
If O is the origin and Q is a variable point of ${{y}^{2}}=x$. Find the locus of the mid-point of OQ.
Answer
522.9k+ views
Hint: We first find the parametric form of the equation of parabola ${{y}^{2}}=x$. We find the value of the parameter $a$. We take the point Q and find the midpoint of OQ. The locus will be defined for the midpoint using the formula of $\left( \dfrac{c+m}{2},\dfrac{d+n}{2} \right)$.
Complete step by step solution:
O is the origin and it will be considered as the coordinates of $\left( 0,0 \right)$.
Q is a variable point of ${{y}^{2}}=x$. Any arbitrary point of a parabola will be considered as the coordinates of $\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)$. It is the parametric form of the parabola. We need to find the value of $a$.
So, \[{{\left( 2at \right)}^{2}}=a{{t}^{2}}\Rightarrow 4{{a}^{2}}=a\]. Now the value of $a$ cannot be 0.
\[\begin{align}
& 4{{a}^{2}}=a \\
& \Rightarrow 4a=1 \\
& \Rightarrow a=\dfrac{1}{4} \\
\end{align}\]
The parametric coordinates of a point on ${{y}^{2}}=x$ will be $Q=\left( \dfrac{{{t}^{2}}}{4},\dfrac{t}{2} \right)$.
Now we need to find the locus of the mid-point of OQ.
The general formula of mid-point of two points $A\left( c,d \right)$ and $B\left( m,n \right)$ will be $\left( \dfrac{c+m}{2},\dfrac{d+n}{2} \right)$.
Following the formula, we get the midpoint of OQ as $\left( h,k \right)\equiv \left( \dfrac{\dfrac{{{t}^{2}}}{4}+0}{2},\dfrac{\dfrac{t}{2}+0}{2} \right)=\left( \dfrac{{{t}^{2}}}{8},\dfrac{t}{4} \right)$.
We get the value of $t$ as $k=\dfrac{t}{4}$ which gives $t=4k$.
We put the value in the equation of $h=\dfrac{{{t}^{2}}}{8}$ and get $h=\dfrac{{{\left( 4k \right)}^{2}}}{8}=2{{k}^{2}}$.
We now change the equation $h=2{{k}^{2}}$ to normal form and get $x=2{{y}^{2}}$.
Therefore, the locus of the mid-point of OQ is $x=2{{y}^{2}}$.
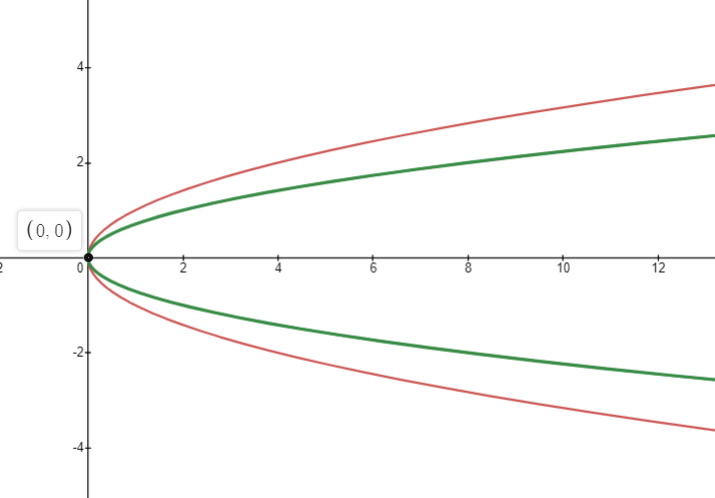
We can see the graph of the parabola $x=y^2$ (red) and the locus of the midpoint of OQ $x=2y^2$ (green)f below.
Note:
We need to be careful about the vertex of the parabola. As it is the origin $\left( 0,0 \right)$, we can take the parametric coordinates as $\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)$.
Complete step by step solution:
O is the origin and it will be considered as the coordinates of $\left( 0,0 \right)$.
Q is a variable point of ${{y}^{2}}=x$. Any arbitrary point of a parabola will be considered as the coordinates of $\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)$. It is the parametric form of the parabola. We need to find the value of $a$.
So, \[{{\left( 2at \right)}^{2}}=a{{t}^{2}}\Rightarrow 4{{a}^{2}}=a\]. Now the value of $a$ cannot be 0.
\[\begin{align}
& 4{{a}^{2}}=a \\
& \Rightarrow 4a=1 \\
& \Rightarrow a=\dfrac{1}{4} \\
\end{align}\]
The parametric coordinates of a point on ${{y}^{2}}=x$ will be $Q=\left( \dfrac{{{t}^{2}}}{4},\dfrac{t}{2} \right)$.
Now we need to find the locus of the mid-point of OQ.
The general formula of mid-point of two points $A\left( c,d \right)$ and $B\left( m,n \right)$ will be $\left( \dfrac{c+m}{2},\dfrac{d+n}{2} \right)$.
Following the formula, we get the midpoint of OQ as $\left( h,k \right)\equiv \left( \dfrac{\dfrac{{{t}^{2}}}{4}+0}{2},\dfrac{\dfrac{t}{2}+0}{2} \right)=\left( \dfrac{{{t}^{2}}}{8},\dfrac{t}{4} \right)$.
We get the value of $t$ as $k=\dfrac{t}{4}$ which gives $t=4k$.
We put the value in the equation of $h=\dfrac{{{t}^{2}}}{8}$ and get $h=\dfrac{{{\left( 4k \right)}^{2}}}{8}=2{{k}^{2}}$.
We now change the equation $h=2{{k}^{2}}$ to normal form and get $x=2{{y}^{2}}$.
Therefore, the locus of the mid-point of OQ is $x=2{{y}^{2}}$.
We can see the graph of the parabola $x=y^2$ (red) and the locus of the midpoint of OQ $x=2y^2$ (green)f below.

Note:
We need to be careful about the vertex of the parabola. As it is the origin $\left( 0,0 \right)$, we can take the parametric coordinates as $\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




