
How do you find the zero correction?
Answer
516.3k+ views
Hint: Let us first understand the concept of zero error and zero correction. While doing the experiment, errors occur sometime. Common sources of error include instrumental, environmental and procedural due to which calculation goes wrong and so the measurement which ruins our efforts. So before doing the experiment it is preferable to check for errors and correction.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The negative of zero error is called zero correction. Zero error arises due to error in the measuring instrument. It occurs when the first marked line of the instrument like Vernier calliper, screw gauge etc. do not coincide with zero marking.
The simple example to understand is - Consider that a metre scale is broken from its zeroth end. The first visible marking on the broken scale is from 2 cm. So if a length is measured with the broken scale of a certain object is 20 cm. Then it will not be the correct length of that object. To get the correct length we need to subtract zero error from that value. As 0-2 cm is missing in that scale, 2 cm has to be subtracted from the measured length. So correct length of that of object will be:
Measured length - zero error=
20 cm - 2cm= 18 cm
Example: Given figure shows error in screw gauge.
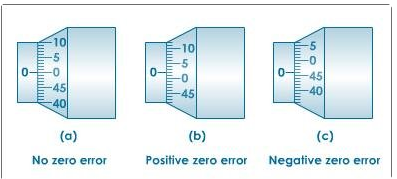
Note: Zero error is algebraically subtracted while Zero correction is algebraically added. In other words zero error is defined as the condition where a measuring instrument registers a reading when there should not be any reading. A zero error can be corrected by calibrating the measuring instruments before an experiment.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The negative of zero error is called zero correction. Zero error arises due to error in the measuring instrument. It occurs when the first marked line of the instrument like Vernier calliper, screw gauge etc. do not coincide with zero marking.
The simple example to understand is - Consider that a metre scale is broken from its zeroth end. The first visible marking on the broken scale is from 2 cm. So if a length is measured with the broken scale of a certain object is 20 cm. Then it will not be the correct length of that object. To get the correct length we need to subtract zero error from that value. As 0-2 cm is missing in that scale, 2 cm has to be subtracted from the measured length. So correct length of that of object will be:
Measured length - zero error=
20 cm - 2cm= 18 cm
Example: Given figure shows error in screw gauge.

Note: Zero error is algebraically subtracted while Zero correction is algebraically added. In other words zero error is defined as the condition where a measuring instrument registers a reading when there should not be any reading. A zero error can be corrected by calibrating the measuring instruments before an experiment.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




