
Identify A, B, C, and D in the given diagram of mRNA
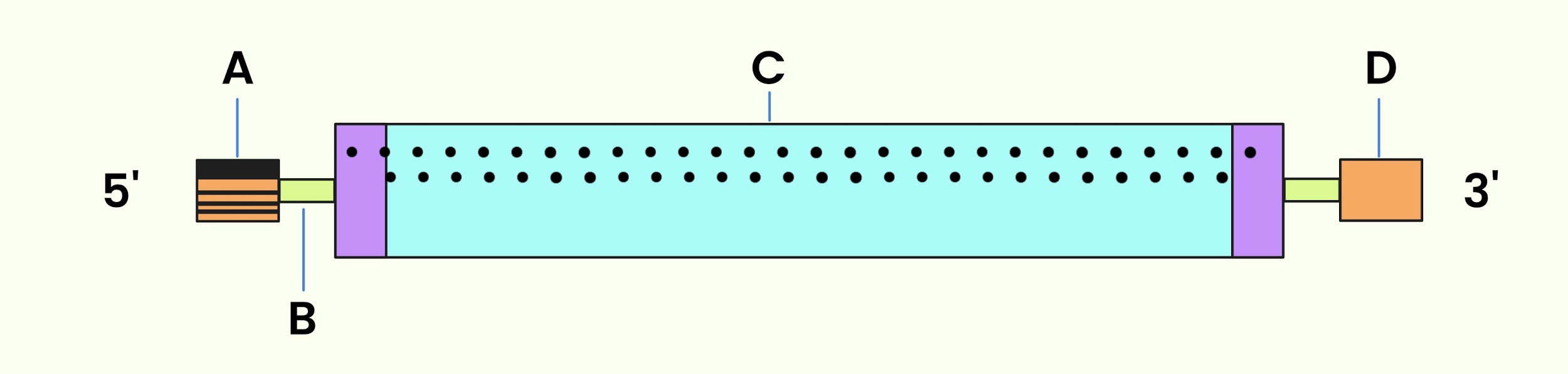
A)Methylated cap, Initiation codon, Termination codon, Poly A tail
B)Poly A tail, Termination codon, Initiation codon, Methylated cap
C)Methylated cap, Non-coding region, coding region, Poly A tail
D)Methylated cap, Coding region, Non-coding region, Poly A tail

Answer
578.7k+ views
Hint: Eukaryotic mRNAs can be present for many hours but the mRNA of typical E.coli is not able to last for five seconds. The RNA-stabilizing protein coats the Pre-mRNAs, these proteins help pre-mRNA when it is processed and exported out of the nucleus and protect it from degeneration.
Complete answer:
PROCESSING OF MESSENGER RNA IN EUKARYOTES
Eukaryotic mRNA is synthesized using a part of one strand of DNA as a template by the RNA Polymerase II enzyme.
-The primary transcript is known as heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA ).
-before being translocated to the cytoplasm, the primary transcript undergoes some type of modifications in the nucleus to give mature or functional mRNA.
-These modifications usually include
5’ Capping
Addition of a poly-A tail at 3’ end
Removal of Introns
The first processing step for hnRNA is the 5’ Capping
To the back of the 5’ terminal end, a 7-methyl-guanosine cap is attached and mRNA forming an unusual 5’-5’ triphosphate linkage catalyzed by nuclear enzyme guanylyltransferase.
-Guanine occurs in the cytosol by guanine 7- methyltransferase by the methylation of this terminal.
-S-adenosylmethionine is the Source of the methyl group.
-The addition of a 5’ cap permits initiation of translation and also provides stability to mRNA
Addition of Poly –A Tail
-A chain of 40 to 200 Adenine nucleotides attached to the 3’end of the most eukaryotic mRNAs.
-From the DNA, this Poly –A Tail is not transcribed but instead added after transcription by nuclear enzyme polyadenylate polymerase.
-The poly-A tail also gives stability and facilitates the exit of mRNA from the nucleus.
-The poly-A tail is gradually shortened after the mRNA enters the cytosol.
Removal of Introns Maturation of eukaryotic mRNA
-It involves the removal of RNA sequences i.e Introns or Intervening sequences, that do not code for proteins from the primary transcript.
-Exons, the remaining coding sequences are spliced together to form mature mRNA with continuous coding stretch.
-Small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) in association with Protein help in the removal of Introns and splicing of exons.
-These complexes are known as small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles (snrnps).
So, the correct answer is,” Methylated cap, Initiation codon, Termination codon, Poly A tail”.
Note: -Between the genetic information in DNA and the amino acid sequence of proteins, mRNA acts as an intermediary.
-Codons are complementary to the sequence of nucleotides on the template DNA that is contained by mRNA and helps in the formation of amino acids through the action of ribosomes and tRNA.
-Multiple regulatory regions that can determine the timing and rate of translation also present in mRNA.
Complete answer:
PROCESSING OF MESSENGER RNA IN EUKARYOTES
Eukaryotic mRNA is synthesized using a part of one strand of DNA as a template by the RNA Polymerase II enzyme.
-The primary transcript is known as heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA ).
-before being translocated to the cytoplasm, the primary transcript undergoes some type of modifications in the nucleus to give mature or functional mRNA.
-These modifications usually include
5’ Capping
Addition of a poly-A tail at 3’ end
Removal of Introns
The first processing step for hnRNA is the 5’ Capping
To the back of the 5’ terminal end, a 7-methyl-guanosine cap is attached and mRNA forming an unusual 5’-5’ triphosphate linkage catalyzed by nuclear enzyme guanylyltransferase.
-Guanine occurs in the cytosol by guanine 7- methyltransferase by the methylation of this terminal.
-S-adenosylmethionine is the Source of the methyl group.
-The addition of a 5’ cap permits initiation of translation and also provides stability to mRNA
Addition of Poly –A Tail
-A chain of 40 to 200 Adenine nucleotides attached to the 3’end of the most eukaryotic mRNAs.
-From the DNA, this Poly –A Tail is not transcribed but instead added after transcription by nuclear enzyme polyadenylate polymerase.
-The poly-A tail also gives stability and facilitates the exit of mRNA from the nucleus.
-The poly-A tail is gradually shortened after the mRNA enters the cytosol.
Removal of Introns Maturation of eukaryotic mRNA
-It involves the removal of RNA sequences i.e Introns or Intervening sequences, that do not code for proteins from the primary transcript.
-Exons, the remaining coding sequences are spliced together to form mature mRNA with continuous coding stretch.
-Small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) in association with Protein help in the removal of Introns and splicing of exons.
-These complexes are known as small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles (snrnps).
So, the correct answer is,” Methylated cap, Initiation codon, Termination codon, Poly A tail”.
Note: -Between the genetic information in DNA and the amino acid sequence of proteins, mRNA acts as an intermediary.
-Codons are complementary to the sequence of nucleotides on the template DNA that is contained by mRNA and helps in the formation of amino acids through the action of ribosomes and tRNA.
-Multiple regulatory regions that can determine the timing and rate of translation also present in mRNA.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




