
(i) A screen is placed at a distance of 100 cm from an object. The image of the object is formed on the screen by a convex lens for two different locations of the lens separated by 20 cm. Calculate the focal length of the lens used.
(ii) A converging lens is kept coaxially in contact with diverging lens-both the lenses being of equal focal length. What is the focal length of the combination?
Answer
610.5k+ views
Hint: As we have been given the distance between the object and the screen and also the two locations of the convex lens, we will use the formula for the focal length of the lens to get the result of the first part of the question.
In the second part, it is given that the converging and diverging, both lenses having equal focal length have been placed coaxially. And we must know that the focal length of a converging lens is positive while that of the diverging lens is negative.
Formulae used:
Focal length of lens, $f=\dfrac{D^2–d^2}{4D}$
Power of a lens, $P=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Complete step by step solution:
We have been given that a screen has been placed at a distance of 100 cm from the object. The image of the object is formed by a convex lens for two different locations separated by 20 cm.
We can illustrate the given conditions as follow,
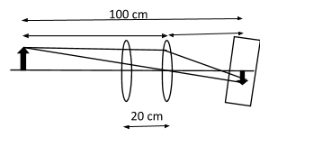
(A.)We will now use the formula to determine the focal length of the lens which is given by $f=\dfrac{D^2 – d^2}{4D}$, where D is the distance between object and screen which is 100 cm and d is the distance between two locations of the convex lens which is 20 cm.
So, we will get $f=\dfrac{(100)^2 – (20)^2}{4\times 100}=\dfrac{(100-20)(100+20)}{400}=\dfrac{80\times 120}{400}=24$ cm.
Hence, the focal length of the concave lens is 24 cm.
(B.)We have been given a converging lens and a diverging lens both having the same focal length. Let us assume that the focal length be f.
So, considering the sign conventions of the lenses, the focal length of the converging lens will be +f and that of the diverging lens will be -f. We know that the power of a lens is given by $P=\dfrac{1}{f}$.
So, the power of converging lens will be ${P}_{1}=\dfrac{1}{f}$ and of the diverging lens will be ${P}_{2}=-\dfrac{1}{f}$.
Thus, power of the combination of lens, $P={P}_{1}+{P}_{2}=\dfrac{1}{f}-\dfrac{1}{f}=0$
Therefore, the focal length of the combination of lenses will be $\dfrac{1}{P}=\dfrac{1}{0}=\infty$
Hence the focal length of the combination of lenses will be $\infty$
Note:
It can happen that one may try to use lens formula in the first part of the question and in that way, we will get two image distance and two object distance which will in turn make everything complex. So, it is advised to use the direct focal length formula for such questions.
In the second part, it is given that the converging and diverging, both lenses having equal focal length have been placed coaxially. And we must know that the focal length of a converging lens is positive while that of the diverging lens is negative.
Formulae used:
Focal length of lens, $f=\dfrac{D^2–d^2}{4D}$
Power of a lens, $P=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Complete step by step solution:
We have been given that a screen has been placed at a distance of 100 cm from the object. The image of the object is formed by a convex lens for two different locations separated by 20 cm.
We can illustrate the given conditions as follow,

(A.)We will now use the formula to determine the focal length of the lens which is given by $f=\dfrac{D^2 – d^2}{4D}$, where D is the distance between object and screen which is 100 cm and d is the distance between two locations of the convex lens which is 20 cm.
So, we will get $f=\dfrac{(100)^2 – (20)^2}{4\times 100}=\dfrac{(100-20)(100+20)}{400}=\dfrac{80\times 120}{400}=24$ cm.
Hence, the focal length of the concave lens is 24 cm.
(B.)We have been given a converging lens and a diverging lens both having the same focal length. Let us assume that the focal length be f.
So, considering the sign conventions of the lenses, the focal length of the converging lens will be +f and that of the diverging lens will be -f. We know that the power of a lens is given by $P=\dfrac{1}{f}$.
So, the power of converging lens will be ${P}_{1}=\dfrac{1}{f}$ and of the diverging lens will be ${P}_{2}=-\dfrac{1}{f}$.
Thus, power of the combination of lens, $P={P}_{1}+{P}_{2}=\dfrac{1}{f}-\dfrac{1}{f}=0$
Therefore, the focal length of the combination of lenses will be $\dfrac{1}{P}=\dfrac{1}{0}=\infty$
Hence the focal length of the combination of lenses will be $\infty$
Note:
It can happen that one may try to use lens formula in the first part of the question and in that way, we will get two image distance and two object distance which will in turn make everything complex. So, it is advised to use the direct focal length formula for such questions.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




