
What is happening at D ?
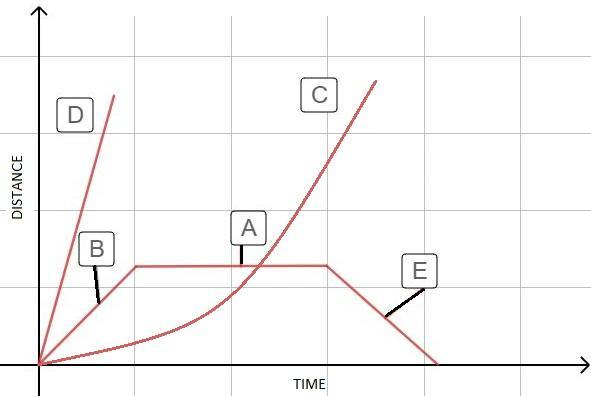
A. Stationary
B. Accelerating
C. Fast steady speed; moving away from starting position
D. Slower steady speed; moving away from starting position

Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: We need to find the nature of the object D, that is, the speed and how it changes with respect to distance and time. We will be using the formula $\text{speed=}\dfrac{\text{distance}}{\text{time}}$ to analyze the nature of the object. We know that speed varies proportionally to the distance and inversely to the time. Accordingly, we can find the nature of D.
Complete step by step answer:
We need to find the nature of D.
From the figure, the plot is distance vs time. A Distance-time graph shows how far an object has traveled in a given time.
We know that $\text{speed=}\dfrac{\text{distance}}{\text{time}}$ . That is speed varies proportionally to the distance and inversely to the time. That is, as time increases (or decreases), speed decreases (or increases). When distance increases (or decreases), speed increases (or decreases).
From, the figure, D is moving away from the starting point. As time increases, D is moving very fast. We can see that it covers more distance in less time.
The Distance-time graph shows the speed. The speed of D is steady, that is, it does not decrease in between. It keeps on increasing.
Hence the correct option is C.
Note:
Let us analyze the nature of other objects in the given figure. The speed of A remains uniform or stationary, that is, it does not increase or decrease. B is moving away from the starting point slowly. The object C is increasing its speed exponentially. Object E is reducing its speed and finally reaches zero.
Complete step by step answer:
We need to find the nature of D.
From the figure, the plot is distance vs time. A Distance-time graph shows how far an object has traveled in a given time.
We know that $\text{speed=}\dfrac{\text{distance}}{\text{time}}$ . That is speed varies proportionally to the distance and inversely to the time. That is, as time increases (or decreases), speed decreases (or increases). When distance increases (or decreases), speed increases (or decreases).
From, the figure, D is moving away from the starting point. As time increases, D is moving very fast. We can see that it covers more distance in less time.
The Distance-time graph shows the speed. The speed of D is steady, that is, it does not decrease in between. It keeps on increasing.
Hence the correct option is C.
Note:
Let us analyze the nature of other objects in the given figure. The speed of A remains uniform or stationary, that is, it does not increase or decrease. B is moving away from the starting point slowly. The object C is increasing its speed exponentially. Object E is reducing its speed and finally reaches zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




