
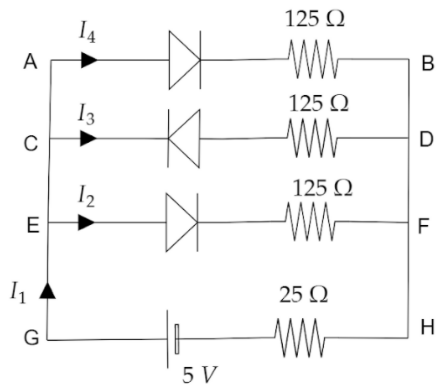
If each diode in figure has a forward resistance of $25{\text{ }}\Omega $ and infinite resistance in reverse bias, what will be the values of the current ${I_1}$, ${I_2}$, ${I_3}$ and ${I_4}$?

Answer
511.5k+ views
Hint:As in reverse bias condition, the resistance is infinite, so from the figure, CD is in reverse bias hence no current flows there. AB and EF are parallel to each other so the currents in both these circuits are the same. We have found the effective resistance of the combined circuit from AB and EF which are in parallel and GH in series. Then Ohm's Law found out the total current in the circuit with the help of the values given in question. Lastly splitting up the total current into its distributed ones as per the rules of parallel combination.
Complete step by step answer:
Since, in reverse biased condition the resistance is infinite, thus from the given figure we find out that ${I_3} = 0$ as CD is in reverse biased condition. Now, AB and EF are parallel to each other.
Total resistance in AB$ = 125 + 25 = 150{\text{ }}\Omega $
And total resistance in EF$ = 125 + 25 = 150{\text{ }}\Omega $
Let their combined resistance be $R$,
$R = \dfrac{{{\text{resistance in (AB}} \times {\text{EF)}}}}{{{\text{resistance in (AB + EF)}}}}$
$\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{150 \times 150}}{{150 + 150}} = 75{\text{ }}\Omega $
As, AB and EF are parallel to each other then, ${I_2} = {I_4}$
Net resistance in the circuit$ = 75 + 25 = 100{\text{ }}\Omega $
As per the given circuit ${I_3} = 0$ so, ${I_1}$ is split up into two equal currents ${I_2}$ and ${I_4}$ as they are in parallel combination.
Thus, ${I_2} = {I_4} = \dfrac{{{I_1}}}{2}$
From Ohm’s Law we get,
$V = IR - - - \left( 1 \right)$
In the given figure potential difference $V = 5{\text{ }}V$
$I = {I_1} = $ to be found
$R = $resistance of the circuit$ = 100{\text{ }}\Omega $
Substituting the values in equation $\left( 1 \right)$ we get,
$5 = I \times 100 = 0.05$
So, ${I_1} = 0.05{\text{ }}\Omega $
And ${I_2} = {I_4} = \dfrac{{{I_1}}}{2} = \dfrac{{0.05}}{2} = 0.025{\text{ }}\Omega $
So, finally the values of ${I_1} = 0.05{\text{ }}\Omega $, ${I_2} = 0.025{\text{ }}\Omega $, ${I_3} = 0{\text{ }}\Omega $ and ${I_4} = 0.025{\text{ }}\Omega $.
Note: As the diode in the circuit CD is in reverse condition, where the resistance is infinite according to the question, so the current CD is zero. In a parallel combination, an equal amount of current splits up from the main current. There is always an individual resistance in diodes rather than in the circuit.
Complete step by step answer:
Since, in reverse biased condition the resistance is infinite, thus from the given figure we find out that ${I_3} = 0$ as CD is in reverse biased condition. Now, AB and EF are parallel to each other.
Total resistance in AB$ = 125 + 25 = 150{\text{ }}\Omega $
And total resistance in EF$ = 125 + 25 = 150{\text{ }}\Omega $
Let their combined resistance be $R$,
$R = \dfrac{{{\text{resistance in (AB}} \times {\text{EF)}}}}{{{\text{resistance in (AB + EF)}}}}$
$\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{150 \times 150}}{{150 + 150}} = 75{\text{ }}\Omega $
As, AB and EF are parallel to each other then, ${I_2} = {I_4}$
Net resistance in the circuit$ = 75 + 25 = 100{\text{ }}\Omega $
As per the given circuit ${I_3} = 0$ so, ${I_1}$ is split up into two equal currents ${I_2}$ and ${I_4}$ as they are in parallel combination.
Thus, ${I_2} = {I_4} = \dfrac{{{I_1}}}{2}$
From Ohm’s Law we get,
$V = IR - - - \left( 1 \right)$
In the given figure potential difference $V = 5{\text{ }}V$
$I = {I_1} = $ to be found
$R = $resistance of the circuit$ = 100{\text{ }}\Omega $
Substituting the values in equation $\left( 1 \right)$ we get,
$5 = I \times 100 = 0.05$
So, ${I_1} = 0.05{\text{ }}\Omega $
And ${I_2} = {I_4} = \dfrac{{{I_1}}}{2} = \dfrac{{0.05}}{2} = 0.025{\text{ }}\Omega $
So, finally the values of ${I_1} = 0.05{\text{ }}\Omega $, ${I_2} = 0.025{\text{ }}\Omega $, ${I_3} = 0{\text{ }}\Omega $ and ${I_4} = 0.025{\text{ }}\Omega $.
Note: As the diode in the circuit CD is in reverse condition, where the resistance is infinite according to the question, so the current CD is zero. In a parallel combination, an equal amount of current splits up from the main current. There is always an individual resistance in diodes rather than in the circuit.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




