
If the chords of contact of tangent from the two points $ \left( -4,2 \right) $ and $ \left( 2,1 \right) $ to the hyperbola $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ are at right angle, then find the eccentricity of the given hyperbola?
(a) $ \dfrac{\sqrt{7}}{2} $
(b) $ \sqrt{\dfrac{5}{3}} $
(c) $ \sqrt{\dfrac{3}{2}} $
(d) $ \sqrt{2} $
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint: We start solving the problem by drawing the figure representing the given information. We then make use of the fact that the chord of contact from the point $ \left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right) $ to the hyperbola $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ is $ \dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ to find the chord of contacts from points $ \left( -4,2 \right) $ and $ \left( 2,1 \right) $ . We then find the slopes of both the chords and then make use of the fact that the product of slopes of two perpendicular lines is –1. We then make the necessary calculations to get the relation between $ {{a}^{2}} $ and $ {{b}^{2}} $ . We then make use of the fact that the eccentricity of the hyperbola $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ is defined as $ e=\sqrt{\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}} $ to get the required answer.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the problem, we are given that the chords of contact of tangent from the two points $ \left( -4,2 \right) $ and $ \left( 2,1 \right) $ to the hyperbola $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ are at right angle. We need to find the eccentricity of the given hyperbola.
Let us draw the figure representing the given information.
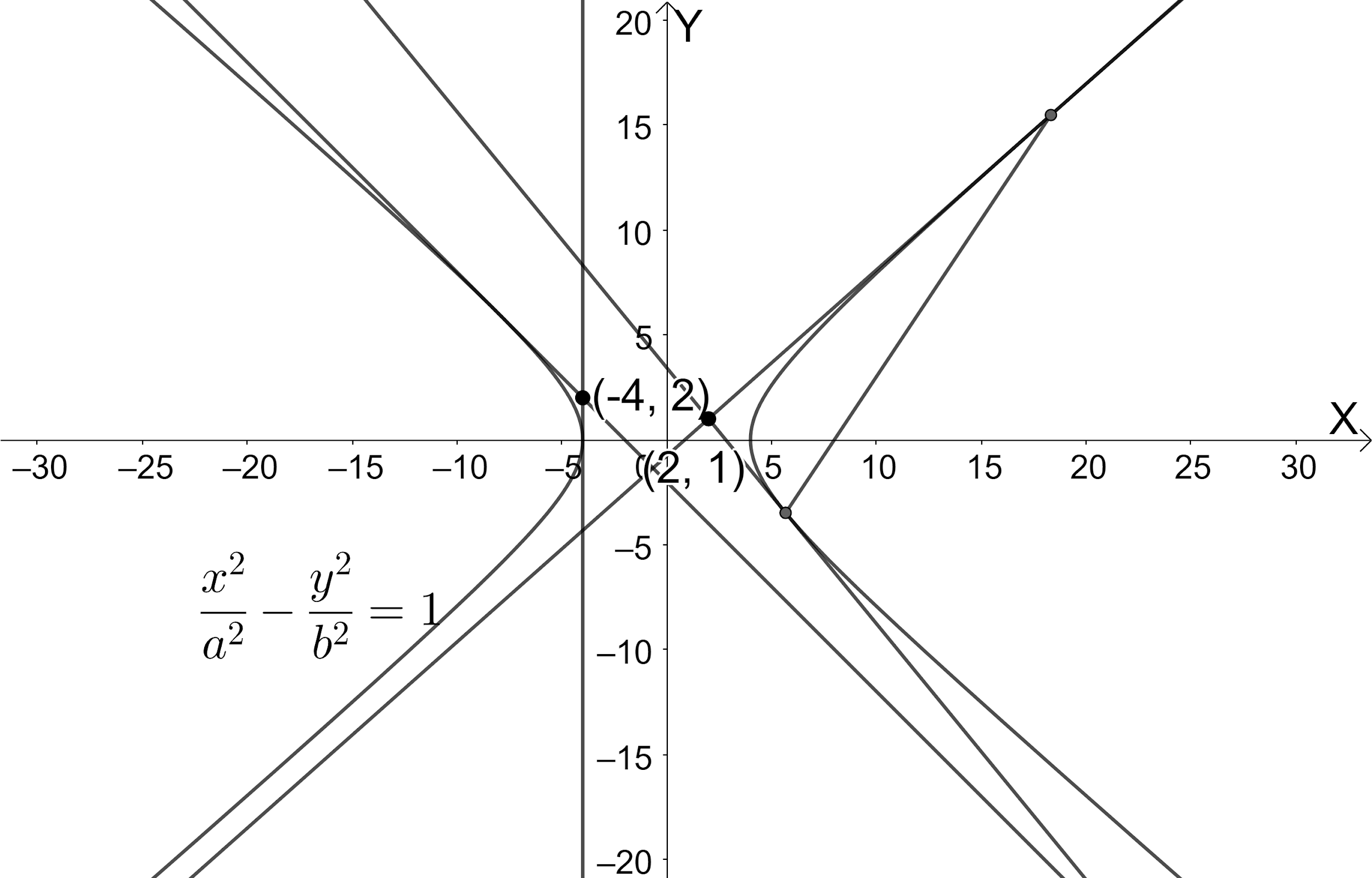
We know that the chord of contact from the point $ \left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right) $ to the hyperbola $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ is $ \dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ .
Now, let us find the chord of contact from the point $ \left( -4,2 \right) $ to the hyperbola $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ is $ \dfrac{x\left( -4 \right)}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{y\left( 2 \right)}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ .
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{-4{{b}^{2}}x-2{{a}^{2}}y}{{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ .
$ \Rightarrow -4{{b}^{2}}x-2{{a}^{2}}y={{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}} $ .
