
Why is the heart a muscle and not an organ? Is it both an organ and a muscle?
Answer
487.5k+ views
Hint: The human heart plays a very crucial role in the circulatory system of any organism. The location of the human heart is- in between the lungs, behind the breastbone, and slightly to the left of the middle line. It is a four-chambered structure in the human body. The main function of the heart is to supply oxygenated blood and the purification of deoxygenated blood.
Complete answer:
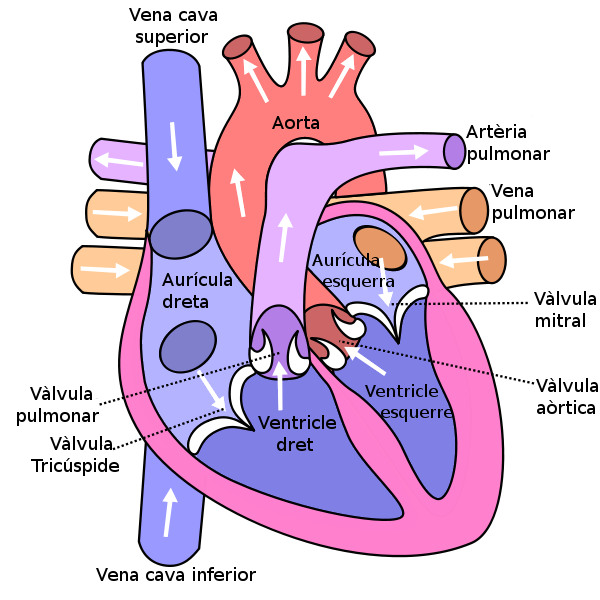
The main functions of the heart are-
1) The heart receives the deoxygenated blood from the various body tissues and in return it supplies the oxygenated blood.
2) It also pumps blood to various organs of the body.
3) It also helps to maintain the blood pressure level in an individual. This is usually done by providing an adequate supply of blood in our body.
4) It also removes the waste products and even the carbon dioxide from the blood. These waste products are further removed from the human body. Overall, we can say that the heart purifies the blood and makes it oxygen-rich.
Organs are defined as the collection of tissues that are mainly specialised for their own different purposes. Muscle, on the other hand, is a type of tissue. Heart can actually be referred to as a muscular organ. In the case of the heart, its function is to pump blood throughout the body. Additionally, the heart is also largely made up of a special type of muscle tissue which is known as cardiac muscle.
Note:
It is important to note that double circulation is a characteristic that takes place in all birds and mammals. Double circulation is only possible due to the presence of a four-chambered heart. The deoxygenated blood is dark red in colour and it contains a high amount of carbon dioxide and waste particles. Whereas the oxygenated blood is bright red in colour and contains a large amount of oxygen and a very low amount of carbon dioxide.
Complete answer:

The main functions of the heart are-
1) The heart receives the deoxygenated blood from the various body tissues and in return it supplies the oxygenated blood.
2) It also pumps blood to various organs of the body.
3) It also helps to maintain the blood pressure level in an individual. This is usually done by providing an adequate supply of blood in our body.
4) It also removes the waste products and even the carbon dioxide from the blood. These waste products are further removed from the human body. Overall, we can say that the heart purifies the blood and makes it oxygen-rich.
Organs are defined as the collection of tissues that are mainly specialised for their own different purposes. Muscle, on the other hand, is a type of tissue. Heart can actually be referred to as a muscular organ. In the case of the heart, its function is to pump blood throughout the body. Additionally, the heart is also largely made up of a special type of muscle tissue which is known as cardiac muscle.
Note:
It is important to note that double circulation is a characteristic that takes place in all birds and mammals. Double circulation is only possible due to the presence of a four-chambered heart. The deoxygenated blood is dark red in colour and it contains a high amount of carbon dioxide and waste particles. Whereas the oxygenated blood is bright red in colour and contains a large amount of oxygen and a very low amount of carbon dioxide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




