
If $\angle B$ and $\angle Q$ are acute angles such that$\sin B=\sin Q$, then prove that$\angle B=\angle Q$.

Answer
609k+ views
Hint: SSS stands for side-side-side and means that we have two triangles with all three sides equal. If three sides of one triangle are equal to three sides of another triangle, the triangles are congruent.
Complete step-by-step answer:
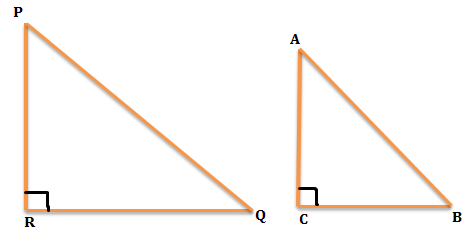
The given two right angle triangles are ABC and PQR.
The basic definition of the sine trigonometric function is
The sine function of an angle is the ratio between the opposite side length to that of the hypotenuse.
$\sin B=\dfrac{\text{side opposite to angle B}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}=\dfrac{AC}{AB}$ and $\sin Q=\dfrac{\text{side opposite to angle Q}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}=\dfrac{PR}{PQ}$
It is given that
$\sin B=\sin Q$
$\dfrac{AC}{AB}=\dfrac{PR}{PQ}$
Rearranging the ratios, we get
$\dfrac{AC}{PR}=\dfrac{AB}{PQ}$
Let us assume that $\dfrac{AC}{PR}=\dfrac{AB}{PQ}=k.......................(1)$
Therefore $AC=k(PR)$ and $AB=k(PQ)$
By using Pythagoras Theorem
${{\left( \text{Hypotenuse} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \text{Height} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( Base
\right)}^{2}}$
In the right angled triangle ABC,
${{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AC \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}$
${{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( AC \right)}^{2}}$
$BC=\sqrt{{{(AB)}^{2}}-{{(AC)}^{2}}}$
Also, in the right angled triangle PQR,
${{\left( PQ \right)}^{2}}={{\left( PR \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( QR \right)}^{2}}$
${{\left( QR \right)}^{2}}={{\left( PQ \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( PR \right)}^{2}}$
$QR=\sqrt{{{(PQ)}^{2}}-{{(PR)}^{2}}}$
Let us consider,
$\dfrac{BC}{QR}=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{(AB)}^{2}}-{{(AC)}^{2}}}}{\sqrt{{{(PQ)}^{2}}-{{(PR)}^{2}}}}$
Form the equation (1), we get
$\dfrac{BC}{QR}=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{k}^{2}}{{(PQ)}^{2}}-{{k}^{2}}{{(PR)}^{2}}}}{\sqrt{{{(PQ)}^{2}}-{{(
PR)}^{2}}}}$
$\dfrac{BC}{QR}=\dfrac{k\sqrt{{{(PQ)}^{2}}-{{(PR)}^{2}}}}{\sqrt{{{(PQ)}^{2}}-{{(PR)}^{2}}}}=k$
$\dfrac{BC}{QR}=k............................(2)$
From the equation (1) and equation (2), we get
$\dfrac{AC}{PR}=\dfrac{AB}{PQ}=\dfrac{BC}{QR}$
Hence corresponding sides of triangle ABC and triangle POR are in the same ratio.
By using SSS similarity,
$\Delta ABC\sim \Delta PQR$
The corresponding angles of a similar triangle are equal.
Therefore $\angle B=\angle Q$
This is the desired result.
Note: Two triangles are said to be similar if their corresponding angles are congruent and the corresponding sides are in proportion. In other words, similar triangles are the same shape, but not necessarily the same size.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The given two right angle triangles are ABC and PQR.
The basic definition of the sine trigonometric function is
The sine function of an angle is the ratio between the opposite side length to that of the hypotenuse.
$\sin B=\dfrac{\text{side opposite to angle B}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}=\dfrac{AC}{AB}$ and $\sin Q=\dfrac{\text{side opposite to angle Q}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}=\dfrac{PR}{PQ}$
It is given that
$\sin B=\sin Q$
$\dfrac{AC}{AB}=\dfrac{PR}{PQ}$
Rearranging the ratios, we get
$\dfrac{AC}{PR}=\dfrac{AB}{PQ}$
Let us assume that $\dfrac{AC}{PR}=\dfrac{AB}{PQ}=k.......................(1)$
Therefore $AC=k(PR)$ and $AB=k(PQ)$
By using Pythagoras Theorem
${{\left( \text{Hypotenuse} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \text{Height} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( Base
\right)}^{2}}$
In the right angled triangle ABC,
${{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AC \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}$
${{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( AC \right)}^{2}}$
$BC=\sqrt{{{(AB)}^{2}}-{{(AC)}^{2}}}$
Also, in the right angled triangle PQR,
${{\left( PQ \right)}^{2}}={{\left( PR \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( QR \right)}^{2}}$
${{\left( QR \right)}^{2}}={{\left( PQ \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( PR \right)}^{2}}$
$QR=\sqrt{{{(PQ)}^{2}}-{{(PR)}^{2}}}$
Let us consider,
$\dfrac{BC}{QR}=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{(AB)}^{2}}-{{(AC)}^{2}}}}{\sqrt{{{(PQ)}^{2}}-{{(PR)}^{2}}}}$
Form the equation (1), we get
$\dfrac{BC}{QR}=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{k}^{2}}{{(PQ)}^{2}}-{{k}^{2}}{{(PR)}^{2}}}}{\sqrt{{{(PQ)}^{2}}-{{(
PR)}^{2}}}}$
$\dfrac{BC}{QR}=\dfrac{k\sqrt{{{(PQ)}^{2}}-{{(PR)}^{2}}}}{\sqrt{{{(PQ)}^{2}}-{{(PR)}^{2}}}}=k$
$\dfrac{BC}{QR}=k............................(2)$
From the equation (1) and equation (2), we get
$\dfrac{AC}{PR}=\dfrac{AB}{PQ}=\dfrac{BC}{QR}$
Hence corresponding sides of triangle ABC and triangle POR are in the same ratio.
By using SSS similarity,
$\Delta ABC\sim \Delta PQR$
The corresponding angles of a similar triangle are equal.
Therefore $\angle B=\angle Q$
This is the desired result.
Note: Two triangles are said to be similar if their corresponding angles are congruent and the corresponding sides are in proportion. In other words, similar triangles are the same shape, but not necessarily the same size.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




