
How to convert phenol to aspirin?
Answer
532.4k+ views
Hint: To determine the answer to this question we should know the structure of phenol and aspirin so, we can determine what changes in the reactant we have to do. We should also know the function of some simple acid and bases such as carbon dioxide and sodium hydroxide.
Complete solution:
The structure of phenol is as follows:
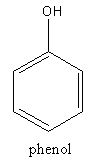
The structure of aspirin is as follows:
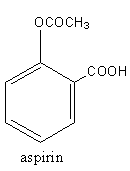
Aspirin has one carboxylic group, so we have to add a carboxylic group to phenol. We will use the Kolbe-Schmitt reaction for this. The Kolbe-Schmitt reaction is a carboxylation reaction. The heating of phenol with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide is known as Kolbe-Schmitt reaction. Kolbe-Schmitt reaction is an additional type reaction.
The base abstract a proton from the hydroxide group of the phenol generating a negative charge on oxygen. Delocalization of negative charge generates a carbon nucleophile. Which attacks on carbon dioxide. The protonation give the product having carboxylic group.
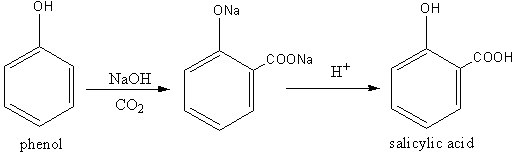
The product of Kolbe-Schmitt reaction is salicylic acid.
We will treat the salicylic acid with acetic anhydride for the preparation of aspirin as follows:
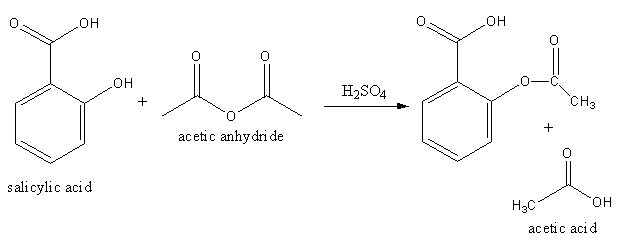
The above reaction is known as acetylation of salicylic acid. The acetylation of salicylic acid take place in presence of strong acid like sulphuric acid.
The salicylic acid reacts with acetic anhydride in presence of sulphuric acid to form acetylated salicylic acid and acetic acid.
Therefore, we can convert phenol to aspirin by treating phenol with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide in an acidic medium. Then treated the product salicylic acid with acetic anhydride.
Note:The molecular formula of aspirin is ${{\text{C}}_{\text{9}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$. It is soluble in water. The acetylsalicylic acid is known as aspirin. It is a drug used as a pain reliever or in fever. It has adverse effects that upset the stomach. In presence of moisture aspirin hydrolysed into salicylic acid and acetic acid. Aspirin is stable in dry air. The formation of aspirin from salicylic acid is an esterification reaction.
Complete solution:
The structure of phenol is as follows:

The structure of aspirin is as follows:

Aspirin has one carboxylic group, so we have to add a carboxylic group to phenol. We will use the Kolbe-Schmitt reaction for this. The Kolbe-Schmitt reaction is a carboxylation reaction. The heating of phenol with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide is known as Kolbe-Schmitt reaction. Kolbe-Schmitt reaction is an additional type reaction.
The base abstract a proton from the hydroxide group of the phenol generating a negative charge on oxygen. Delocalization of negative charge generates a carbon nucleophile. Which attacks on carbon dioxide. The protonation give the product having carboxylic group.

The product of Kolbe-Schmitt reaction is salicylic acid.
We will treat the salicylic acid with acetic anhydride for the preparation of aspirin as follows:

The above reaction is known as acetylation of salicylic acid. The acetylation of salicylic acid take place in presence of strong acid like sulphuric acid.
The salicylic acid reacts with acetic anhydride in presence of sulphuric acid to form acetylated salicylic acid and acetic acid.
Therefore, we can convert phenol to aspirin by treating phenol with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide in an acidic medium. Then treated the product salicylic acid with acetic anhydride.
Note:The molecular formula of aspirin is ${{\text{C}}_{\text{9}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$. It is soluble in water. The acetylsalicylic acid is known as aspirin. It is a drug used as a pain reliever or in fever. It has adverse effects that upset the stomach. In presence of moisture aspirin hydrolysed into salicylic acid and acetic acid. Aspirin is stable in dry air. The formation of aspirin from salicylic acid is an esterification reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




