
How do you read a codon table?
Answer
510.6k+ views
Hint: A codon is a triplet code which determines which amino acid is to be synthesised. The codon has three alphabets which stands for the amino acid. The first codon read by mRNA is a start codon and the translation stops after reading stop codons.
Complete answer:
During protein synthesis, the DNA is transcribed into mRNA and mRNA translates into amino acids. The mRNA formed in the nucleus carries a code which consist of three nucleotides. The nucleotides that are present in DNA and RNA are Adenine(A), Guanine (G). cytosine (C), Thymine (T), uracil (U). This triplet code specify the amino acid to be formed. The translation begins with the start codon AUG which codes for methionine and stops when it carries the message UAA, UAG, UGA which do not code for any amino acid and are nonsense codons.
These codons are read from the start codon in the 5’ to 3’ direction. This specifies the order of the amino acid from N-terminus to C terminus. The codon table is a table which shows the way a triplet codon is read by the tRNA so as to map an amino acid.
The codon table is shown below:
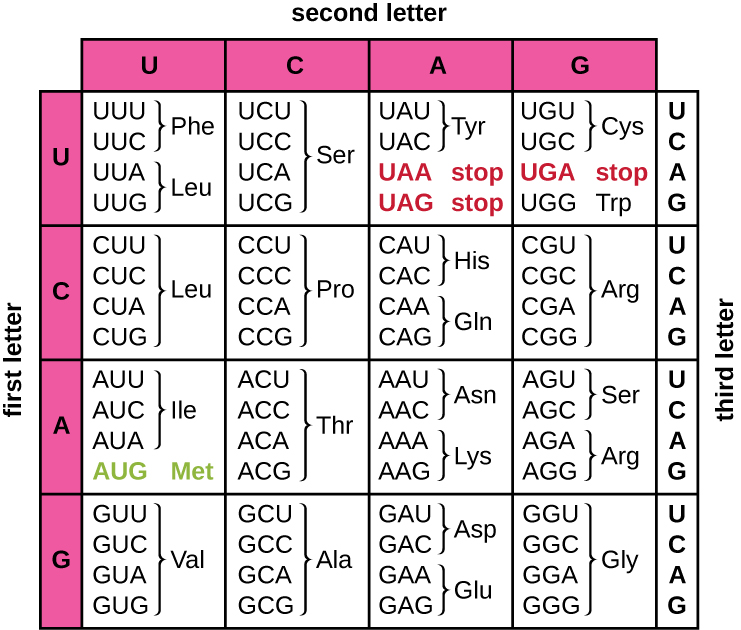
From the table, we can find out which sequence of mRNA will be read for which amino acid. For example, ACU will code for threonine.
Note: There are 64 codons for 20 amino acids. These codons are universal as they are similar for all kinds of organisms. The essential amino acids are not produced in our bodies. They are to be taken through food.
Complete answer:
During protein synthesis, the DNA is transcribed into mRNA and mRNA translates into amino acids. The mRNA formed in the nucleus carries a code which consist of three nucleotides. The nucleotides that are present in DNA and RNA are Adenine(A), Guanine (G). cytosine (C), Thymine (T), uracil (U). This triplet code specify the amino acid to be formed. The translation begins with the start codon AUG which codes for methionine and stops when it carries the message UAA, UAG, UGA which do not code for any amino acid and are nonsense codons.
These codons are read from the start codon in the 5’ to 3’ direction. This specifies the order of the amino acid from N-terminus to C terminus. The codon table is a table which shows the way a triplet codon is read by the tRNA so as to map an amino acid.
The codon table is shown below:

From the table, we can find out which sequence of mRNA will be read for which amino acid. For example, ACU will code for threonine.
Note: There are 64 codons for 20 amino acids. These codons are universal as they are similar for all kinds of organisms. The essential amino acids are not produced in our bodies. They are to be taken through food.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

Which out of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition class 11 chemistry CBSE




