
High density polyethene is obtained by:
A. Polymerization of ethane in a hydrocarbon solvent in the presence of Ziegler-Natta catalyst.
B. Polymerization of ethene under high pressure and temperature.
C. Free radical polymerization of ethane at low-temperature polymerization peroxide
D. Polymerization of ethane in presence of carbon tetrachloride
Answer
601.8k+ views
Hint:
Think about what the monomer unit of polyethene may be. As the name suggests, polyethene is the polymer of ethene. Think about what conditions may be required to generate high density polymers.
Complete step by step solution:
Polymers are the macromolecules or molecules having high molecular mass formed by joining a large number of relatively simple monomeric units in a repetitive fashion.
Polymerization includes the formation of the monomer units and joining them together. A monomer unit is denoted by square brackets with atoms having unsatisfied valencies.
To form a high density, we know that application of high pressure and temperature is required since the density of most materials increases under high pressure and temperature.
The reaction to for high density polyethene is as follows:
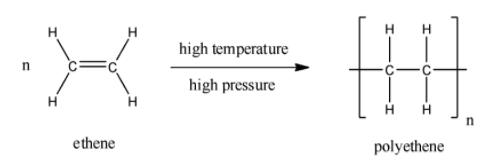
The chemical formula for the polyethene or polyethylene is ${{\left( {{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}} \right)}_{n}}$. The formed polyethene may be low density polyethylene (LDPE) or high-density polyethylene (HDPE). High density polyethene (HDPE) is made under controlled conditions by applying intense heat to petroleum.
Hence, the correct answer is ‘B. Polymerization of ethene under high pressure and temperature.’
Additional Information:
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE) are thermoplastic polyethylene materials, they have different properties and uses. Low density polyethylene undergoes branching during polymerization where polymer chains have secondary polymer chains attached to them. This branching weakens the intermolecular forces in the polymer. That is why the LDPE has a lower strength-to-density ratio than HDPE.
Note:
We know that another name for ethene is ethylene; thus, polyethene can also be called polyethylene. The other options are incorrect as they contain ethane as the starting material and not ethene.
Think about what the monomer unit of polyethene may be. As the name suggests, polyethene is the polymer of ethene. Think about what conditions may be required to generate high density polymers.
Complete step by step solution:
Polymers are the macromolecules or molecules having high molecular mass formed by joining a large number of relatively simple monomeric units in a repetitive fashion.
Polymerization includes the formation of the monomer units and joining them together. A monomer unit is denoted by square brackets with atoms having unsatisfied valencies.
To form a high density, we know that application of high pressure and temperature is required since the density of most materials increases under high pressure and temperature.
The reaction to for high density polyethene is as follows:

The chemical formula for the polyethene or polyethylene is ${{\left( {{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}} \right)}_{n}}$. The formed polyethene may be low density polyethylene (LDPE) or high-density polyethylene (HDPE). High density polyethene (HDPE) is made under controlled conditions by applying intense heat to petroleum.
Hence, the correct answer is ‘B. Polymerization of ethene under high pressure and temperature.’
Additional Information:
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE) are thermoplastic polyethylene materials, they have different properties and uses. Low density polyethylene undergoes branching during polymerization where polymer chains have secondary polymer chains attached to them. This branching weakens the intermolecular forces in the polymer. That is why the LDPE has a lower strength-to-density ratio than HDPE.
Note:
We know that another name for ethene is ethylene; thus, polyethene can also be called polyethylene. The other options are incorrect as they contain ethane as the starting material and not ethene.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




