
If ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right)+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{12}{x} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$, the find the value of $x$.
A. $\dfrac{7}{13}$
B. $\dfrac{4}{3}$
C. 13
D. $\dfrac{13}{7}$
Answer
522.3k+ views
Hint: We first use the associative angle formula to find the simplified from. Then we use the trigonometric ratio of the right-angle triangle to find the value of $x$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We simplify the equation by taking one ratio of sin on the other side
${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right)+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{12}{x} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
So,
${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{12}{x} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{2}-{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right)$.
Now we take ratio of sine on both sides to get
$\sin \left[ {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{12}{x} \right) \right]=\sin \left[ \dfrac{\pi }{2}-{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right) \right]$.
We get
$\sin \left[ \dfrac{\pi }{2}-{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right) \right]=\dfrac{12}{x}=\cos \left[ {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right) \right]$.
We can take the representation of a right-angle triangle with height and hypotenuse ratio being $\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right)$ and the angle being $\theta $. The height and base were considered with respect to that particular angle $\theta $.
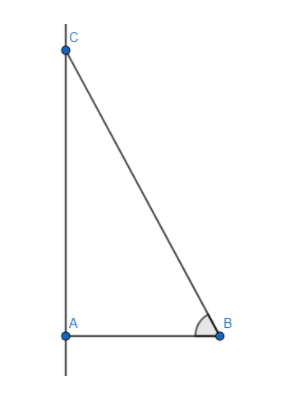
In this case we take $BC=x$ and keeping the ratio in mind we have $AC=5$ as the ratio has to be $\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right)$.
Now we apply the Pythagoras’ theorem to find the length of AB. $B{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}$.
So, $A{{B}^{2}}={{5}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}$ which gives $AB=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-25}$.
We need to find $\cos \left[ {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right) \right]$ which is equal to \[\cos \theta \].
This ratio gives \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{\text{base}}{\text{hypotenuse}}\]. So,
\[\cos \theta =\dfrac{AB}{BC}=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-25}}{x}\].
$\begin{align}
& \cos \left[ {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right) \right]=\dfrac{12}{x} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-25}}{x}=\dfrac{12}{x} \\
\end{align}$
Simplification gives ${{x}^{2}}-25={{12}^{2}}=144\Rightarrow x=13$. The correct option is C.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: We can also apply the trigonometric image form to get the value of $\cos \left[ {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right) \right]$.
It’s given that $\sin \theta =\dfrac{5}{x}$ and we need to find \[\cos \theta \]. We know $\cos \theta =\sqrt{1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta }$.
Putting the values, we get $\cos \theta =\sqrt{1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta }=\sqrt{1-{{\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right)}^{2}}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-25}}{x}$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We simplify the equation by taking one ratio of sin on the other side
${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right)+{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{12}{x} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
So,
${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{12}{x} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{2}-{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right)$.
Now we take ratio of sine on both sides to get
$\sin \left[ {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{12}{x} \right) \right]=\sin \left[ \dfrac{\pi }{2}-{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right) \right]$.
We get
$\sin \left[ \dfrac{\pi }{2}-{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right) \right]=\dfrac{12}{x}=\cos \left[ {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right) \right]$.
We can take the representation of a right-angle triangle with height and hypotenuse ratio being $\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right)$ and the angle being $\theta $. The height and base were considered with respect to that particular angle $\theta $.

In this case we take $BC=x$ and keeping the ratio in mind we have $AC=5$ as the ratio has to be $\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right)$.
Now we apply the Pythagoras’ theorem to find the length of AB. $B{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}$.
So, $A{{B}^{2}}={{5}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}$ which gives $AB=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-25}$.
We need to find $\cos \left[ {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right) \right]$ which is equal to \[\cos \theta \].
This ratio gives \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{\text{base}}{\text{hypotenuse}}\]. So,
\[\cos \theta =\dfrac{AB}{BC}=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-25}}{x}\].
$\begin{align}
& \cos \left[ {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right) \right]=\dfrac{12}{x} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-25}}{x}=\dfrac{12}{x} \\
\end{align}$
Simplification gives ${{x}^{2}}-25={{12}^{2}}=144\Rightarrow x=13$. The correct option is C.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: We can also apply the trigonometric image form to get the value of $\cos \left[ {{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right) \right]$.
It’s given that $\sin \theta =\dfrac{5}{x}$ and we need to find \[\cos \theta \]. We know $\cos \theta =\sqrt{1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta }$.
Putting the values, we get $\cos \theta =\sqrt{1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta }=\sqrt{1-{{\left( \dfrac{5}{x} \right)}^{2}}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-25}}{x}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

What is the difference between biodegradable and nonbiodegradable class 11 biology CBSE

Proton was discovered by A Thomson B Rutherford C Chadwick class 11 chemistry CBSE




