
Hydrazobenzene on treatment with ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ forms:
A) Azobenzene
B) Azobenzene sulfonic acid
C) Benzidine
D) None of the above
Answer
570.9k+ views
Hint: To solve this we must know that hydrazobenzene is also known as diphenylhydrazine. The structure is two benzene rings to which $ - {\text{NH}}$ groups are attached. These two rings are then connected through the nitrogen-nitrogen $\left( {{\text{N}} - {\text{N}}} \right)$ bond. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ which is known as sulphuric acid creates an acidic medium. A rearrangement reaction occurs.
Complete solution:
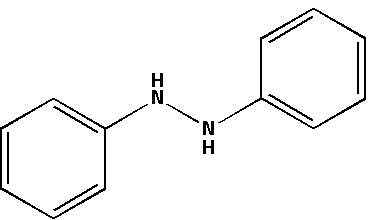
We know that hydrazobenzene as the name suggests hydrazo group is $ - {\text{NH}}$ group and benzene indicates that this hydrazo group is attached to the benzene ring.
Hydrazobenzene is two benzene rings to which $ - {\text{NH}}$ groups are attached. These two rings are then connected through the nitrogen-nitrogen $\left( {{\text{N}} - {\text{N}}} \right)$ bond.
The structure for hydrazobenzene is as follows:
${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ which is known as sulphuric acid creates an acidic medium. Hydrazobenzene in an acidic medium accepts protons from the sulphuric acid. In an acidic medium, hydrazobenzene undergoes a rearrangement reaction.
The mechanism of the reaction when hydrazobenzene reacts with sulphuric acid i.e. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is as follows:
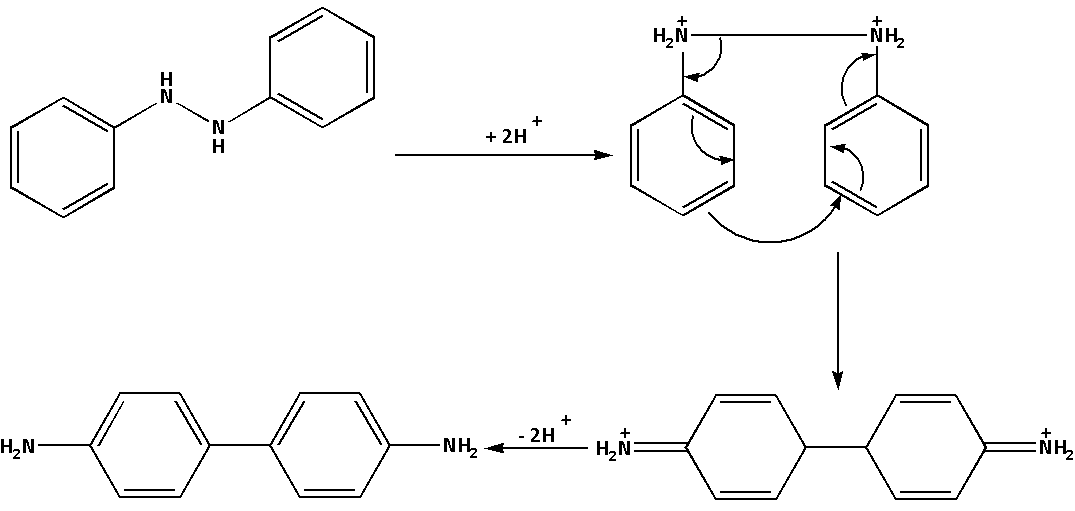
In the reaction, where hydrazobenzene reacts with sulphuric acid i.e. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ a rearrangement reaction leads to the formation of benzidine. Thus, benzidine is a product of rearrangement of hydrazobenzene in an acidic medium.
Benzidine is not a naturally occurring substance and is synthesized mainly from hydrazobenzene on reacting it with sulphuric acid i.e. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$.
Thus, hydrazobenzene on treatment with ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ forms benzidine.
Thus, the correct option is (C) benzidine.
Note: Benzidine is greyish-red, yellowish or white coloured powder. Benzidine can also be synthesized from nitrobenzene. Nitrobenzene is first converted to diphenylhydrazine or hydrazobenzene using iron powder as a reducing agent which then undergoes the same rearrangement reaction in acidic medium as shown above.
Complete solution:
We know that hydrazobenzene as the name suggests hydrazo group is $ - {\text{NH}}$ group and benzene indicates that this hydrazo group is attached to the benzene ring.
Hydrazobenzene is two benzene rings to which $ - {\text{NH}}$ groups are attached. These two rings are then connected through the nitrogen-nitrogen $\left( {{\text{N}} - {\text{N}}} \right)$ bond.
The structure for hydrazobenzene is as follows:

${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ which is known as sulphuric acid creates an acidic medium. Hydrazobenzene in an acidic medium accepts protons from the sulphuric acid. In an acidic medium, hydrazobenzene undergoes a rearrangement reaction.
The mechanism of the reaction when hydrazobenzene reacts with sulphuric acid i.e. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is as follows:

In the reaction, where hydrazobenzene reacts with sulphuric acid i.e. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ a rearrangement reaction leads to the formation of benzidine. Thus, benzidine is a product of rearrangement of hydrazobenzene in an acidic medium.
Benzidine is not a naturally occurring substance and is synthesized mainly from hydrazobenzene on reacting it with sulphuric acid i.e. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$.
Thus, hydrazobenzene on treatment with ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ forms benzidine.
Thus, the correct option is (C) benzidine.
Note: Benzidine is greyish-red, yellowish or white coloured powder. Benzidine can also be synthesized from nitrobenzene. Nitrobenzene is first converted to diphenylhydrazine or hydrazobenzene using iron powder as a reducing agent which then undergoes the same rearrangement reaction in acidic medium as shown above.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




