
If a full wave rectifier circuit is operating from \[\text{50Hz}\] mains, the fundamental frequency in the ripple will be
\[\begin{align}
& A)25Hz \\
& B)50Hz \\
& C)70.7Hz \\
& D)100Hz \\
\end{align}\]
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: A circuit which converts alternating current into direct current is known as rectifier. A full wave rectifier produces output for both positive and negative half cycles of input. Hence, we get twice the input value at the output terminal.
Formula used:
\[{{f}_{output}}=2{{f}_{input}}\]
Complete answer:
A full-wave rectifier rectifies the negative component of the input voltage to a positive voltage, and converts the AC input into DC. In a full wave rectifier, when the AC voltage is applied at the input, during positive and negative half cycles, current flows through the load in the same direction. And it is achieved by using diodes. For \[n\] cycles, a full wave rectifier generates \[2n\] cycles as the output.
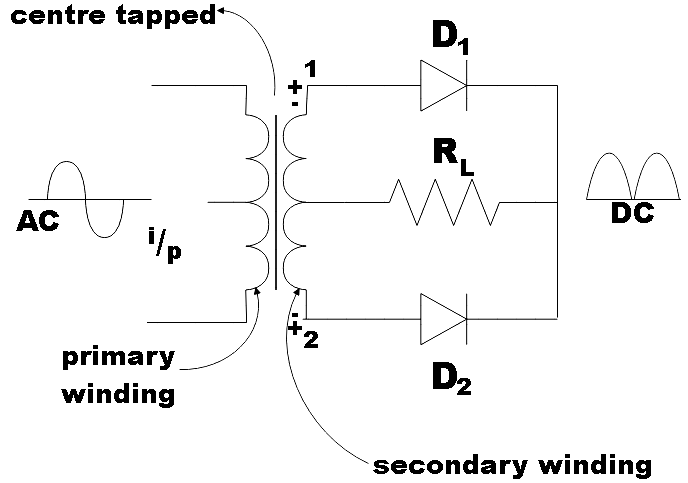
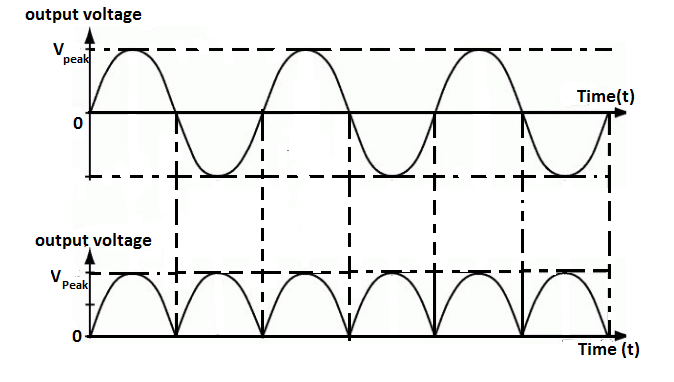
Figure shows the input and output voltage graph of a full wave rectifier. For positive and negative half cycles, a positive output is generated across the load resistor.
Hence, if \[nHz\] frequency is applied at the input then, we get \[2nHz\] as output frequency.
i.e.,
\[{{f}_{output}}=2{{f}_{input}}\]
Here, the full wave rectifier circuit is operating from \[\text{50Hz}\] mains, the fundamental frequency in the ripple will be\[100Hz\].
Answer is option D.
Note:
Compared to a half wave rectifier, full wave rectifiers have higher rectifying efficiency, as they convert AC to DC more efficiently.
Since, no voltage signal is wasted in the rectification process; these rectifiers have low power loss. Its output has fewer ripples compared to half wave rectifiers. This makes it easier to produce a smooth output waveform.
Formula used:
\[{{f}_{output}}=2{{f}_{input}}\]
Complete answer:
A full-wave rectifier rectifies the negative component of the input voltage to a positive voltage, and converts the AC input into DC. In a full wave rectifier, when the AC voltage is applied at the input, during positive and negative half cycles, current flows through the load in the same direction. And it is achieved by using diodes. For \[n\] cycles, a full wave rectifier generates \[2n\] cycles as the output.


Figure shows the input and output voltage graph of a full wave rectifier. For positive and negative half cycles, a positive output is generated across the load resistor.
Hence, if \[nHz\] frequency is applied at the input then, we get \[2nHz\] as output frequency.
i.e.,
\[{{f}_{output}}=2{{f}_{input}}\]
Here, the full wave rectifier circuit is operating from \[\text{50Hz}\] mains, the fundamental frequency in the ripple will be\[100Hz\].
Answer is option D.
Note:
Compared to a half wave rectifier, full wave rectifiers have higher rectifying efficiency, as they convert AC to DC more efficiently.
Since, no voltage signal is wasted in the rectification process; these rectifiers have low power loss. Its output has fewer ripples compared to half wave rectifiers. This makes it easier to produce a smooth output waveform.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




