
Given,ABCD is a quadrilateral. Force $\vec {BA},\vec{BC},\vec{CD},\vec{DA}$ act at a point, their resultant is
\[\begin{align}
& A.2\overrightarrow{AB} \\
& B.2\overrightarrow{DA} \\
& C.0 \\
& D.\overrightarrow{2BA} \\
\end{align}\]
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: We know that we can find the resultant of any two given vectors from the parallelogram of vector addition, by moving the vectors if required such that they have a common point and the direction of the vectors are away from the point of contact.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us consider the quadrilateral ABCD as shown below,
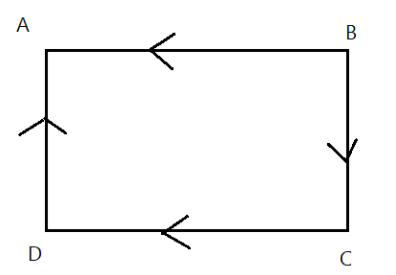
Since it is given that ABCD is a quadrilateral, we can say that $\vec AB+\vec BC+\vec CD+\vec DA=0$
Also, clearly, $\vec AB=-\vec BA$
Then we have
$\implies \vec BA=\vec BC+\vec CD+\vec DA$
From the given figure, we can say that $R=\vec BA+\vec BC+\vec CD+\vec DA$
$\implies R=\vec BA+\vec BA$
$\therefore R=2\vec BA$
Hence the correct answer is option \[D.\overrightarrow{2BA}\].
Additional information:
We know that vectors have both magnitude and direction. We also know that we can add, or multiply two given vectors.
Parallelogram law of vector addition states that the sum of the squares of all the sides of the parallelogram, give the squares of the two diagonals of the parallelogram. This law gives both the direction and the magnitude of the resultant vector.
Or, in simple terms the resultant vector due to the adjacent sides of a parallelogram, is the diagonal of the parallelogram.
The triangle law of vector addition is derived from the parallelogram of vector addition. Also, the parallelogram law of vector addition is often used in physics as most of the physical terms like force, work , tension and so on are vectors, and need to be added or subtracted often.
Note:
This sum may seem very hard at first glance, but if one draws the diagram and labels the diagram correctly, it is easy to solve the question. The question uses only the basic parallelogram law of vector addition and speed formula.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us consider the quadrilateral ABCD as shown below,

Since it is given that ABCD is a quadrilateral, we can say that $\vec AB+\vec BC+\vec CD+\vec DA=0$
Also, clearly, $\vec AB=-\vec BA$
Then we have
$\implies \vec BA=\vec BC+\vec CD+\vec DA$
From the given figure, we can say that $R=\vec BA+\vec BC+\vec CD+\vec DA$
$\implies R=\vec BA+\vec BA$
$\therefore R=2\vec BA$
Hence the correct answer is option \[D.\overrightarrow{2BA}\].
Additional information:
We know that vectors have both magnitude and direction. We also know that we can add, or multiply two given vectors.
Parallelogram law of vector addition states that the sum of the squares of all the sides of the parallelogram, give the squares of the two diagonals of the parallelogram. This law gives both the direction and the magnitude of the resultant vector.
Or, in simple terms the resultant vector due to the adjacent sides of a parallelogram, is the diagonal of the parallelogram.
The triangle law of vector addition is derived from the parallelogram of vector addition. Also, the parallelogram law of vector addition is often used in physics as most of the physical terms like force, work , tension and so on are vectors, and need to be added or subtracted often.
Note:
This sum may seem very hard at first glance, but if one draws the diagram and labels the diagram correctly, it is easy to solve the question. The question uses only the basic parallelogram law of vector addition and speed formula.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




