
What happens when 1,3-dibromopropane reacts with zinc in the presence of ethanol?
Answer
498.3k+ views
Hint: Free radicals are defined as the species which consist of one unshared electron on its atom and is formed by homolytic cleavage of covalent molecules. They are generally less stable and thus, are very reactive species and react in fractions of seconds with other molecules. The given reaction involves free radicals as an intermediate to form a product.
Complete answer:
When 1,3-dihalopropanes are treated with zinc dust, then the formation of cyclopropane takes place. This reaction is known as the Gustavson reaction. Hass further modified the Gustavson reaction by raising the temperature of the reaction mixture with high-boiling solvents like alcohols, due to which the rate of the reaction accelerated remarkably. So, when 1,3-dihalopropane reacts with zinc dust in aqueous alcohol in the presence of a catalytic amount of sodium iodide, the formation of cyclopropane takes place and this reaction is known as the Hass cyclopropane process. The reaction will proceed as follows:
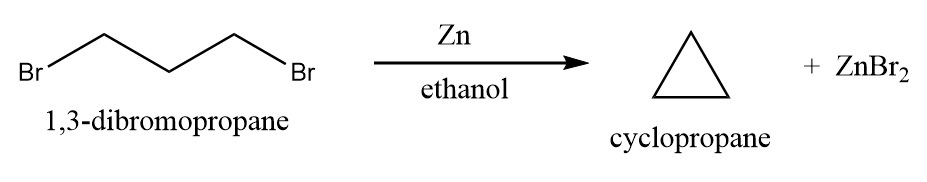
The mechanism of the given reaction is discussed below:
The mechanism of this reaction is more likely to be similar to the Wurtz reaction which follows a free radical mechanism. In the catalytic sodium iodide, the homolytic cleavage of the carbon-bromine bond takes place forming free radicals which, in reaction with zinc, forms cyclopropane. The mechanism of the reaction can be represented as follows:
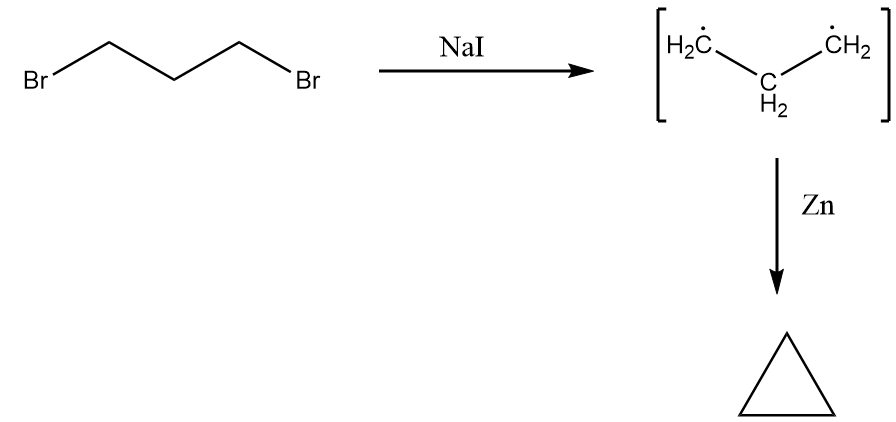
Thus, we can conclude that when 1,3-dibromopropane reacts with zinc in the presence of ethanol, cyclopropane is formed.
Note:
It is important to note that Gustavson reaction and Hass cyclopropane process is modified to Freund reaction according to which the cyclopropane derivatives are prepared from internal nucleophilic displacement of 1,3-dihalopropanes by treating it with sodium. The Freund reaction was unsatisfactory in certain cases because of the formation of olefins as the principal product. Thus, modified conditions are more commonly used in chemistry labs.
Complete answer:
When 1,3-dihalopropanes are treated with zinc dust, then the formation of cyclopropane takes place. This reaction is known as the Gustavson reaction. Hass further modified the Gustavson reaction by raising the temperature of the reaction mixture with high-boiling solvents like alcohols, due to which the rate of the reaction accelerated remarkably. So, when 1,3-dihalopropane reacts with zinc dust in aqueous alcohol in the presence of a catalytic amount of sodium iodide, the formation of cyclopropane takes place and this reaction is known as the Hass cyclopropane process. The reaction will proceed as follows:

The mechanism of the given reaction is discussed below:
The mechanism of this reaction is more likely to be similar to the Wurtz reaction which follows a free radical mechanism. In the catalytic sodium iodide, the homolytic cleavage of the carbon-bromine bond takes place forming free radicals which, in reaction with zinc, forms cyclopropane. The mechanism of the reaction can be represented as follows:

Thus, we can conclude that when 1,3-dibromopropane reacts with zinc in the presence of ethanol, cyclopropane is formed.
Note:
It is important to note that Gustavson reaction and Hass cyclopropane process is modified to Freund reaction according to which the cyclopropane derivatives are prepared from internal nucleophilic displacement of 1,3-dihalopropanes by treating it with sodium. The Freund reaction was unsatisfactory in certain cases because of the formation of olefins as the principal product. Thus, modified conditions are more commonly used in chemistry labs.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




