
How is fluorine added to Benzene?
Answer
516.3k+ views
Hint: We need to know that the process of addition of Halogens to organic compounds is known as halogenation. If Chlorine is added its chlorination, for bromine its bromination, similarly for fluorine its fluorination. Halogenation is commonly an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Complete answer:
We need to remember that the halogens comprise Group $17$ of the periodic table. The electrophilicity and electronegativity of halogens decreases as we move down the group. Hence Fluorine is the most reactive and Iodine is the least reactive. The process of fluorination is highly reactive and iodination is highly unreactive.
The exothermic rates also decrease as we move down the group. Fluorination is highly exothermic and explosive and yields polyfluorinated products. Hence direct fluorination of benzene is very difficult and hazardous.
Indirect ways are used to add fluorine to aromatic rings. Fluorobenzene can be obtained from benzene diazonium chloride by using Balz–Schiemann reaction. In this reaction an aromatic amine is converted into an aryl fluoride via a diazonium tetrafluoroborate intermediate. This method is used commonly to obtain Fluorobenzene and its derivatives.
The conversion happens as follows: Aniline is treated with nitrous acid to form benzene diazonium chloride, further on reaction with $HB{F_4}$ to give benzene diazonium fluoroborate. On further heating it undergoes decomposition to give fluorobenzene. The reaction is shown below:
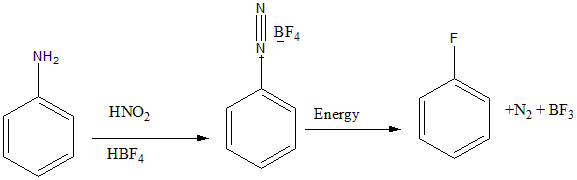
Derivatives like 4-fluorobenzoic acid are also obtained by this method.
Note:
We need to know that the diazotization is the reaction that includes reaction of $HCl$ and $NaN{O_3}$ under very low temperature of $0 - 5^\circ C$ to obtain nitrous acid. This reaction occurs primarily with aromatic amines. This reaction is used to obtain many derivatives and also in the dye industry.
Complete answer:
We need to remember that the halogens comprise Group $17$ of the periodic table. The electrophilicity and electronegativity of halogens decreases as we move down the group. Hence Fluorine is the most reactive and Iodine is the least reactive. The process of fluorination is highly reactive and iodination is highly unreactive.
The exothermic rates also decrease as we move down the group. Fluorination is highly exothermic and explosive and yields polyfluorinated products. Hence direct fluorination of benzene is very difficult and hazardous.
Indirect ways are used to add fluorine to aromatic rings. Fluorobenzene can be obtained from benzene diazonium chloride by using Balz–Schiemann reaction. In this reaction an aromatic amine is converted into an aryl fluoride via a diazonium tetrafluoroborate intermediate. This method is used commonly to obtain Fluorobenzene and its derivatives.
The conversion happens as follows: Aniline is treated with nitrous acid to form benzene diazonium chloride, further on reaction with $HB{F_4}$ to give benzene diazonium fluoroborate. On further heating it undergoes decomposition to give fluorobenzene. The reaction is shown below:

Derivatives like 4-fluorobenzoic acid are also obtained by this method.
Note:
We need to know that the diazotization is the reaction that includes reaction of $HCl$ and $NaN{O_3}$ under very low temperature of $0 - 5^\circ C$ to obtain nitrous acid. This reaction occurs primarily with aromatic amines. This reaction is used to obtain many derivatives and also in the dye industry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