$ \Rightarrow -2{{a}^{2}}y=4{{b}^{2}}x+{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}} $ .
\[\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{4{{b}^{2}}}{-2{{a}^{2}}}x+\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}}{\left( -2{{a}^{2}} \right)}\].
\[\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-2{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}x-\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{2}\]. Comparing this with the equation of line $ y=mx+c $ , we get the slope as $ \dfrac{-2{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}} $ ---(1).
Now, let us find the chord of contact from the point $ \left( 2,1 \right) $ to the hyperbola $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ is $ \dfrac{x\left( 2 \right)}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{y\left( 1 \right)}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ .
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{2{{b}^{2}}x-{{a}^{2}}y}{{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ .
$ \Rightarrow 2{{b}^{2}}x-{{a}^{2}}y={{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}} $ .
$ \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}y=2{{b}^{2}}x+{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}} $ .
\[\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{2{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}x+\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}\].
\[\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{2{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}x+{{b}^{2}}\]. Comparing this with the equation of line $ y=mx+c $ , we get the slope as $ \dfrac{2{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}} $ ---(2).
We know that the product of slopes of two perpendicular lines is –1.
So, we get $ \left( \dfrac{-2{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}} \right)\times \left( \dfrac{2{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}} \right)=-1 $ .
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{-4{{b}^{4}}}{{{a}^{4}}}=-1 $ .
$ \Rightarrow 4{{b}^{4}}={{a}^{4}} $ .
$ \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}=2{{b}^{2}} $ ---(3).
We know that the eccentricity of the hyperbola $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ is defined as $ e=\sqrt{\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}} $ .
From equation (3), we get $ e=\sqrt{\dfrac{2{{b}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}{2{{b}^{2}}}} $ .
$ \Rightarrow e=\sqrt{\dfrac{3{{b}^{2}}}{2{{b}^{2}}}} $ .
$ \Rightarrow e=\sqrt{\dfrac{3}{2}} $ .
We have found the eccentricity of the given hyperbola as $ \sqrt{\dfrac{3}{2}} $ .
$ \therefore $ The correct option for the given problem is (c).
Note:
We can see that the given problem contains a huge amount of calculation so, we need to perform each step carefully to avoid confusion and mistakes. We should not consider the negative root for $ {{a}^{2}} $ in equation (3), as it is positive for all real numbers. Here we are considered that the transverse axis of the parabola is the x-axis to solve the problem. Similarly, we can expect the problem to find the length of the latus-rectum of the given hyperbola.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the problem, we are given that the chords of contact of tangent from the two points $ \left( -4,2 \right) $ and $ \left( 2,1 \right) $ to the hyperbola $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ are at right angle. We need to find the eccentricity of the given hyperbola.
Let us draw the figure representing the given information.

We know that the chord of contact from the point $ \left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right) $ to the hyperbola $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ is $ \dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ .
Now, let us find the chord of contact from the point $ \left( -4,2 \right) $ to the hyperbola $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ is $ \dfrac{x\left( -4 \right)}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{y\left( 2 \right)}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ .
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{-4{{b}^{2}}x-2{{a}^{2}}y}{{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ .
$ \Rightarrow -4{{b}^{2}}x-2{{a}^{2}}y={{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}} $ .
$ \Rightarrow -2{{a}^{2}}y=4{{b}^{2}}x+{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}} $ .
\[\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{4{{b}^{2}}}{-2{{a}^{2}}}x+\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}}{\left( -2{{a}^{2}} \right)}\].
\[\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{-2{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}x-\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{2}\]. Comparing this with the equation of line $ y=mx+c $ , we get the slope as $ \dfrac{-2{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}} $ ---(1).
Now, let us find the chord of contact from the point $ \left( 2,1 \right) $ to the hyperbola $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ is $ \dfrac{x\left( 2 \right)}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{y\left( 1 \right)}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ .
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{2{{b}^{2}}x-{{a}^{2}}y}{{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ .
$ \Rightarrow 2{{b}^{2}}x-{{a}^{2}}y={{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}} $ .
$ \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}y=2{{b}^{2}}x+{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}} $ .
\[\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{2{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}x+\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}\].
\[\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{2{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}x+{{b}^{2}}\]. Comparing this with the equation of line $ y=mx+c $ , we get the slope as $ \dfrac{2{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}} $ ---(2).
We know that the product of slopes of two perpendicular lines is –1.
So, we get $ \left( \dfrac{-2{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}} \right)\times \left( \dfrac{2{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}} \right)=-1 $ .
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{-4{{b}^{4}}}{{{a}^{4}}}=-1 $ .
$ \Rightarrow 4{{b}^{4}}={{a}^{4}} $ .
$ \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}=2{{b}^{2}} $ ---(3).
We know that the eccentricity of the hyperbola $ \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1 $ is defined as $ e=\sqrt{\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}} $ .
From equation (3), we get $ e=\sqrt{\dfrac{2{{b}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}{2{{b}^{2}}}} $ .
$ \Rightarrow e=\sqrt{\dfrac{3{{b}^{2}}}{2{{b}^{2}}}} $ .
$ \Rightarrow e=\sqrt{\dfrac{3}{2}} $ .
We have found the eccentricity of the given hyperbola as $ \sqrt{\dfrac{3}{2}} $ .
$ \therefore $ The correct option for the given problem is (c).
Note:
We can see that the given problem contains a huge amount of calculation so, we need to perform each step carefully to avoid confusion and mistakes. We should not consider the negative root for $ {{a}^{2}} $ in equation (3), as it is positive for all real numbers. Here we are considered that the transverse axis of the parabola is the x-axis to solve the problem. Similarly, we can expect the problem to find the length of the latus-rectum of the given hyperbola.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




