
If $\Delta ABC$ is such that $\angle A={{90}^{\circ }},\angle B=\angle C,$ then $\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}}\sin \left( B-C \right)=$
a) $\dfrac{1}{3}$
b) $\dfrac{1}{2}$
c) $1$
d) $\dfrac{3}{2}$
Answer
623.1k+ views
Hint: Use sine rule to this equation it is given as
$\dfrac{\sin A}{a}=\dfrac{\sin B}{b}=\dfrac{\sin C}{c}$, where a, b, c are sides of the triangle opposite to $\angle A,\angle B,\angle C$ respectively. Suppose the terms involved in sine rule as a constant and hence try to further simplify the problem by putting values of b and c in terms of A and B.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we know the sine rule of a triangle can be given as
$\dfrac{\sin A}{a}=\dfrac{\sin B}{b}=\dfrac{\sin C}{c}.........................\left( i \right)$
Where (a, b, c) are the sides opposite to the angle A, B, C in a triangle ABC. Now, it is given that $\Delta ABC$ is a right angled triangle at angle A as $\angle A={{90}^{\circ }}$ and $\angle B,\angle C$ are equal to each other as well. So we can draw diagram as
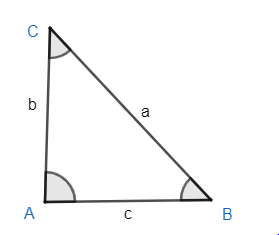
As we know, the sum of all interior angles of a triangle is ${{180}^{\circ }}$ . So, we get
$\begin{align}
& \angle A+\angle B+\angle C={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& {{90}^{\circ }}+\angle B+\angle C={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \angle B+\angle C={{180}^{\circ }}-{{90}^{\circ }}={{90}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
As we know $\angle B=\angle C$ so, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \angle B+\angle B={{90}^{\circ }} \\
& 2\angle B={{90}^{\circ }} \\
& \angle B={{45}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
So, we get
$\angle B=\angle C={{45}^{\circ }}$
Now, coming to question as we need to calculate the value of the expression
$\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}}\sin \left( B-C \right)$
As, we can suppose the value of all the terms involved in sine rule as ‘k’ and can get equation of sine rule as
$\dfrac{\sin A}{a}=\dfrac{\sin B}{b}=\dfrac{\sin C}{c}=k.....................\left( ii \right)$
Now, we can get the values of a, b, c by equating individual terms in sine rule to ‘k’. So, we get
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\sin A}{a}=k,\dfrac{\sin B}{b}=k,\dfrac{\sin C}{c}=k \\
& \Rightarrow a=\dfrac{\sin A}{k},b=\dfrac{\sin B}{k},c=\dfrac{\sin C}{k}...................\left( iii \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, let us suppose the value of the given expression be ’M’ i.e.
$M=\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}}\sin \left( B-C \right)..................\left( iv \right)$
Now, put values of b and c from the equation (iii). So, we get
$\begin{align}
& M=\left( \dfrac{\dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}B}{{{k}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}C}{{{k}^{2}}}}{\dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}B}{{{k}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}C}{{{k}^{2}}}} \right)\sin \left( B-C \right) \\
& M=\left( \dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}B+{{\sin }^{2}}C}{{{\sin }^{2}}B-{{\sin }^{2}}C} \right)\sin \left( B-C \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we the trigonometric identity
$si{{n}^{2}}B-{{\sin }^{2}}C=\sin \left( B+C \right)\sin \left( B-C \right)$
So, we get value of M as
$\begin{align}
& M=\dfrac{si{{n}^{2}}B+{{\sin }^{2}}C}{\sin \left( B-c \right)\sin \left( B+C \right)}\sin \left( B-C \right) \\
& \Rightarrow M=\dfrac{si{{n}^{2}}B+{{\sin }^{2}}C}{\sin \left( B+C \right)} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know
$\angle B=\angle C={{45}^{\circ }}$
So, we get
$\begin{align}
& M=\dfrac{si{{n}^{2}}45+{{\sin }^{2}}45}{\sin \left( 45+45 \right)} \\
& M=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}}{1}=1 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the value of the given expression is 1.
$\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}}\sin \left( B-C \right)=1$
So, option (c) is correct.
Note: One may directly put values of $\angle A,\angle B,\angle C$ to the sine rule and get the equation as
$a=\sqrt{2b}=\sqrt{2c}$
Now, if someone puts the values of b and c, $\angle B,\angle C$ to the given expression it will be of the form $\dfrac{0}{0}$ i.e. indeterminate form. So, don’t confuse with it, just remember the identity in limit as
$\underset{x\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\dfrac{\sin x}{x}=1$
So, replace the $\dfrac{\sin B-C}{b-c}$ by 1 with the help of a given relation.
