
Ground tissue includes
(a) All tissues internal to endodermis
(b) All tissues external to endodermis
(c) All tissues except epidermis and vascular bundles
(d) Epidermis and cortex
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Based on the nature of the cell walls ground tissues are divided into three types, which are parenchyma cells, collenchyma cells, and sclerenchyma cells. Even though they are differentiated based on the cell wall, they carry common characteristics too.
Complete step by step answer:
Ground tissue includes all tissues except epidermal and vascular tissues. These tissues are divided into three types based on the structure of the cell walls. Cells with thin primary walls and remain alive on maturation are called Parenchyma cells. Cells which have thin cell walls with certain areas with thickening are called Collenchyma cells. Cells that have cell walls with secondary thickening and are usually dead are called Sclerenchyma cells.
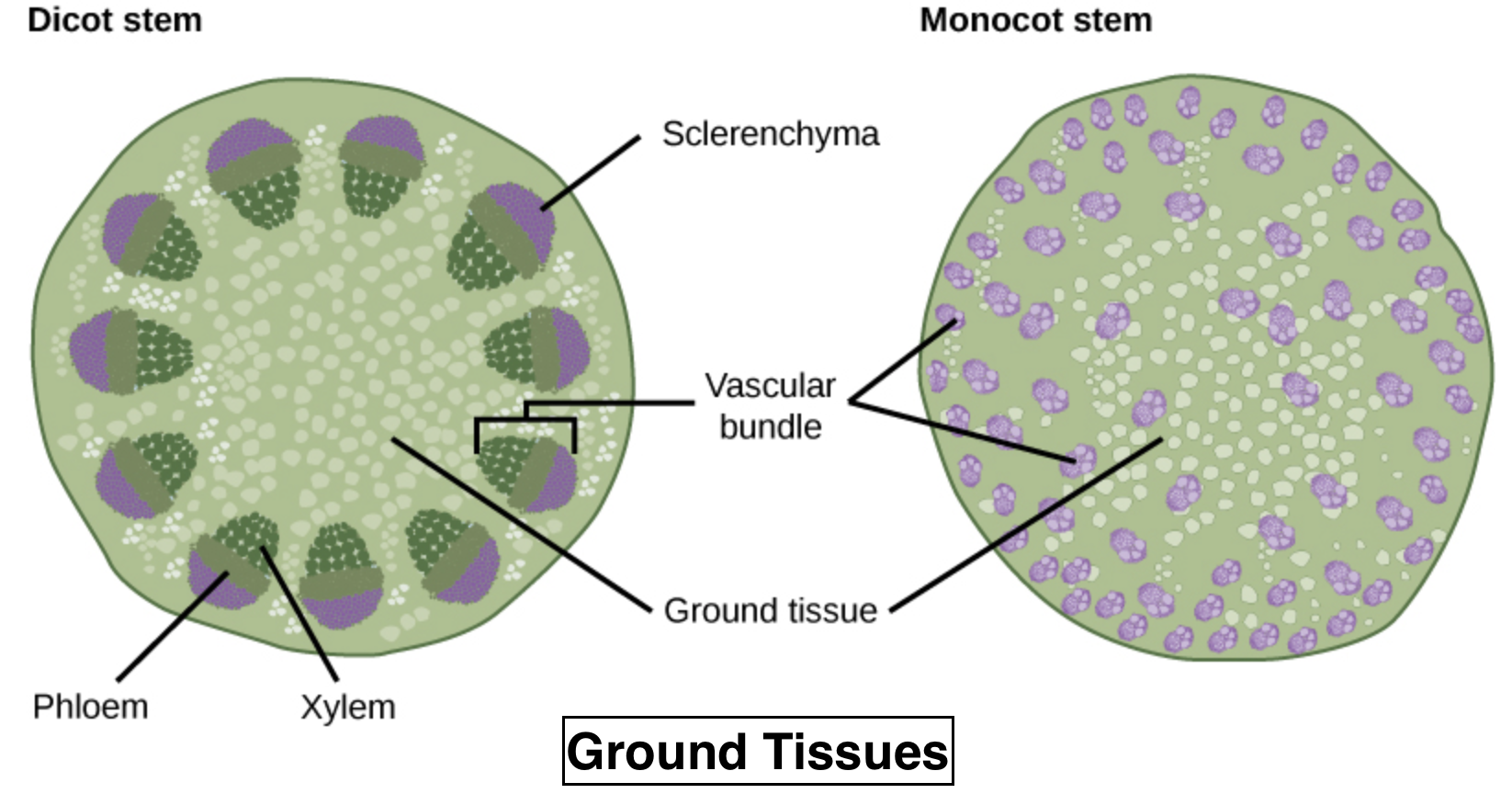
So, the correct answer is 'All tissues except epidermis and vascular bundles'.
Additional information:
- Parenchyma cells contain cell walls with fine primary walls and normally stay alive after they get mature. They produce filler tissue in the weak areas of plants and commonly present in areas such as cortex, pericycle, pith, etc.
- Collenchyma cells have narrow primary walls with certain parts with secondary thickening. The extra mechanical and structural support especially in the regions of replication or elongation is provided by Collenchyma.
- Sclerenchyma cells that contain strong secondary walls and mostly die when they get mature. The major mechanical support to the plant is given by Sclerenchyma.
Note:
- One feature that distinguishes plant cells is the presence of chloroplasts, unique organelles which aid plants to produce energy and biomass from the Sun.
- Chloroplasts are similar to mitochondria which are covered by two membranes where the outer membrane is a permeable membrane for tiny organic molecules and an inner membrane that is not permeable and is embedded with transport proteins.
- Plant cells contain large vacuoles which cover 30% of a plant cell and aids in the storage of materials.
Complete step by step answer:
Ground tissue includes all tissues except epidermal and vascular tissues. These tissues are divided into three types based on the structure of the cell walls. Cells with thin primary walls and remain alive on maturation are called Parenchyma cells. Cells which have thin cell walls with certain areas with thickening are called Collenchyma cells. Cells that have cell walls with secondary thickening and are usually dead are called Sclerenchyma cells.

So, the correct answer is 'All tissues except epidermis and vascular bundles'.
Additional information:
- Parenchyma cells contain cell walls with fine primary walls and normally stay alive after they get mature. They produce filler tissue in the weak areas of plants and commonly present in areas such as cortex, pericycle, pith, etc.
- Collenchyma cells have narrow primary walls with certain parts with secondary thickening. The extra mechanical and structural support especially in the regions of replication or elongation is provided by Collenchyma.
- Sclerenchyma cells that contain strong secondary walls and mostly die when they get mature. The major mechanical support to the plant is given by Sclerenchyma.
Note:
- One feature that distinguishes plant cells is the presence of chloroplasts, unique organelles which aid plants to produce energy and biomass from the Sun.
- Chloroplasts are similar to mitochondria which are covered by two membranes where the outer membrane is a permeable membrane for tiny organic molecules and an inner membrane that is not permeable and is embedded with transport proteins.
- Plant cells contain large vacuoles which cover 30% of a plant cell and aids in the storage of materials.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




