
How do you graph $ y = 4\sin (x - \dfrac{\pi }{3}) + 2 $ ?
Answer
545.7k+ views
Hint: In this question, we have to plot the graph of the given sine function. We have to first convert any function to the standard form for plotting the graph of that function, and then we compare it with the standard equation. This way we can find out how the graph should be plotted. The standard form of the sine equation is $ y = A\sin (Bx + C) + D $ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given that $ y = 4\sin (x - \dfrac{\pi }{3}) + 2 $ and we know that the standard form is $ y = A\sin (Bx + C) + D $ ,
Comparing these two equations, we get –
$ A = 4,\,B = 1,\,C = - \dfrac{\pi }{3}\,and\,D = 2 $
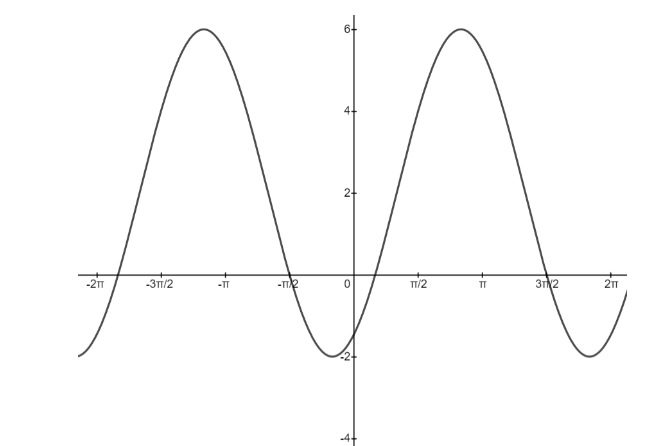
Thus, the given function has a vertical shift of 2 and horizontal shift of $ - \dfrac{\pi }{3} $ , and the amplitude of this function is 4, so the given sine function has peak values at 4+2=6 and -4+2=-2, that is, it oscillates between 6 and -2, and the given sine function completes one oscillations between 0 and $ 2\pi $ , but for plotting the graph, we have to find out the period of the function. Period of a sine function is –
$
p = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{B} \\
\Rightarrow p = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{1} = 2\pi \;
$
That is the given function repeats the oscillation after every $ 2\pi $ radians, it completes 1 oscillation in the interval $ - \dfrac{\pi }{3} $ to $ \dfrac{{5\pi }}{3} $ .
Now, We know all the quantities for plotting the graph of the given function, so the graph of $ y = 4\sin (x - \dfrac{\pi }{3}) + 2 $ is plotted as follows –
Note: We know that the general form of the sine function is $ y = A\sin (Bx + C) + D $ where
A is the amplitude, that is, A tells us the value of the peaks of the function.
B is the frequency, that is, B tells us the number of oscillations a function does in a fixed interval.
C and D denote the horizontal and vertical shift of a function respectively. The value of C and D is zero for the given function, so there is no horizontal or vertical shift.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given that $ y = 4\sin (x - \dfrac{\pi }{3}) + 2 $ and we know that the standard form is $ y = A\sin (Bx + C) + D $ ,
Comparing these two equations, we get –
$ A = 4,\,B = 1,\,C = - \dfrac{\pi }{3}\,and\,D = 2 $
Thus, the given function has a vertical shift of 2 and horizontal shift of $ - \dfrac{\pi }{3} $ , and the amplitude of this function is 4, so the given sine function has peak values at 4+2=6 and -4+2=-2, that is, it oscillates between 6 and -2, and the given sine function completes one oscillations between 0 and $ 2\pi $ , but for plotting the graph, we have to find out the period of the function. Period of a sine function is –
$
p = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{B} \\
\Rightarrow p = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{1} = 2\pi \;
$
That is the given function repeats the oscillation after every $ 2\pi $ radians, it completes 1 oscillation in the interval $ - \dfrac{\pi }{3} $ to $ \dfrac{{5\pi }}{3} $ .
Now, We know all the quantities for plotting the graph of the given function, so the graph of $ y = 4\sin (x - \dfrac{\pi }{3}) + 2 $ is plotted as follows –

Note: We know that the general form of the sine function is $ y = A\sin (Bx + C) + D $ where
A is the amplitude, that is, A tells us the value of the peaks of the function.
B is the frequency, that is, B tells us the number of oscillations a function does in a fixed interval.
C and D denote the horizontal and vertical shift of a function respectively. The value of C and D is zero for the given function, so there is no horizontal or vertical shift.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




