
What is the hybridisation state of benzyl carbonium?
$(a)s{p^3}$
$(b)s{p^2}$
$(c)sp{d^2}$
$(d)s{p^2}d$
Answer
512.7k+ views
Hint: Ions are the species which are formed when an atom loses or gains electrons. Ions can have positive charge or negative charge. In a compound, when a carbon atom possesses a positive charge, then it is known as carbocation or carbonium ion and benzyl refers to the benzene ring present in the compound. So, here in this question we will see the structure of benzyl carbonium and find its oxidation state.
Complete answer:
An atom is considered as a neutral species but when it loses or gains any electrons, then it forms ions. If the charge on the species is positive, then it is known as cation and if the charge on the species is negative, then it is known as anion.
So, we can define carbonium as a species in which the carbon atom possesses a positive charge which is also known as carbocation.
Hence, the benzyl carbonium is the species with a carbocation attached to a benzene ring and its structure is given as:
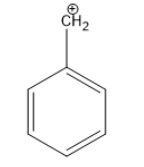
So, we can see that the given structure has carbocation (carbonium) and we know that carbocation has a triangular planar structure and have the hybridisation of $s{p^2}.$
Therefore, the correct option is $(b)s{p^2}$ .
Note:
So, basically carbonium ions are known as carbocations and they are of two types such as: classical carbonium ions and non-classical carbonium ions. Classical carbonium ions are those which have a valency of three and have $s{p^2}$ hybridisation. Non-classical carbonium ions are those which have three bonds and are attached to one atom with a double bond and methonium ion is an example of this.
Complete answer:
An atom is considered as a neutral species but when it loses or gains any electrons, then it forms ions. If the charge on the species is positive, then it is known as cation and if the charge on the species is negative, then it is known as anion.
So, we can define carbonium as a species in which the carbon atom possesses a positive charge which is also known as carbocation.
Hence, the benzyl carbonium is the species with a carbocation attached to a benzene ring and its structure is given as:

So, we can see that the given structure has carbocation (carbonium) and we know that carbocation has a triangular planar structure and have the hybridisation of $s{p^2}.$
Therefore, the correct option is $(b)s{p^2}$ .
Note:
So, basically carbonium ions are known as carbocations and they are of two types such as: classical carbonium ions and non-classical carbonium ions. Classical carbonium ions are those which have a valency of three and have $s{p^2}$ hybridisation. Non-classical carbonium ions are those which have three bonds and are attached to one atom with a double bond and methonium ion is an example of this.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




