
What happens when carbonyl compounds are treated with hydrazine? Write the reaction.
Answer
554.7k+ views
Hint :Carbonyl compounds are the compounds having a carbonyl group attached to the molecule. A carbonyl carbon is a functional group in which a carbon atom is double bonded to the oxygen and the general carbonyl compound is represented as $ R - C(R) = O $ .
Complete Step By Step Answer:
First of all, we start with what is hydrazine.
Hydrazine: Hydrazine is an alkaline liquid which is a very powerful reducing agent having the chemical formula $ N{H_2} - N{H_2} $ .
Carbonyl compounds: The organic compounds aldehyde and ketones are carbonyl compounds, as have carbonyl groups.
Now, we will treat carbonyl compounds with the hydrazine.
The reaction of carbonyl compounds with the hydrazine:
First of all, the carbonyl group is reacted with hydrazine. This forms hydrazone.
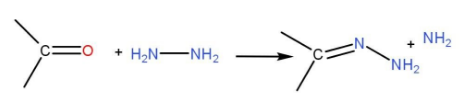
When the medium is basic. The terminal nitrogen atom of the hydrazone is deprotonated and makes double bonds with the neighbouring nitrogen. The proton which is released is attached to hydroxide ion to form water. As oxygen is more electron withdrawing than carbon, the carbon is protonated by the water. The terminal nitrogen is deprotonated again and the triple bond with the nitrogen atom at the neighbour which forms carbanion. Another proton forms water from the environment which is basic. Then, the carbonyl compound is converted into alkane.
Hence, the complete reaction is as follows:
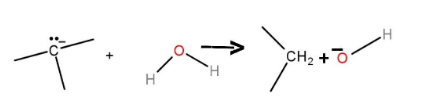
The reaction is also known as Wolf-Kishner reduction. In these reactions, carbonyl carbon is reduced to alkane.
Note :
There are various other methods to convert carbonyl compounds to alkanes like Clemmensen reduction in which the carbonyl is reacted with zinc amalgam in presence of aqueous hydrochloric acid.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
First of all, we start with what is hydrazine.
Hydrazine: Hydrazine is an alkaline liquid which is a very powerful reducing agent having the chemical formula $ N{H_2} - N{H_2} $ .
Carbonyl compounds: The organic compounds aldehyde and ketones are carbonyl compounds, as have carbonyl groups.
Now, we will treat carbonyl compounds with the hydrazine.
The reaction of carbonyl compounds with the hydrazine:
First of all, the carbonyl group is reacted with hydrazine. This forms hydrazone.

When the medium is basic. The terminal nitrogen atom of the hydrazone is deprotonated and makes double bonds with the neighbouring nitrogen. The proton which is released is attached to hydroxide ion to form water. As oxygen is more electron withdrawing than carbon, the carbon is protonated by the water. The terminal nitrogen is deprotonated again and the triple bond with the nitrogen atom at the neighbour which forms carbanion. Another proton forms water from the environment which is basic. Then, the carbonyl compound is converted into alkane.
Hence, the complete reaction is as follows:

The reaction is also known as Wolf-Kishner reduction. In these reactions, carbonyl carbon is reduced to alkane.
Note :
There are various other methods to convert carbonyl compounds to alkanes like Clemmensen reduction in which the carbonyl is reacted with zinc amalgam in presence of aqueous hydrochloric acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




