
Identify ‘Z’ in the following reaction series:
$C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}Br\xrightarrow{NaOH}\left( X \right)\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}}\left( Y \right)\xrightarrow{HOCl}\left( Z \right)$
(A)
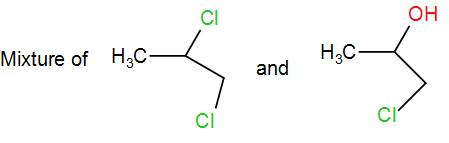
(B)
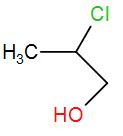
(C)
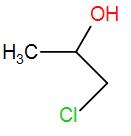
(D)
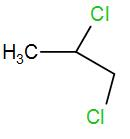




Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: Here, a bromoalkene is given to you that will undergo a series of reactions upon addition of the given reagents. To find the ‘Z’ in the reaction, precede stepwise by finding X and Y and then arriving at Z. Remember that base will form alcohol from the bromo derivative. The aluminium oxide will form an alkene from the alcohol and HOCl will chlorinate the alkene. Use this to answer the given question.
Complete step by step solution:
In the given question, a bromo derivative of an alkane is given to us. Its name is 1-bromopropane or is also known as n-propyl bromide.
To find ‘Z’ in the given reaction series, let us see the effects of the added reagents and then arrive at the final result.
Firstly, a base is added to the bromo derivative. The base will reduce the derivation to give us alcohol. This will give us propanol. We can write the reaction as-
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}Br\xrightarrow{NaOH}C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}OH\]
Thus the alcohol formed is our ‘X’. To this aluminium oxide is added and the solution is heated. Aluminium oxide forms terminal alkenes from alcohol. We can write the reaction as-
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}OH\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}}C{{H}_{3}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}\]
The alkene thus obtained is our ‘Y’. To this, HOCl is added. This will be a chlorination reaction that is the alkene will be chlorinated. The terminal alkene will be halogenated and will give rise to a carbocation. We can write the reaction as-
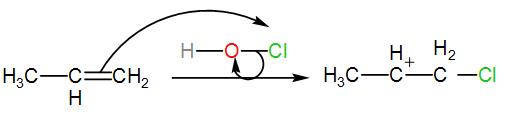
The carbocation thus formed will react with the free hydroxide ion which is eliminated from HOCl when the alkene is chlorinated. This will give us chlorinated alcohol. We can write the reaction as-
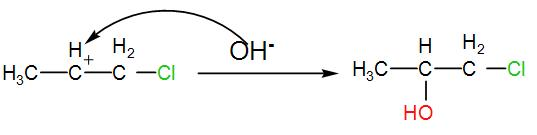
The product obtained is 4-chloropropan-2-ol. This is the required ‘Z’.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Alkene halogenation is generally carried out for bromination and chlorination. This is done using dihalides like $C{{l}_{2}}$ and $B{{r}_{2}}$. After breaking the double bond the di-halide is added and here the halide gets attached to the neighbouring carbons from the opposite faces of the molecules.
Complete step by step solution:
In the given question, a bromo derivative of an alkane is given to us. Its name is 1-bromopropane or is also known as n-propyl bromide.
To find ‘Z’ in the given reaction series, let us see the effects of the added reagents and then arrive at the final result.
Firstly, a base is added to the bromo derivative. The base will reduce the derivation to give us alcohol. This will give us propanol. We can write the reaction as-
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}Br\xrightarrow{NaOH}C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}OH\]
Thus the alcohol formed is our ‘X’. To this aluminium oxide is added and the solution is heated. Aluminium oxide forms terminal alkenes from alcohol. We can write the reaction as-
\[C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}OH\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}}C{{H}_{3}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}\]
The alkene thus obtained is our ‘Y’. To this, HOCl is added. This will be a chlorination reaction that is the alkene will be chlorinated. The terminal alkene will be halogenated and will give rise to a carbocation. We can write the reaction as-

The carbocation thus formed will react with the free hydroxide ion which is eliminated from HOCl when the alkene is chlorinated. This will give us chlorinated alcohol. We can write the reaction as-

The product obtained is 4-chloropropan-2-ol. This is the required ‘Z’.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Alkene halogenation is generally carried out for bromination and chlorination. This is done using dihalides like $C{{l}_{2}}$ and $B{{r}_{2}}$. After breaking the double bond the di-halide is added and here the halide gets attached to the neighbouring carbons from the opposite faces of the molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




