
Hexacanth larva is formed in
(a) Eucestoda
(b) Cestodaria
(c) Turbellaria
(d) Trematoda
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: In a group commonly referred to as tapeworms, the hexacanth larva is produced, the larger of the two subclasses of flatworms in the Cestoda class. On the scolex (head), the larvae have six posterior hooks. The larval stage of Taenia, which is released when eggs are hatched, is Hexacanth.
Complete step by step answer:
The larger of the two subclasses of flatworms in the Cestoda class is Eucestoda. Its hexacanth larvae, compared to the ten-hooked Cestodaria, have six hooks on the head.
- Taenia solium hexacanth larvae move into the intestine and, with the help of its hooks, bind to the mucous layer of the intestine, penetrate the intestinal wall with the assistance of substances secreted by the penetration glands.
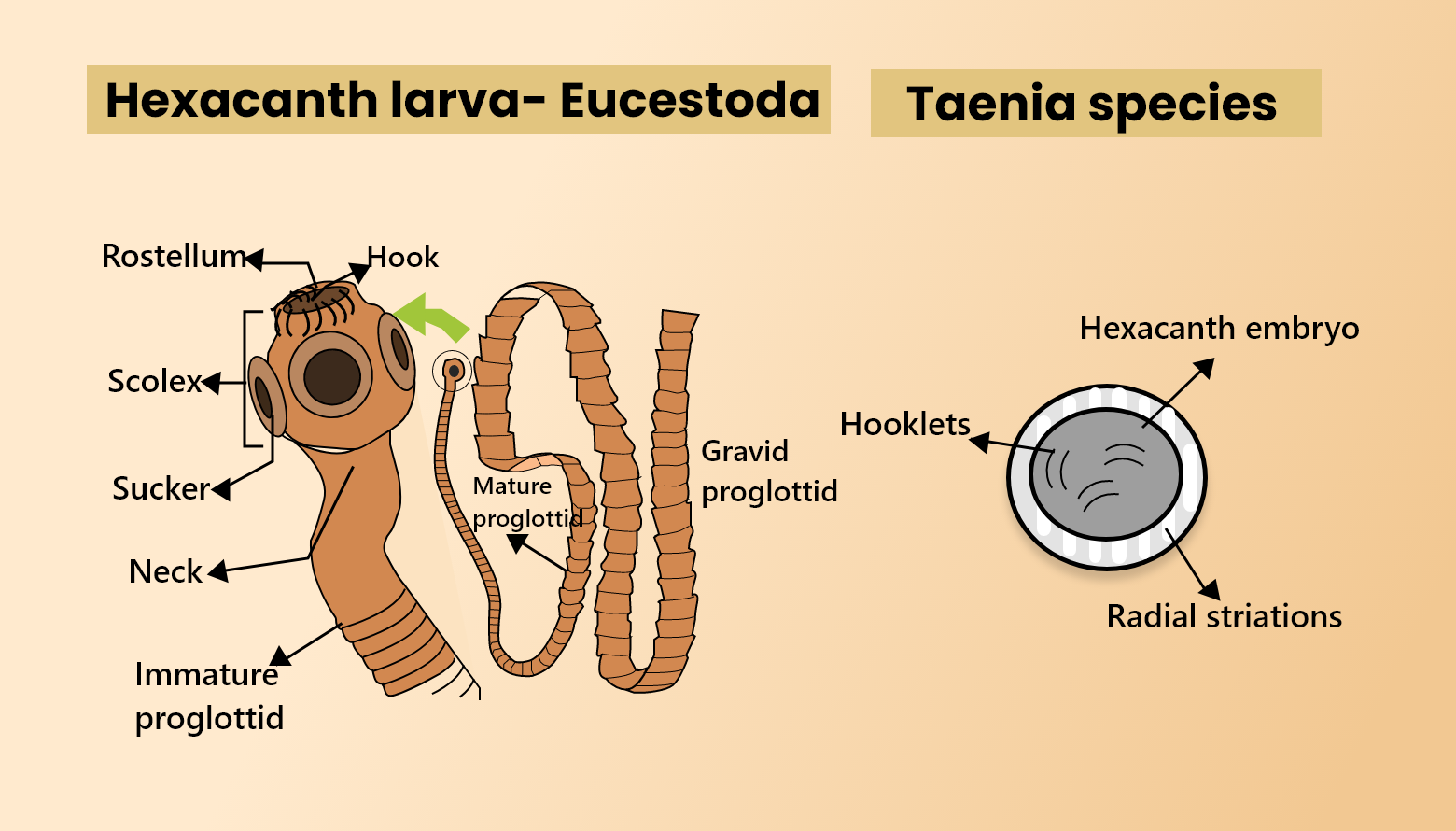
- Later, hexacanth larva enters the hepatic portal vein that goes to the liver through it. Finally, the Hexacanth larva develops into a cysticercus larva that absorbs nutrients from the tissues and grows in size.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Eucestoda’.
Additional information:
- Due to mesenchymal disintegration, a cavity appears in the middle of the cell mass and is filled with liquid content. This fluid comprises substantial amounts of host blood plasma.
- In the shape of a knob, the wall of the embryo on one side becomes thickened and invaginates into its cavity. Four suckers, a small rostellum, and hooks at its base are formed internally by the knob. Proscolex is the name of this inverted scolex. Now, a mature cysticercus, or bladder worm, is an embryo.
Note: Both tapeworms, living in the digestive tract or associated ducts, are vertebrate endoparasites. The pork tapeworm (Taenia solium) with a human definitive host, and pigs as the secondary host, are examples, and Moniezia expansa, whose ruminants are the definitive hosts.
Complete step by step answer:
The larger of the two subclasses of flatworms in the Cestoda class is Eucestoda. Its hexacanth larvae, compared to the ten-hooked Cestodaria, have six hooks on the head.
- Taenia solium hexacanth larvae move into the intestine and, with the help of its hooks, bind to the mucous layer of the intestine, penetrate the intestinal wall with the assistance of substances secreted by the penetration glands.

- Later, hexacanth larva enters the hepatic portal vein that goes to the liver through it. Finally, the Hexacanth larva develops into a cysticercus larva that absorbs nutrients from the tissues and grows in size.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Eucestoda’.
Additional information:
- Due to mesenchymal disintegration, a cavity appears in the middle of the cell mass and is filled with liquid content. This fluid comprises substantial amounts of host blood plasma.
- In the shape of a knob, the wall of the embryo on one side becomes thickened and invaginates into its cavity. Four suckers, a small rostellum, and hooks at its base are formed internally by the knob. Proscolex is the name of this inverted scolex. Now, a mature cysticercus, or bladder worm, is an embryo.
Note: Both tapeworms, living in the digestive tract or associated ducts, are vertebrate endoparasites. The pork tapeworm (Taenia solium) with a human definitive host, and pigs as the secondary host, are examples, and Moniezia expansa, whose ruminants are the definitive hosts.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




