
How would you prepare Grignard reagent?
Answer
555.9k+ views
Hint: Haloalkanes react with dry magnesium powder in dry ether to form alkyl magnesium halides commonly known as Grignard reagent. It is commonly represented by the general formula$RMgX$, where$R = $Haloalkane, $X = $Halogen$(I,Br,Cl)$. We can prepare Grignard reagents in the lab easily by adding halogen to alkane to make haloalkanes. Further adding magnesium in the presence of dry ether to haloalkanes and it leads to formation of Grignard reagents.
Complete step-by-step answer: Grignard reagent is an organometallic compound because of organometallic bond between magnesium (metal) and alkanes. Grignard reagents are strong bases and strong nucleophiles (that can donate an electron pair). It is very reactive. We know that magnesium is electropositive and it will donate electron pairs to alkane and acquire partially positive charge and alkane acquire partially negative charge.
${R^{\delta - }} - M{g^{\delta + }}$
Polarity creates due to difference in their electronegativity. It becomes a polar molecule. Because of its polarity, it is highly reactive.
To prepare Grignard reagent we will take first alkyl halide (we can take aryl halide also), then We will add magnesium (dry powder) in presence of dry ether.

Mechanism:
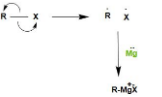
The bond between R and X breaks and both R and X take up one electron each. Magnesium have $2$ valence electrons and it can donates its electrons. One electron of magnesium makes covalent bond ($\sigma $bond) with R that means sharing of electrons and magnesium donates another electron to X and leads to formation of ionic bond.
We can understand this preparation by taking an example. Take methyl iodide and add some dry powder of magnesium in the presence of dry ether. After reaction methyl magnesium iodide will formed.
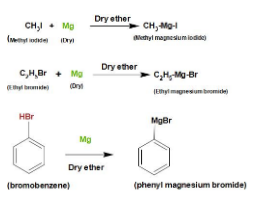
Note:Keep in mind that everything which we are adding to form Grignard reagent should be in dry form because Grignard reagent reacts with water. Remember that organometallic bond is covalent bond but the bond between magnesium and halogen is ionic bond. Grignard reagent can be stored in dry ether because it stabilizes the Grignard reagent. Grignard reagents are used for making a very large number of organic compounds. Reactivity order should be remembered i.e.$RI > RBr > RCl$.
Complete step-by-step answer: Grignard reagent is an organometallic compound because of organometallic bond between magnesium (metal) and alkanes. Grignard reagents are strong bases and strong nucleophiles (that can donate an electron pair). It is very reactive. We know that magnesium is electropositive and it will donate electron pairs to alkane and acquire partially positive charge and alkane acquire partially negative charge.
${R^{\delta - }} - M{g^{\delta + }}$
Polarity creates due to difference in their electronegativity. It becomes a polar molecule. Because of its polarity, it is highly reactive.
To prepare Grignard reagent we will take first alkyl halide (we can take aryl halide also), then We will add magnesium (dry powder) in presence of dry ether.

Mechanism:

The bond between R and X breaks and both R and X take up one electron each. Magnesium have $2$ valence electrons and it can donates its electrons. One electron of magnesium makes covalent bond ($\sigma $bond) with R that means sharing of electrons and magnesium donates another electron to X and leads to formation of ionic bond.
We can understand this preparation by taking an example. Take methyl iodide and add some dry powder of magnesium in the presence of dry ether. After reaction methyl magnesium iodide will formed.

Note:Keep in mind that everything which we are adding to form Grignard reagent should be in dry form because Grignard reagent reacts with water. Remember that organometallic bond is covalent bond but the bond between magnesium and halogen is ionic bond. Grignard reagent can be stored in dry ether because it stabilizes the Grignard reagent. Grignard reagents are used for making a very large number of organic compounds. Reactivity order should be remembered i.e.$RI > RBr > RCl$.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