Don’t get confused with the terms in sine rule identity. One may go wrong if he or she changes the position of angle and sides to it. So, use the correct sine rule.
$\dfrac{\sin A}{a}=\dfrac{\sin B}{b}=\dfrac{\sin C}{c}$, where a, b, c are sides of the triangle opposite to $\angle A,\angle B,\angle C$ respectively. Suppose the terms involved in sine rule as a constant and hence try to further simplify the problem by putting values of b and c in terms of A and B.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we know the sine rule of a triangle can be given as
$\dfrac{\sin A}{a}=\dfrac{\sin B}{b}=\dfrac{\sin C}{c}.........................\left( i \right)$
Where (a, b, c) are the sides opposite to the angle A, B, C in a triangle ABC. Now, it is given that $\Delta ABC$ is a right angled triangle at angle A as $\angle A={{90}^{\circ }}$ and $\angle B,\angle C$ are equal to each other as well. So we can draw diagram as

As we know, the sum of all interior angles of a triangle is ${{180}^{\circ }}$ . So, we get
$\begin{align}
& \angle A+\angle B+\angle C={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& {{90}^{\circ }}+\angle B+\angle C={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \angle B+\angle C={{180}^{\circ }}-{{90}^{\circ }}={{90}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
As we know $\angle B=\angle C$ so, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \angle B+\angle B={{90}^{\circ }} \\
& 2\angle B={{90}^{\circ }} \\
& \angle B={{45}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
So, we get
$\angle B=\angle C={{45}^{\circ }}$
Now, coming to question as we need to calculate the value of the expression
$\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}}\sin \left( B-C \right)$
As, we can suppose the value of all the terms involved in sine rule as ‘k’ and can get equation of sine rule as
$\dfrac{\sin A}{a}=\dfrac{\sin B}{b}=\dfrac{\sin C}{c}=k.....................\left( ii \right)$
Now, we can get the values of a, b, c by equating individual terms in sine rule to ‘k’. So, we get
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\sin A}{a}=k,\dfrac{\sin B}{b}=k,\dfrac{\sin C}{c}=k \\
& \Rightarrow a=\dfrac{\sin A}{k},b=\dfrac{\sin B}{k},c=\dfrac{\sin C}{k}...................\left( iii \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, let us suppose the value of the given expression be ’M’ i.e.
$M=\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}}\sin \left( B-C \right)..................\left( iv \right)$
Now, put values of b and c from the equation (iii). So, we get
$\begin{align}
& M=\left( \dfrac{\dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}B}{{{k}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}C}{{{k}^{2}}}}{\dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}B}{{{k}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}C}{{{k}^{2}}}} \right)\sin \left( B-C \right) \\
& M=\left( \dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}B+{{\sin }^{2}}C}{{{\sin }^{2}}B-{{\sin }^{2}}C} \right)\sin \left( B-C \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we the trigonometric identity
$si{{n}^{2}}B-{{\sin }^{2}}C=\sin \left( B+C \right)\sin \left( B-C \right)$
So, we get value of M as
$\begin{align}
& M=\dfrac{si{{n}^{2}}B+{{\sin }^{2}}C}{\sin \left( B-c \right)\sin \left( B+C \right)}\sin \left( B-C \right) \\
& \Rightarrow M=\dfrac{si{{n}^{2}}B+{{\sin }^{2}}C}{\sin \left( B+C \right)} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know
$\angle B=\angle C={{45}^{\circ }}$
So, we get
$\begin{align}
& M=\dfrac{si{{n}^{2}}45+{{\sin }^{2}}45}{\sin \left( 45+45 \right)} \\
& M=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}}{1}=1 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the value of the given expression is 1.
$\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}}\sin \left( B-C \right)=1$
So, option (c) is correct.
Note: One may directly put values of $\angle A,\angle B,\angle C$ to the sine rule and get the equation as
$a=\sqrt{2b}=\sqrt{2c}$
Now, if someone puts the values of b and c, $\angle B,\angle C$ to the given expression it will be of the form $\dfrac{0}{0}$ i.e. indeterminate form. So, don’t confuse with it, just remember the identity in limit as
$\underset{x\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\dfrac{\sin x}{x}=1$
So, replace the $\dfrac{\sin B-C}{b-c}$ by 1 with the help of a given relation.
Don’t get confused with the terms in sine rule identity. One may go wrong if he or she changes the position of angle and sides to it. So, use the correct sine rule.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




