
If ABCD is a quadrilateral, then $\overline{AC}=\overline{AD}-\_\_\_\_\_$ .
(a) $\overline{AD}$
(b) $\overline{BC}$
(c) $\overline{CD}$
(d) $\overline{AC}$
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: As ABCD is a quadrilateral and ACD is a triangle which is also a polygon, we can use the rule of vector addition of a polygon to solve the above question. According to the rule the sum of the vectors forming all the sides of the polygon such that the tail of one vector coincides with the head of the other vector is zero. Also, use the identity that $\overline{DA}=-\overline{AD}$ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us start the solution to the above question by drawing a representative diagram of the situation given in the question.
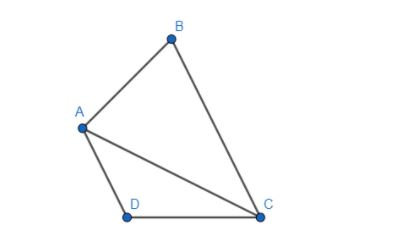
We know that according to the polygon law of vector addition the sum of the vectors forming all the sides of the polygon such that the tail of one vector coincides with the head of the other vector is zero. So, if we apply this on triangle ADC, we get
$\overline{DA}+\overline{CD}+\overline{AC}=0$
$\Rightarrow \overline{AC}=-\overline{DA}-\overline{CD}$
We also know that $\overline{DA}=-\overline{AD}$ .
\[\overline{AC}=\overline{AD}-\overline{CD}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: You should know that polygon law is an extension of triangle law of vector addition and the above question could have been solved using triangle law as well. Also, remember that for applying the polygon law, the head of one vector must coincide with the tail of the other and directions of vectors are very important.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us start the solution to the above question by drawing a representative diagram of the situation given in the question.

We know that according to the polygon law of vector addition the sum of the vectors forming all the sides of the polygon such that the tail of one vector coincides with the head of the other vector is zero. So, if we apply this on triangle ADC, we get
$\overline{DA}+\overline{CD}+\overline{AC}=0$
$\Rightarrow \overline{AC}=-\overline{DA}-\overline{CD}$
We also know that $\overline{DA}=-\overline{AD}$ .
\[\overline{AC}=\overline{AD}-\overline{CD}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: You should know that polygon law is an extension of triangle law of vector addition and the above question could have been solved using triangle law as well. Also, remember that for applying the polygon law, the head of one vector must coincide with the tail of the other and directions of vectors are very important.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




