
If A is the area of a right angled triangle and b is one of the sides containing the right angle, then the length of the altitude on the hypotenuse is
\[
A.{\text{ }}\dfrac{{2Ab}}{{\sqrt {{b^2} + 4{A^2}} }} \\
B.{\text{ }}\dfrac{{2Ab}}{{{b^2} + 4{A^2}}} \\
C.{\text{ }}\dfrac{{2Ab}}{{\sqrt {{b^4} + 4{A^4}} }} \\
D.{\text{ }}\dfrac{{2Ab}}{{\sqrt {{b^4} + 4{A^2}} }} \\
\]
Answer
616.8k+ views
Hint- In order to solve the question start with the basic formula of area of triangle in terms base and altitude and then at the later stage proceed with Pythagoras theorem of some right angled triangle within the figure.
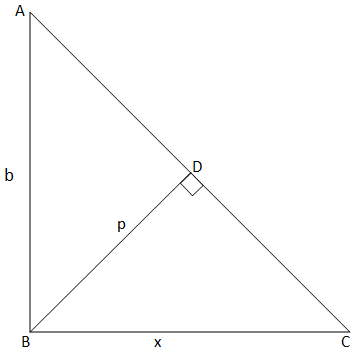
Complete step-by-step answer:
Solve the problem with the help of the figure.
According to the figure and the problem, given that
Height of right angled triangle = b units
Area of the right angled triangle = A sq. units
As we know the formula of triangle in terms of base and altitude is given by:
${\text{Area}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times {\text{base}} \times {\text{height}}$
So for the given problem
\[
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times x \times b \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{2A}}{b} \\
\]
So, another side (base) of the right angled triangle $ = \dfrac{{2A}}{b}$
According to the Pythagoras theorem for right angled triangles.
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{height}}} \right)^2}\]
So using Pythagoras theorem for right angled triangle ABC
\[
\Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{2A}}{b}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\text{b}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = \left( {\dfrac{{4{A^2}}}{{{b^2}}}} \right) + {\left( {\text{b}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow \left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right) = \sqrt {\left( {\dfrac{{4{A^2}}}{{{b^2}}}} \right) + {{\left( {\text{b}} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow \left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right) = \sqrt {\dfrac{{4{A^2} + {{\left( {\text{b}} \right)}^4}}}{{{b^2}}}} \\
\Rightarrow \left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right) = \dfrac{1}{b}\sqrt {{{\left( {\text{b}} \right)}^4} + 4{A^2}} \\
\]
Now, we have found out the length of hypotenuse. We can also find the area of the right angled triangle ABC by considering side AC as base and the altitude BD to the side AC.
\[
\because {\text{Area}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times {\text{base}} \times {\text{height}} \\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times AC \times BD \\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left( {\dfrac{1}{b}\sqrt {{{\left( {\text{b}} \right)}^4} + 4{A^2}} } \right) \times h \\
\Rightarrow 2Ab = \sqrt {{{\left( {\text{b}} \right)}^4} + 4{A^2}} \times h \\
\Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{2Ab}}{{\sqrt {{{\left( {\text{b}} \right)}^4} + 4{A^2}} }} \\
\]
Therefore, the length of the altitude on the hypotenuse of the right angled triangle is \[\dfrac{{2Ab}}{{\sqrt {{{\left( {\text{b}} \right)}^4} + 4{A^2}} }}\]
So, option D is the correct option.
Note- In order to solve such problems involving the concept of geometry, figure is the utmost priority for easy understanding. Pythagoras theorem states that “In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides“. Students must remember Pythagoras theorem and the formula for the area of the triangle.

Complete step-by-step answer:
Solve the problem with the help of the figure.
According to the figure and the problem, given that
Height of right angled triangle = b units
Area of the right angled triangle = A sq. units
As we know the formula of triangle in terms of base and altitude is given by:
${\text{Area}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times {\text{base}} \times {\text{height}}$
So for the given problem
\[
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times x \times b \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{2A}}{b} \\
\]
So, another side (base) of the right angled triangle $ = \dfrac{{2A}}{b}$
According to the Pythagoras theorem for right angled triangles.
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{height}}} \right)^2}\]
So using Pythagoras theorem for right angled triangle ABC
\[
\Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{2A}}{b}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\text{b}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = \left( {\dfrac{{4{A^2}}}{{{b^2}}}} \right) + {\left( {\text{b}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow \left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right) = \sqrt {\left( {\dfrac{{4{A^2}}}{{{b^2}}}} \right) + {{\left( {\text{b}} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow \left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right) = \sqrt {\dfrac{{4{A^2} + {{\left( {\text{b}} \right)}^4}}}{{{b^2}}}} \\
\Rightarrow \left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right) = \dfrac{1}{b}\sqrt {{{\left( {\text{b}} \right)}^4} + 4{A^2}} \\
\]
Now, we have found out the length of hypotenuse. We can also find the area of the right angled triangle ABC by considering side AC as base and the altitude BD to the side AC.
\[
\because {\text{Area}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times {\text{base}} \times {\text{height}} \\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times AC \times BD \\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left( {\dfrac{1}{b}\sqrt {{{\left( {\text{b}} \right)}^4} + 4{A^2}} } \right) \times h \\
\Rightarrow 2Ab = \sqrt {{{\left( {\text{b}} \right)}^4} + 4{A^2}} \times h \\
\Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{2Ab}}{{\sqrt {{{\left( {\text{b}} \right)}^4} + 4{A^2}} }} \\
\]
Therefore, the length of the altitude on the hypotenuse of the right angled triangle is \[\dfrac{{2Ab}}{{\sqrt {{{\left( {\text{b}} \right)}^4} + 4{A^2}} }}\]
So, option D is the correct option.
Note- In order to solve such problems involving the concept of geometry, figure is the utmost priority for easy understanding. Pythagoras theorem states that “In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides“. Students must remember Pythagoras theorem and the formula for the area of the triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

The Equation xxx + 2 is Satisfied when x is Equal to Class 10 Maths

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What is Contraception List its four different methods class 10 biology CBSE




