
Grape-like aggregate of coccus bacteria constitute
(a) Sarcina
(b) Staphylococcus
(c) Streptococcus
(d) Diplococcus
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: Bacteria with spherical or round structure come under coccus, plural form - cocci. The orientation of cocci can be string- like, pairs, and clusters depending on the way the cells attach during cell division. This grape- like aggregate of coccus bacteria is found in the environment and the nasal passages of normal individuals.
Complete answer:
A grape-like aggregate of coccus bacteria constitutes Staphylococcus. Staphylococcus can grow both in aerobic and anaerobic conditions and they are gram- positive bacteria and under the microscope, they will be seen as grape- like clusters. Staphylococcus aureus is a common example that shows grape- like clustering.
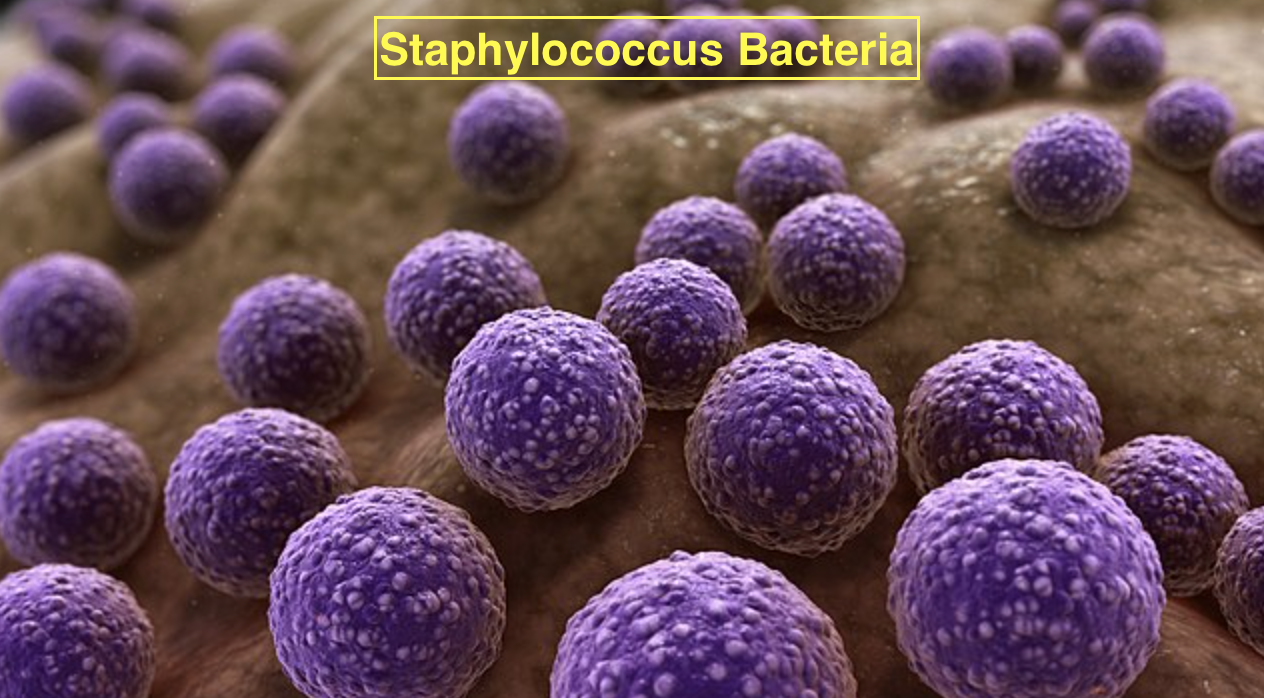
So, the correct answer is ‘Staphylococcus’.
Additional information:
- Staphylococcus was named by a Scottish microbiologist called Alexander Ogston in the year 1880. Alexander Ogston was born in 1844 and died in 1929.
- The name is taken from two languages- ancient Greek and Latin, in which 'Staphylo' is from Greek meaning 'bunch of grapes and 'coccus' meaning 'spherical bacteria'.
- The genus Staphylococcus includes 40 species, in which most of them do not have virulence characteristics and mostly a part of soil microbes. Most Staphylococcus species can grow fermentative, other than one species that grows oxidatively which is S.saprophyticus.
Note:
- Staphylococcus can be identified using a simple biochemical test such as gram staining in which Staphylococcus will show purple colour under a light microscope.
- Gram staining involves a primary stain which is crystal violet, iodide, ethanol as decolourizer, and Safranin as counterstain. Iodide helps in sustaining the primary stain to the cells, which will be washed off by ethanol or acetone.
- Staphylococcus takes up the crystal violet stain due to its thick Peptidoglycan cell wall, which is less in other gram-negative bacteria.
Complete answer:
A grape-like aggregate of coccus bacteria constitutes Staphylococcus. Staphylococcus can grow both in aerobic and anaerobic conditions and they are gram- positive bacteria and under the microscope, they will be seen as grape- like clusters. Staphylococcus aureus is a common example that shows grape- like clustering.

So, the correct answer is ‘Staphylococcus’.
Additional information:
- Staphylococcus was named by a Scottish microbiologist called Alexander Ogston in the year 1880. Alexander Ogston was born in 1844 and died in 1929.
- The name is taken from two languages- ancient Greek and Latin, in which 'Staphylo' is from Greek meaning 'bunch of grapes and 'coccus' meaning 'spherical bacteria'.
- The genus Staphylococcus includes 40 species, in which most of them do not have virulence characteristics and mostly a part of soil microbes. Most Staphylococcus species can grow fermentative, other than one species that grows oxidatively which is S.saprophyticus.
Note:
- Staphylococcus can be identified using a simple biochemical test such as gram staining in which Staphylococcus will show purple colour under a light microscope.
- Gram staining involves a primary stain which is crystal violet, iodide, ethanol as decolourizer, and Safranin as counterstain. Iodide helps in sustaining the primary stain to the cells, which will be washed off by ethanol or acetone.
- Staphylococcus takes up the crystal violet stain due to its thick Peptidoglycan cell wall, which is less in other gram-negative bacteria.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




