
If a ball is thrown vertically upwards with speed u, the distance covered during the last t seconds of its ascent is:
A. ut
B. $\dfrac{1}{2}gt^2$
C. $ut - \dfrac{1}{2}gt^2$
D. (u + gt)t
Answer
524.9k+ views
Hint: When the ball will be thrown upwards it will undergo retardation due to gravity (g). In the last t seconds of its path during its ascent, it will start with some velocity v and reach a final velocity of zero before it starts to fall back (descent).
Formula used:
The final velocity of a body undergoing acceleration a with initial velocity u, in time interval t is:
v = u + at .
The distance covered by the (same) body in time interval t is given by:
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}at^2$ .
Complete answer:
We are given that the ball is thrown vertically upwards with an initial velocity of u. We break the trajectory of ascent into three different times.
1. At t= 0, velocity is u
2. At t = T, velocity reaches zero (Let the total time of ascent be T).
3. At t = T-t, let the velocity be some v.
We are to determine the distance traveled between the points where time is T-t and T ( as T - (T-t) = t s).
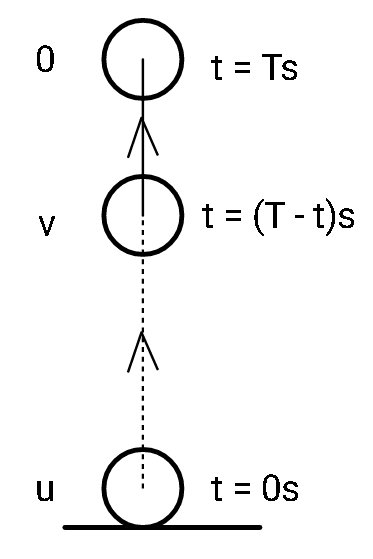
First, let us use the first law of motion to determine the velocity that the ball will attain after a time T-t s,
v = u + at
We know that a = -g due to retardation, so:
v = u - g(T-t).
For the second half of the journey, from T-t seconds to T seconds, we get
0 = v - gt
so, v= gt.
This will be the initial velocity for the ball when it enters the last t seconds of its ascent.
Therefore, we write in second law of motion:
$s = (gt)t - \dfrac{1}{2}gt^2$
$s = \dfrac{1}{2}gt^2$
In last t seconds, the ball will cover a distance of $\dfrac{1}{2}gt^2$
Therefore, the correct answer is option (B).
Note:
Since the ball is undergoing retardation one should not forget to put a minus sign in front of g. Also one could get confused in the use of t. We always use a difference of final and initial time in the laws of motion. Here, in the first part of the ascent, the time interval was T-t - 0 = T-t seconds and in the second part it was T - (T-t) = t seconds.
Formula used:
The final velocity of a body undergoing acceleration a with initial velocity u, in time interval t is:
v = u + at .
The distance covered by the (same) body in time interval t is given by:
$s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}at^2$ .
Complete answer:
We are given that the ball is thrown vertically upwards with an initial velocity of u. We break the trajectory of ascent into three different times.
1. At t= 0, velocity is u
2. At t = T, velocity reaches zero (Let the total time of ascent be T).
3. At t = T-t, let the velocity be some v.
We are to determine the distance traveled between the points where time is T-t and T ( as T - (T-t) = t s).

First, let us use the first law of motion to determine the velocity that the ball will attain after a time T-t s,
v = u + at
We know that a = -g due to retardation, so:
v = u - g(T-t).
For the second half of the journey, from T-t seconds to T seconds, we get
0 = v - gt
so, v= gt.
This will be the initial velocity for the ball when it enters the last t seconds of its ascent.
Therefore, we write in second law of motion:
$s = (gt)t - \dfrac{1}{2}gt^2$
$s = \dfrac{1}{2}gt^2$
In last t seconds, the ball will cover a distance of $\dfrac{1}{2}gt^2$
Therefore, the correct answer is option (B).
Note:
Since the ball is undergoing retardation one should not forget to put a minus sign in front of g. Also one could get confused in the use of t. We always use a difference of final and initial time in the laws of motion. Here, in the first part of the ascent, the time interval was T-t - 0 = T-t seconds and in the second part it was T - (T-t) = t seconds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




