
What is the hybridisation of \[{\left[ {PtC{l_4}} \right]^{2 - }}\] and how?
Answer
516.3k+ views
Hint: Hybridisation is defined as the mixing of atomic orbitals belonging to the same atom but with slightly varying energies, resulting in an energy redistribution between them and the production of new orbitals of equal energies and shape.
Complete answer:
The \[{\left[ {PtC{l_4}} \right]^{2 - }}\] hybridization is square planar.
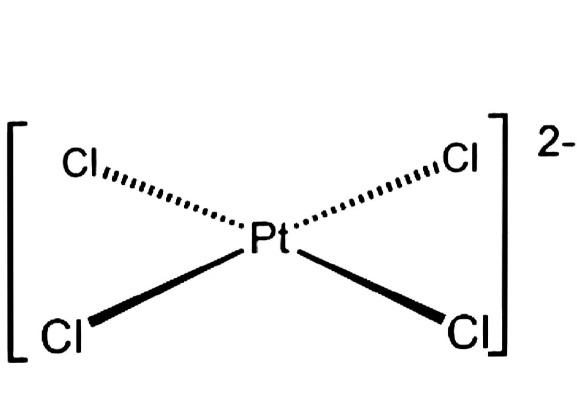
1. Platinum has a valence electron count of six. \[\left( {2 - } \right)\] signifies that platinum has gained two additional electrons.
2. To complete its octet, each chlorine atom requires one electron.
3. In between the platinum atoms, there is a high repulsion between the electron and the ligand, resulting in a strong crystal field splitting.
4. As a result of the splitting, the degeneracy of \[{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\] and \[{d_{{z^2}}}\] is broken.
5. This degeneracy is more stable in a square planar layout than in a tetrahedral design.
Additional information:
Hybridization is a general chemical term that can be applied to both organic and inorganic chemistry. Its significance in organic chemistry stems from the fact that it is the only simple model that can explain the molecular geometry of organic molecules (roughly). Because the original valence bond theory couldn't handle it, it had to be expanded.
Note:
Theoretically, the complex should be tetrahedral rather than square planar. However, because of its size, Pt establishes a strong connection with the ligand. As a result of the significant repulsion between the electrons of Pt and the ligand, substantial crystal field splitting occurs. The degeneracy of \[{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\] and \[{d_{{z^2}}}\] orbital is broken by severe field splitting. As a result, the square planar arrangement is more stable than the tetrahedral arrangement, hence it should be square planar.
Complete answer:
The \[{\left[ {PtC{l_4}} \right]^{2 - }}\] hybridization is square planar.

1. Platinum has a valence electron count of six. \[\left( {2 - } \right)\] signifies that platinum has gained two additional electrons.
2. To complete its octet, each chlorine atom requires one electron.
3. In between the platinum atoms, there is a high repulsion between the electron and the ligand, resulting in a strong crystal field splitting.
4. As a result of the splitting, the degeneracy of \[{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\] and \[{d_{{z^2}}}\] is broken.
5. This degeneracy is more stable in a square planar layout than in a tetrahedral design.
Additional information:
Hybridization is a general chemical term that can be applied to both organic and inorganic chemistry. Its significance in organic chemistry stems from the fact that it is the only simple model that can explain the molecular geometry of organic molecules (roughly). Because the original valence bond theory couldn't handle it, it had to be expanded.
Note:
Theoretically, the complex should be tetrahedral rather than square planar. However, because of its size, Pt establishes a strong connection with the ligand. As a result of the significant repulsion between the electrons of Pt and the ligand, substantial crystal field splitting occurs. The degeneracy of \[{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\] and \[{d_{{z^2}}}\] orbital is broken by severe field splitting. As a result, the square planar arrangement is more stable than the tetrahedral arrangement, hence it should be square planar.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




