
Identify the T-shaped molecule.
(A)$B{{F}_{3}}$
(B)$N{{H}_{3}}$
(C)$N{{F}_{3}}$
(D)$Cl{{F}_{3}}$
(E)$PC{{l}_{3}}$
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: The VSEPR model can be used to determine the shape of a molecule. The valence shell electron pair repulsion theory states that the molecules around the central atom will arrange in such a way that there is minimum repulsion between valence electron pairs of the atom.
Complete answer:
The VSEPR model of arrangement helps in increasing the stability of the molecule and decreasing its energy.
The repulsion between the electron pair increases in the following order
Bond pair-bond pair < bond pair-lone pair < lone pair-lone pair
Now, the formula $A{{X}_{n}}{{E}_{m}}$ can be used while applying the VSEPR theory to represent the number of electron pairs around a central atom.
Where the central atom is represented by A, ligand bonded to the central atom is represented by X, and lone pairs are represented by E.
Subscripts n and m represent the number of ligands and the number of lone pairs.
Steric Number = n + m
Now, the molecular geometry of the compound according to the steric number and the $A{{X}_{n}}{{E}_{m}}$ formula is
From this table we can see that the T-shape molecules are of type $A{{X}_{3}}{{E}_{2}}$.
$A{{X}_{3}}{{E}_{2}}$ molecule is bonded to 3 ligands and has 2 lone pairs.
This means that it has 7 electrons in its outermost shell, 3 from the bond pairs, and 4 from the lone pairs.
Since halides have 7 electrons in their outermost shell, the t-shape molecule will be $Cl{{F}_{3}}$.
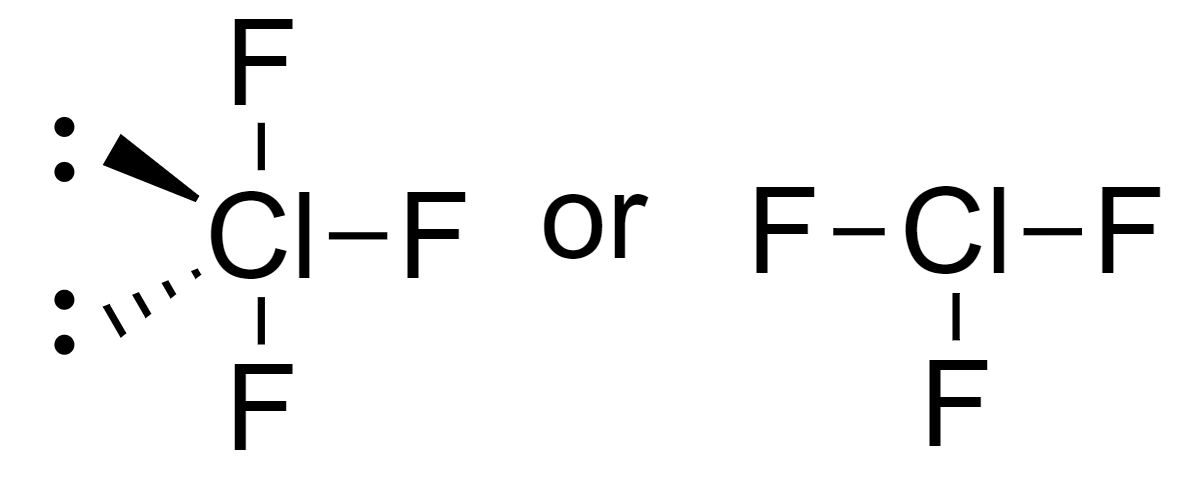
So, the T-shaped molecule is option (D) $Cl{{F}_{3}}$.
Note:
It should be noted that the VSEPR theory does not explain the molecular geometry and shapes of the isoelectronic species. It also does not properly explain the molecules of transition metals. It does not consider the inactive lone pairs and the size of the ligand attached to the central atom.
Complete answer:
The VSEPR model of arrangement helps in increasing the stability of the molecule and decreasing its energy.
The repulsion between the electron pair increases in the following order
Bond pair-bond pair < bond pair-lone pair < lone pair-lone pair
Now, the formula $A{{X}_{n}}{{E}_{m}}$ can be used while applying the VSEPR theory to represent the number of electron pairs around a central atom.
