
What happens when:
(i) ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ is heated?
(ii) ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ is heated:
Also write the reactions involved.
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: When ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ is heated it undergoes an equilibrium reaction. When ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ is heated it undergoes a disproportionation reaction.
Step by step answer:
(i)
The structure of ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ is a trigonal bipyramidal structure. It has three equatorial bonds and two axial bonds. The structure of ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ is as follows:
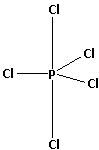
The three equatorial bonds lie in the plane. One axial bond lies above the plane while the other axial bond lies below the plane.
The axial bonds are at an angle of ${\text{9}}{{\text{0}}^ \circ }$ from the equatorial bonds. The equatorial bonds are at an angle of ${\text{12}}{{\text{0}}^ \circ }$ from each other. Thus, the repulsion in the axial bonds is more and the axial bonds elongate. The elongation of axial bonds makes them less stable.
When ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ is heated the less stable axial bonds break and ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ is converted to ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ and ${\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$.
The reaction when ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ is heated is as follows:
${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{heat}}}}{\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_3} + {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_2}$
(ii)
When ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ is heated it undergoes a disproportionation reaction. During the disproportionation reaction, ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ undergoes oxidation as well as reduction. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ and ${\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ are formed during the reaction.
The reaction when ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ is heated is as follows:
${\text{4}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{heat}}}}3{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}} + {\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$
The oxidation state of phosphorus in ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ is ${\text{ + 3}}$, in ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ it becomes ${\text{ + 5}}$ and in ${\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ it becomes $ - {\text{3}}$.
The oxidation state of phosphorus increases from ${\text{ + 3}}$ to ${\text{ + 5}}$ thus, oxidation reaction occurs. The oxidation state of phosphorous decreases from ${\text{ + 3}}$ to $ - {\text{3}}$ thus, reduction reaction occurs
Note: Remember that all the ${\text{P}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bonds in ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ are not similar. ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ has three equatorial bonds and two axial bonds.
The reaction in which both oxidation as well as reduction occurs is known as a disproportionation reaction.
Step by step answer:
(i)
The structure of ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ is a trigonal bipyramidal structure. It has three equatorial bonds and two axial bonds. The structure of ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ is as follows:

The three equatorial bonds lie in the plane. One axial bond lies above the plane while the other axial bond lies below the plane.
The axial bonds are at an angle of ${\text{9}}{{\text{0}}^ \circ }$ from the equatorial bonds. The equatorial bonds are at an angle of ${\text{12}}{{\text{0}}^ \circ }$ from each other. Thus, the repulsion in the axial bonds is more and the axial bonds elongate. The elongation of axial bonds makes them less stable.
When ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ is heated the less stable axial bonds break and ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ is converted to ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ and ${\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$.
The reaction when ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ is heated is as follows:
${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{heat}}}}{\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_3} + {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_2}$
(ii)
When ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ is heated it undergoes a disproportionation reaction. During the disproportionation reaction, ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ undergoes oxidation as well as reduction. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ and ${\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ are formed during the reaction.
The reaction when ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ is heated is as follows:
${\text{4}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{heat}}}}3{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}} + {\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$
The oxidation state of phosphorus in ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ is ${\text{ + 3}}$, in ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ it becomes ${\text{ + 5}}$ and in ${\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ it becomes $ - {\text{3}}$.
The oxidation state of phosphorus increases from ${\text{ + 3}}$ to ${\text{ + 5}}$ thus, oxidation reaction occurs. The oxidation state of phosphorous decreases from ${\text{ + 3}}$ to $ - {\text{3}}$ thus, reduction reaction occurs
Note: Remember that all the ${\text{P}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bonds in ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ are not similar. ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ has three equatorial bonds and two axial bonds.
The reaction in which both oxidation as well as reduction occurs is known as a disproportionation reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Identify the subject of the following imperative sentence class 10 english CBSE

List out three methods of soil conservation

The point equidistant from the three sides of a tr-class-10-maths-CBSE




