
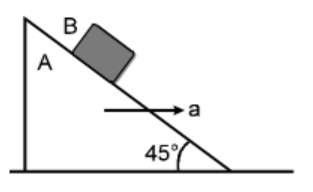
If the coefficient of friction between A and B is $\mu $. The maximum horizontal acceleration of the wedge A for which B will remain at rest w.r.t the wedge is
A. $\mu g$
B. $g(\dfrac{{1 + \mu }}{{1 - \mu }})$
C. $\dfrac{g}{\mu }$
D. $g(\dfrac{{1 - \mu }}{{1 + \mu }})$

Answer
579k+ views
Hint: Try to solve by taking A as a frame of reference and use pseudo force concept it will be easy that way you can also solve by taking ground as a frame of reference but then you will have to apply constraint equations which will make it little complex.
Complete step by step answer:
We will solve this question by taking wedge A as a frame of reference.
So free body diagram according as we observe B from A will be
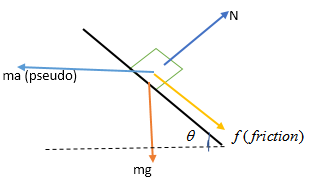
balancing force perpendicular to incline we have,
$N = mg\cos \theta + ma\sin \theta $so
Friction $f = \mu N = \mu (mg\cos \theta + ma\sin \theta )$
And balancing force along the incline we have,
$f + mg\sin \theta = ma\cos \theta $
$ \Rightarrow \mu (mg\cos \theta + ma\sin \theta ) + mg\sin \theta = ma\cos \theta $
$ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{g\sin \theta + \mu g\cos \theta }}{{a\cos \theta - \mu a\sin \theta }}$ putting $\theta = {45^ \circ }$we have
$\therefore a = g(\dfrac{{1 + \mu }}{{1 - \mu }})$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
In these types of questions, choosing a frame of reference is critical because choosing a better frame of reference makes a lot of things easy here. For example, once we take wedge A as a frame of reference we won’t have to worry about constraint equations and it makes it easier to solve such questions.
Complete step by step answer:
We will solve this question by taking wedge A as a frame of reference.
So free body diagram according as we observe B from A will be

balancing force perpendicular to incline we have,
$N = mg\cos \theta + ma\sin \theta $so
Friction $f = \mu N = \mu (mg\cos \theta + ma\sin \theta )$
And balancing force along the incline we have,
$f + mg\sin \theta = ma\cos \theta $
$ \Rightarrow \mu (mg\cos \theta + ma\sin \theta ) + mg\sin \theta = ma\cos \theta $
$ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{g\sin \theta + \mu g\cos \theta }}{{a\cos \theta - \mu a\sin \theta }}$ putting $\theta = {45^ \circ }$we have
$\therefore a = g(\dfrac{{1 + \mu }}{{1 - \mu }})$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
In these types of questions, choosing a frame of reference is critical because choosing a better frame of reference makes a lot of things easy here. For example, once we take wedge A as a frame of reference we won’t have to worry about constraint equations and it makes it easier to solve such questions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




