we define forces on free body diagrams.
Formula used:
${{F}_{L}}=\mu N$
Complete step by step solution:

$\to $ From the figure we can give below formula
$N=mg\sin \theta ....\left( 1 \right)$
And frictional force will be equal to
${{F}_{L}}=mg\cos \theta ....\left( 2 \right)$
$\to $Now let’s divide equation (1) by equation (2) we will get
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{N}{{{F}_{L}}}=\dfrac{mg\sin \theta }{mg\cos \theta } \\
& \therefore \tan \theta =\dfrac{N}{{{F}_{L}}}.....\left( 3 \right) \\
\end{align}$
$\to $From figure (1) if we consider

$\to $From the triangle ABC
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \tan \theta =\dfrac{AC}{BC} \\
& \therefore \tan \theta =\dfrac{X}{\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}-{{X}^{2}}}}......(4) \\
\end{align}$
$\to $Now let’s equalize equation (3) and equation (4) we will get
$\dfrac{N}{{{F}_{L}}}=\dfrac{X}{\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}-{{X}^{2}}}}....\left( 5 \right)$
$\to $We know that frictional force
${{F}_{L}}=\mu N$
${{F}_{L}}$ = frictional force
$\mu $ = coefficient of the friction
N = normal force
$\to $Substitute value at ${{F}_{L}}$ in equation (5)
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{N}{\mu N}=\dfrac{X}{\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}-{{X}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\mu }=\dfrac{X}{\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}-{{X}^{2}}}} \\
& \therefore X=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}-{{X}^{2}}}}{\mu } \\
\end{align}$
$\to $Taking square on the both sides
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{X}^{2}}=\dfrac{{{R}^{2}}-{{X}^{2}}}{{{\mu }^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\mu }^{2}}{{X}^{2}}+{{X}^{2}}={{R}^{2}} \\
& \therefore {{X}^{2}}\left( {{\mu }^{2}}+1 \right)={{R}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
$\to $Taking under root on the both sides we get
$X=\dfrac{R}{\sqrt{{{\mu }^{2}}+1}}....\left( 6 \right)$
$\to $Now from the figure (1) height (h) is
$h=R-X....\left( 7 \right)$
$\to $Now substitute value of x in equation (7) we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow h=R-\dfrac{R}{\sqrt{{{\mu }^{2}}+1}} \\
& \therefore h=R\left( 1-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{{{\mu }^{2}}+1}} \right).....\left( 8 \right) \\
\end{align}$
$\to $Hence the height to which the insect can crawl in the bowl is given by the equation (8).
Additional information:
Definition of frictional force:
“Frictional force can be defined as the force generated by two surface that are in contact and slide against each other.”
Definition of Pseudo force:
“It is an apparent force that acts on all masses whose motion is described using a non-inertial frame of reference frame, such as a rotating reference frame.”
Note:
This question is all dependent on the free body diagram of the insect. If we make any mistake in any single force then it will lead us to the incorrect solution. So be careful when we define forces on free body diagrams.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




