
What happens when
(a) Sodium phenoxide is treated with\[C{H_3}Cl\]?
(b) \[C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - OH\] is oxidized by PCC
(c) Phenol is treated with \[C{H_3}COCl\]/anhydrous \[AlC{l_3}\]
Write the chemical equations to support your answer.
Answer
477k+ views
Hint: All the above reactions are the direct reactions taking place and all of them are one-step reactions. The first reaction is an example of Williamsons synthesis reaction, the second one is the basic oxidation reaction and the third one is the friedel-craft reaction. By the names of the reactions you can guess what might be the products of these reactions.
Complete step by step answer:
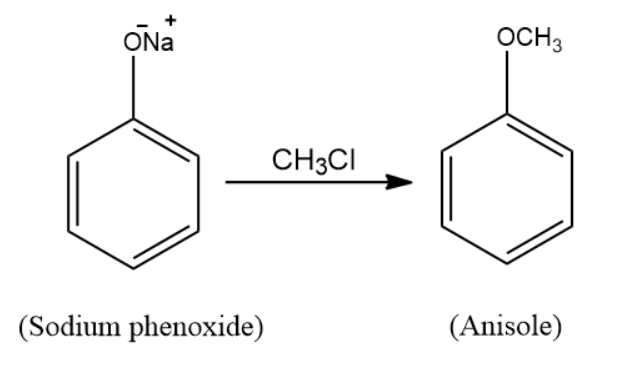
(a) When sodium phenoxide is treated with methyl chloride \[\left( {C{H_3}Cl} \right)\], the product formed is anisole. The reaction taking place here is a nucleophilic substitution reaction. Sodium phenoxide is an alkoxide and methyl chloride is a halide. When the two react, Williamson’s ether synthesis process occurs and the resulting product is ether, which is anisole. The reaction for the following takes place in the following manner:
(b) \[C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - OH\] is a primary alcohol. When a primary alcohol is treated with PCC, it undergoes oxidation and gets oxidized to an aldehyde. PCC is Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC), a complex of chromium trioxide with pyridine and HCl. It is a better reagent for the oxidation of primary alcohols to an aldehyde. The reaction of \[C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - OH\] with PCC takes place in the following manner:
$C{H_2} = CH - CH - OH\xrightarrow{{PCC}}C{H_2} = CH - CHO$
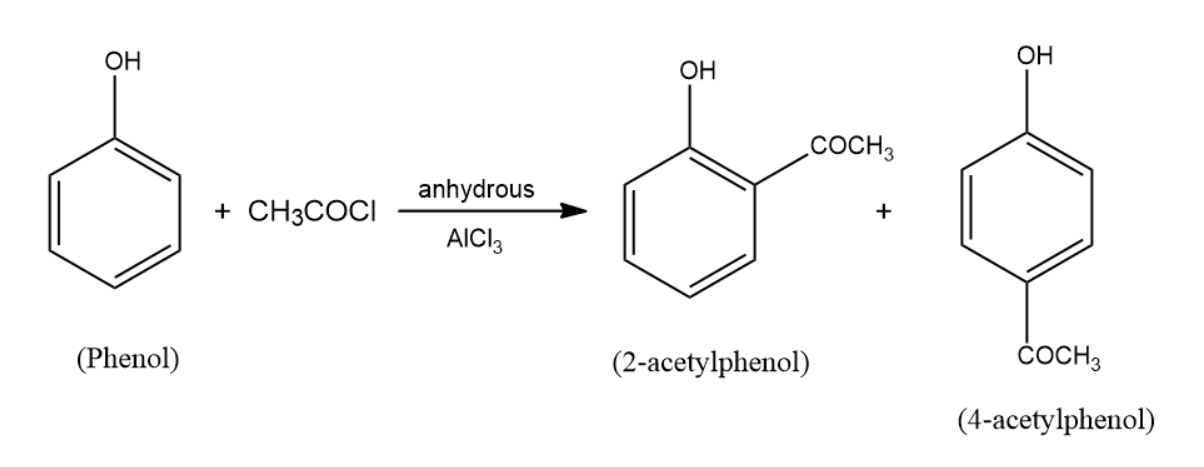
(c) When phenol is treated with \[C{H_3}COCl\]/anhydrous \[AlC{l_3}\] two products are formed among which one of them is major and the other one is minor. The reaction that occurs here is the friedel-craft acylation reaction. The products formed as a result are the two acetylphenol products. These products are $2 - $acetylphenol and $4 - $acetylphenol, among them $4 - $acetylphenol is the major product. The reaction takes place in the following manner:
Note:
Williamson’s synthesis reaction occurs between an organohalide and a deprotonated alcohol to yield ether as the product. This deprotonated alcohol is also called alkoxide. And the reaction occurs via the $Sn2$ mechanism. PCC are very good reagents for converting a primary alcohol to an aldehyde or a secondary alcohol to a ketone. However, PCC cannot oxidize aldehydes to carboxylic acids. Friedel-crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed to attach substituents to an aromatic ring. There is also friedel-craft alkylation in which instead of $C{H_3}COCl$, $C{H_3}Cl$ is used.
Complete step by step answer:
(a) When sodium phenoxide is treated with methyl chloride \[\left( {C{H_3}Cl} \right)\], the product formed is anisole. The reaction taking place here is a nucleophilic substitution reaction. Sodium phenoxide is an alkoxide and methyl chloride is a halide. When the two react, Williamson’s ether synthesis process occurs and the resulting product is ether, which is anisole. The reaction for the following takes place in the following manner:

(b) \[C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - OH\] is a primary alcohol. When a primary alcohol is treated with PCC, it undergoes oxidation and gets oxidized to an aldehyde. PCC is Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC), a complex of chromium trioxide with pyridine and HCl. It is a better reagent for the oxidation of primary alcohols to an aldehyde. The reaction of \[C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - OH\] with PCC takes place in the following manner:
$C{H_2} = CH - CH - OH\xrightarrow{{PCC}}C{H_2} = CH - CHO$
(c) When phenol is treated with \[C{H_3}COCl\]/anhydrous \[AlC{l_3}\] two products are formed among which one of them is major and the other one is minor. The reaction that occurs here is the friedel-craft acylation reaction. The products formed as a result are the two acetylphenol products. These products are $2 - $acetylphenol and $4 - $acetylphenol, among them $4 - $acetylphenol is the major product. The reaction takes place in the following manner:

Note:
Williamson’s synthesis reaction occurs between an organohalide and a deprotonated alcohol to yield ether as the product. This deprotonated alcohol is also called alkoxide. And the reaction occurs via the $Sn2$ mechanism. PCC are very good reagents for converting a primary alcohol to an aldehyde or a secondary alcohol to a ketone. However, PCC cannot oxidize aldehydes to carboxylic acids. Friedel-crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed to attach substituents to an aromatic ring. There is also friedel-craft alkylation in which instead of $C{H_3}COCl$, $C{H_3}Cl$ is used.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




