
How do capacitors store energy?
Answer
562.8k+ views
Hint: You could initially give a brief description of the basic structure of a capacitor. Then you could mention a capacitor’s working. You could then mention how a capacitor is advantageous over a battery. You could also provide a relation that clearly shows the quantities on which the energy stored is tended to depend on.
Complete answer:
In the question, we are asked as to how capacitors store energy. Before going into the storage of energy by a capacitor, let us first discuss its basic structure. A capacitor is known to basically consist of two metallic plates that are separated by a dielectric medium.
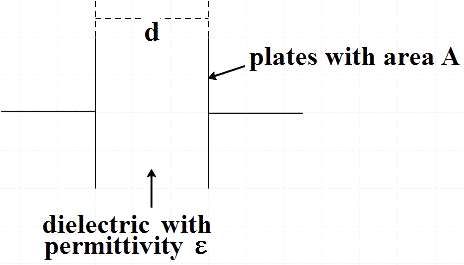
Their sole purpose is to store electrical energy in the form of electrical charge that is accumulated on these metallic plates. They get charged when connected to a power source and this accumulated energy is released on being disconnected from the charging source and hence similar to batteries. The major difference lies in the fact electrochemical processes aid batteries in storing energy and capacitors require no such process and hence the rate of release of energy is higher for capacitors.
The amount of charge that is stored on plates directly determines the amount of energy stored by the capacitor. It could also be expressed in terms of voltage across these plates.
$E=\dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{Q}^{2}}}{C}=\dfrac{1}{2}C{{V}^{2}}$
Where, E is the energy stored, Q is the charge stored, C is the capacitance of the capacitor and V is the voltage across the plates.
Thus, we found that electrical energy is being stored as electric charges in a capacitor.
Note:
We have mentioned above that the non involvement of chemical reactions in storage of electrical energy makes the release process quicker in the case of capacitors when compared to normal batteries. This is also due to the fact that capacitors are known to have very low internal resistance. Capacitors have various applications in audio equipment, camera flashes, etc.
Complete answer:
In the question, we are asked as to how capacitors store energy. Before going into the storage of energy by a capacitor, let us first discuss its basic structure. A capacitor is known to basically consist of two metallic plates that are separated by a dielectric medium.

Their sole purpose is to store electrical energy in the form of electrical charge that is accumulated on these metallic plates. They get charged when connected to a power source and this accumulated energy is released on being disconnected from the charging source and hence similar to batteries. The major difference lies in the fact electrochemical processes aid batteries in storing energy and capacitors require no such process and hence the rate of release of energy is higher for capacitors.
The amount of charge that is stored on plates directly determines the amount of energy stored by the capacitor. It could also be expressed in terms of voltage across these plates.
$E=\dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{Q}^{2}}}{C}=\dfrac{1}{2}C{{V}^{2}}$
Where, E is the energy stored, Q is the charge stored, C is the capacitance of the capacitor and V is the voltage across the plates.
Thus, we found that electrical energy is being stored as electric charges in a capacitor.
Note:
We have mentioned above that the non involvement of chemical reactions in storage of electrical energy makes the release process quicker in the case of capacitors when compared to normal batteries. This is also due to the fact that capacitors are known to have very low internal resistance. Capacitors have various applications in audio equipment, camera flashes, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