Where the central atom is represented by A, ligand bonded to the central atom is represented by X, and lone pairs are represented by E.
Subscripts n and m represent the number of ligands and the number of lone pairs.
Steric Number = n + m
Now, the molecular geometry of the compound according to the steric number and the $A{{X}_{n}}{{E}_{m}}$ formula is
| STERIC NUMBER | $A{{X}_{n}}{{E}_{m}}$ | MOLECULAR GEOMETRY |
| 2 | $A{{X}_{2}}{{E}_{0}}$ | Linear |
| 3 | $A{{X}_{3}}{{E}_{0}}$ | Trigonal Planar |
| 3 | $A{{X}_{2}}{{E}_{1}}$ | Bent |
| 4 | $A{{X}_{4}}{{E}_{0}}$ | Tetrahedral |
| 4 | $A{{X}_{3}}{{E}_{1}}$ | Trigonal Pyramidal |
| 4 | $A{{X}_{2}}{{E}_{2}}$ | Bent |
| 5 | $A{{X}_{5}}{{E}_{0}}$ | Trigonal Bipyramidal |
| 5 | $A{{X}_{4}}{{E}_{1}}$ | Seesaw |
| 5 | $A{{X}_{3}}{{E}_{2}}$ | T-Shaped |
| 5 | $A{{X}_{2}}{{E}_{3}}$ | Linear |
From this table we can see that the T-shape molecules are of type $A{{X}_{3}}{{E}_{2}}$.
$A{{X}_{3}}{{E}_{2}}$ molecule is bonded to 3 ligands and has 2 lone pairs.
This means that it has 7 electrons in its outermost shell, 3 from the bond pairs, and 4 from the lone pairs.
Since halides have 7 electrons in their outermost shell, the t-shape molecule will be $Cl{{F}_{3}}$.
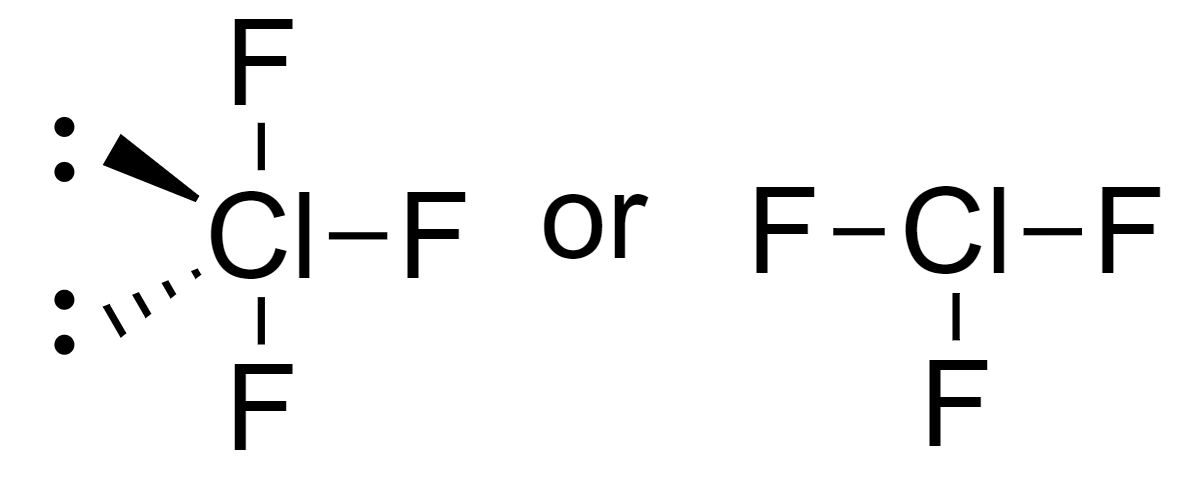
So, the T-shaped molecule is option (D) $Cl{{F}_{3}}$.
Note:
It should be noted that the VSEPR theory does not explain the molecular geometry and shapes of the isoelectronic species. It also does not properly explain the molecules of transition metals. It does not consider the inactive lone pairs and the size of the ligand attached to the central atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




