
Hybridization of silicon atom in silica is:
(A) sp
(B) $s{{p}^{2}}$
(C) $s{{p}^{3}}$
(D) $s{{p}^{3}}d$
Answer
516k+ views
Hint: As we know that hybridization is a hypothetical idea which tells us about the fusion of atomic orbitals to form newly hybridized orbitals which in turn influence the molecular geometry as well as its bonding properties. So here we have to tell the hybridization of Silicon atoms in silica.
Complete answer:
Let us discuss about silica and hybridization followed by finding the hybridization of silicon atom in silica compound as follows:-
-Silica: it is also known as silicon dioxide which is its smallest molecular constituent. It is most commonly found in the form of quartz and also in various living organisms. Its chemical formula is ${{(Si{{O}_{2}})}_{n}}$. It is one of the most complex and also an abundant material present on earth, existing as a compound in several ores, minerals and also as a synthetic product. Its structure is shown below:-
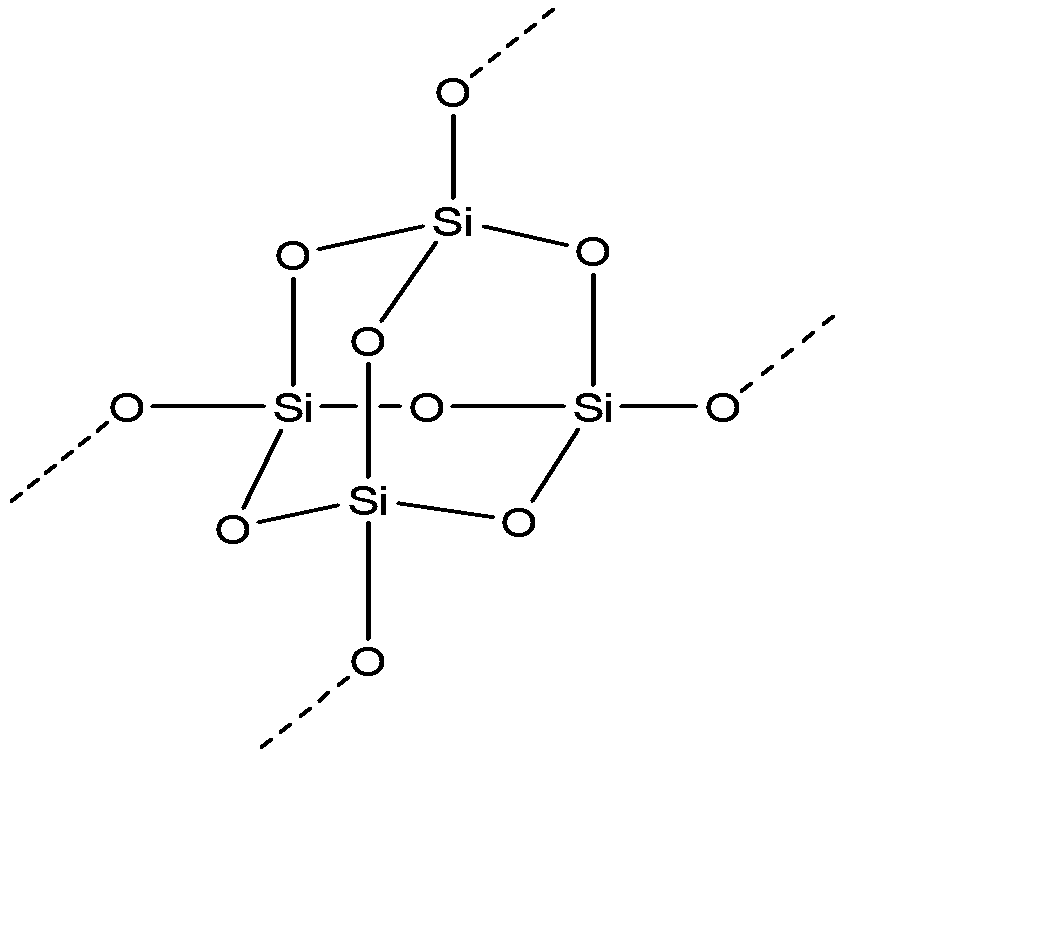
Above structure is a typical subunit of silica at low pressure conditions. Here each silicon (Si) atom is single bonded to four oxygen atoms.
-Hybridization: It is a concept which tells us about the fusion of atomic orbitals to form newly hybridized orbitals which in turn influence the molecular geometry as well as its bonding properties. It helps us to explain the shape of the molecule as the angles between bonds are almost equal to the angles between hybrid orbitals.
-When an atom is connected to different atoms by 4 single bonds, it forms tetrahedral structure with the involvement of 4 orbitals that are one s and three p-orbitals. They hybridize together and form $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybrid orbitals.
Since silicon is connected to oxygen by four single bonds in a silica compound, therefore hybridization of silicon atoms is (C)$s{{p}^{3}}$.
Note:
-Remember that hybridization is preferred in order to decrease the orbital energy of p-orbitals and bring directional character in s-orbitals.
-Also each hybrid orbital has the same energy level for the same hybridization.
Complete answer:
Let us discuss about silica and hybridization followed by finding the hybridization of silicon atom in silica compound as follows:-
-Silica: it is also known as silicon dioxide which is its smallest molecular constituent. It is most commonly found in the form of quartz and also in various living organisms. Its chemical formula is ${{(Si{{O}_{2}})}_{n}}$. It is one of the most complex and also an abundant material present on earth, existing as a compound in several ores, minerals and also as a synthetic product. Its structure is shown below:-

Above structure is a typical subunit of silica at low pressure conditions. Here each silicon (Si) atom is single bonded to four oxygen atoms.
-Hybridization: It is a concept which tells us about the fusion of atomic orbitals to form newly hybridized orbitals which in turn influence the molecular geometry as well as its bonding properties. It helps us to explain the shape of the molecule as the angles between bonds are almost equal to the angles between hybrid orbitals.
-When an atom is connected to different atoms by 4 single bonds, it forms tetrahedral structure with the involvement of 4 orbitals that are one s and three p-orbitals. They hybridize together and form $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybrid orbitals.
Since silicon is connected to oxygen by four single bonds in a silica compound, therefore hybridization of silicon atoms is (C)$s{{p}^{3}}$.
Note:
-Remember that hybridization is preferred in order to decrease the orbital energy of p-orbitals and bring directional character in s-orbitals.
-Also each hybrid orbital has the same energy level for the same hybridization.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




