
Graphs between pressure and volume are plotted at different temperatures. Which of the following isotherms represents Boyle’s law as ${\text{PV}} = {\text{Constant}}$?

A) Only (ii) is a correct representation of Boyle’s law.
B) Only (iv) is the correct representation of Boyle’s law.
C) All are correct representations of Boyle’s law.
D) None of these representations is correct for Boyle’s law.

Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: To solve this we must know Boyle's law. Boyle’s law states that at constant temperature the volume of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the pressure of the gas.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that Boyle's law states that at constant temperature the volume of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the pressure of the gas.
The expression for Boyle’s law is as follows:
${\text{P}} \propto \dfrac{1}{{\text{V}}}$ …… (1)
Where ${\text{P}}$ is the pressure,
${\text{V}}$ is the volume.
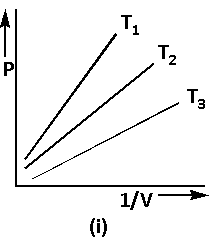
Using equation (1), the graph of Boyle’s law is as follows:
The equation (1) can be written as follows:
${\text{P}} = {\text{K}}\dfrac{1}{{\text{V}}}$ …… (2)
Where ${\text{K}}$ is the constant.
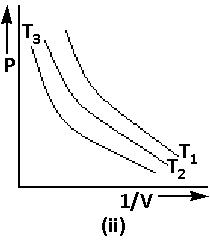
Using equation (2), the graph of Boyle’s law is as follows:
We are given that ${\text{PV}} = {\text{Constant}}$. Thus,
${\text{PV}} = {\text{K}}$ …… (3)
The equation (3) can also be written as follows:
${\text{PV}} = \dfrac{{\text{K}}}{{\text{P}}} \times {\text{P}}$ …… (4)
Using equation (4), the graph of Boyle’s law is as follows:
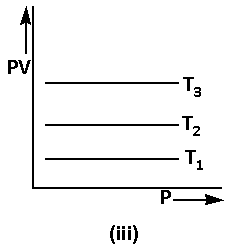
The equation (2) can be written in the form of log as follows:
${\text{log P}} = - \log {\text{ V}} + \log {\text{ K}}$ …… (5)
Using equation (5), the graph of Boyle’s law is as follows:

From the above graphs, we can say that all the graphs are the correct representations of Boyle’s law.
Thus, the correct option is (C).
Note: We know that Boyle's law states that at constant temperature the volume of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the pressure of the gas. Thus, as the volume of the gas increases, the pressure decreases or as the volume of the gas decreases, the pressure increases.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that Boyle's law states that at constant temperature the volume of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the pressure of the gas.
The expression for Boyle’s law is as follows:
${\text{P}} \propto \dfrac{1}{{\text{V}}}$ …… (1)
Where ${\text{P}}$ is the pressure,
${\text{V}}$ is the volume.
Using equation (1), the graph of Boyle’s law is as follows:

The equation (1) can be written as follows:
${\text{P}} = {\text{K}}\dfrac{1}{{\text{V}}}$ …… (2)
Where ${\text{K}}$ is the constant.
Using equation (2), the graph of Boyle’s law is as follows:

We are given that ${\text{PV}} = {\text{Constant}}$. Thus,
${\text{PV}} = {\text{K}}$ …… (3)
The equation (3) can also be written as follows:
${\text{PV}} = \dfrac{{\text{K}}}{{\text{P}}} \times {\text{P}}$ …… (4)
Using equation (4), the graph of Boyle’s law is as follows:

The equation (2) can be written in the form of log as follows:
${\text{log P}} = - \log {\text{ V}} + \log {\text{ K}}$ …… (5)
Using equation (5), the graph of Boyle’s law is as follows:

From the above graphs, we can say that all the graphs are the correct representations of Boyle’s law.
Thus, the correct option is (C).
Note: We know that Boyle's law states that at constant temperature the volume of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the pressure of the gas. Thus, as the volume of the gas increases, the pressure decreases or as the volume of the gas decreases, the pressure increases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




