
If \[\cos \theta = \dfrac{2}{3}\] and $\theta $ is in the 4th quadrant, then $\dfrac{{\sin \theta + \tan \theta }}{{\sin \theta - \tan \theta }}$ is equal to
(A) $\dfrac{{ - 1}}{5}$
(B) $\dfrac{1}{5}$
(C) $ - 5$
(D) $5$
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint:
First of all find the value of $\sin \theta $ by using the identity ${\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1$ and then find $\tan \theta $ by using, $\tan \theta = \dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }}$ to evaluate $\dfrac{{\sin \theta + \tan \theta }}{{\sin \theta - \tan \theta }}$.
Complete step by step solution:
Given, \[\cos \theta = \dfrac{2}{3}\] and $\theta $ is in the 4th quadrant.
To evaluate $\dfrac{{\sin \theta + \tan \theta }}{{\sin \theta - \tan \theta }}$; we will need to find the value of $\sin \theta $ and $\tan \theta $.
Now, find the value of $\sin \theta $by using the identity:
${\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1$
$ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}\theta = 1 - {\cos ^2}\theta $
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \pm \sqrt {1 - {{\cos }^2}\theta } $
We have given that $\theta $ is in the 4th quadrant. Therefore, $\sin \theta $will be negative.
$\sin \theta = - \sqrt {1 - {{\cos }^2}\theta } $
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = - \sqrt {1 - {{\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right)}^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = - \sqrt {1 - \dfrac{4}{9}} $
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = - \sqrt {\dfrac{{9 - 4}}{9}} $
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{{ - \sqrt 5 }}{3}$
Now, $\tan \theta = \dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }}$
$ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{ - \sqrt 5 }}{3}}}{{\dfrac{2}{3}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{{ - \sqrt 5 }}{2}$
$\therefore \dfrac{{\sin \theta + \tan \theta }}{{\sin \theta - \tan \theta }} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{ - \sqrt 5 }}{3} + \left( {\dfrac{{ - \sqrt 5 }}{2}} \right)}}{{\dfrac{{ - \sqrt 5 }}{3} - \left( {\dfrac{{ - \sqrt 5 }}{2}} \right)}}$
$ = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{ - \sqrt 5 }}{3} - \dfrac{{\sqrt 5 }}{2}}}{{\dfrac{{ - \sqrt 5 }}{3} + \dfrac{{\sqrt 5 }}{2}}}$
\[ = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{ - 2\sqrt 5 - 3\sqrt 5 }}{6}}}{{\dfrac{{ - 2\sqrt 5 + 3\sqrt 5 }}{6}}}\]
\[ = \dfrac{{ - 5\sqrt 5 }}{{\sqrt 5 }}\]
$ = - 5$
$\therefore \dfrac{{\sin \theta + \tan \theta }}{{\sin \theta - \tan \theta }} = - 5$
Hence, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note:
By ASTC formula, only $\cos \theta $ and $\sec \theta $ are positive in 4th quadrant while other trigonometry ratios $\left( {\sin \theta ,\tan \theta ,\cot \theta ,\cos ec\theta } \right)$are negative in 4th quadrant.
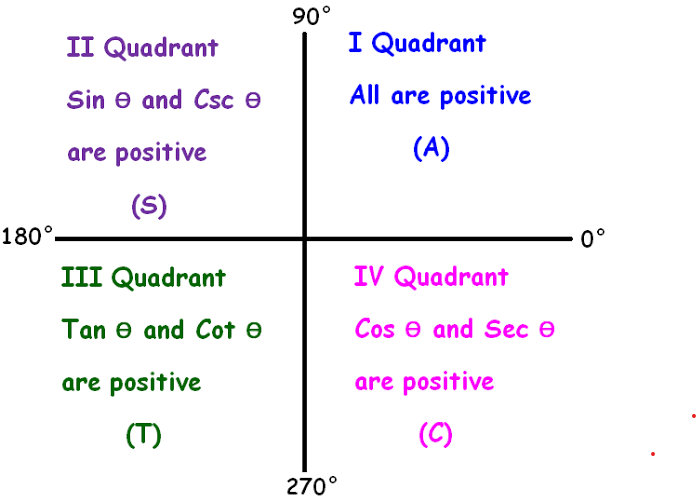
First of all find the value of $\sin \theta $ by using the identity ${\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1$ and then find $\tan \theta $ by using, $\tan \theta = \dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }}$ to evaluate $\dfrac{{\sin \theta + \tan \theta }}{{\sin \theta - \tan \theta }}$.
Complete step by step solution:
Given, \[\cos \theta = \dfrac{2}{3}\] and $\theta $ is in the 4th quadrant.
To evaluate $\dfrac{{\sin \theta + \tan \theta }}{{\sin \theta - \tan \theta }}$; we will need to find the value of $\sin \theta $ and $\tan \theta $.
Now, find the value of $\sin \theta $by using the identity:
${\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1$
$ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}\theta = 1 - {\cos ^2}\theta $
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \pm \sqrt {1 - {{\cos }^2}\theta } $
We have given that $\theta $ is in the 4th quadrant. Therefore, $\sin \theta $will be negative.
$\sin \theta = - \sqrt {1 - {{\cos }^2}\theta } $
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = - \sqrt {1 - {{\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right)}^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = - \sqrt {1 - \dfrac{4}{9}} $
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = - \sqrt {\dfrac{{9 - 4}}{9}} $
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{{ - \sqrt 5 }}{3}$
Now, $\tan \theta = \dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }}$
$ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{ - \sqrt 5 }}{3}}}{{\dfrac{2}{3}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{{ - \sqrt 5 }}{2}$
$\therefore \dfrac{{\sin \theta + \tan \theta }}{{\sin \theta - \tan \theta }} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{ - \sqrt 5 }}{3} + \left( {\dfrac{{ - \sqrt 5 }}{2}} \right)}}{{\dfrac{{ - \sqrt 5 }}{3} - \left( {\dfrac{{ - \sqrt 5 }}{2}} \right)}}$
$ = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{ - \sqrt 5 }}{3} - \dfrac{{\sqrt 5 }}{2}}}{{\dfrac{{ - \sqrt 5 }}{3} + \dfrac{{\sqrt 5 }}{2}}}$
\[ = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{ - 2\sqrt 5 - 3\sqrt 5 }}{6}}}{{\dfrac{{ - 2\sqrt 5 + 3\sqrt 5 }}{6}}}\]
\[ = \dfrac{{ - 5\sqrt 5 }}{{\sqrt 5 }}\]
$ = - 5$
$\therefore \dfrac{{\sin \theta + \tan \theta }}{{\sin \theta - \tan \theta }} = - 5$
Hence, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note:
By ASTC formula, only $\cos \theta $ and $\sec \theta $ are positive in 4th quadrant while other trigonometry ratios $\left( {\sin \theta ,\tan \theta ,\cot \theta ,\cos ec\theta } \right)$are negative in 4th quadrant.

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

Draw the diagram of the sectional view of the human class 10 biology CBSE




